What are muscles?

Some muscles, like our arm muscles, we can choose whether to move or not.
Muscles are found all over our body and do some important jobs:
- They help our body to move.
- They help to keep our body standing upright and tall - a bit like the strings of a puppet.
- They can act like a shield to protect our internal organs and bones, keeping them safe from harm.
If we think about moving some muscles, like our arm muscles, they move. Other muscles, like our heart, move on their own without us thinking about it.

Watch: How muscles work
The way that muscles work is quite complicated. Watch this video which shows how muscles, tendons and the skeleton work together.
Zoom in on the muscles in our body.
Narrator: So you're going to put muscles on this skeleton are you?
Great. What are those floppy things?
Woman: Muscles!
Narrator: Muscles! Really? They don't look much use.
They don't even stay on…
Oh you need those tendon things to fix them on.
Alright well yes it's on, but what does it do?
Oh wow! That's very clever.
It just pulls itself tight and then the arm goes up …
And when it relaxes the arm goes back down.
Brilliant! How many more do you have to put on?
Six hundred and thirty eight??
Blimey
Magnificent muscle facts
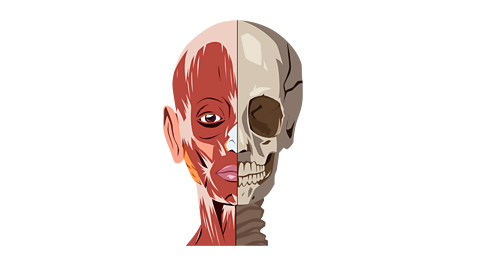
Muscles make up around 40% of your total body weight.
The human body has over 600muscles.
Humans have three types of muscles in their body: skeletal (which controls movement), cardiac (which are found in your heart) and smooth (which do other important jobs).
The largestmuscle in the human body is the gluteus maximus, which is the muscle that you sit on when you sit down!
The smallest muscle in the human body is the stapedius, which is found in the ear.
Muscles are attached to our bones with tendons.
Muscles can only contract and relax.

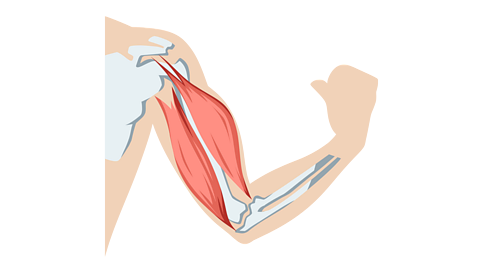
How muscles work
Muscles often work in pairs, pulling on your bones so that you can move.
When we want to move a particular body part, such as our arm, our brain sends a message to the muscles in that area. The muscle then tightens or contracts, becoming shorter and thicker, which pulls on the bone and causes the movement.
Once the muscle has done its job, it relaxes and goes back to its original length. Muscles can only pull bones, they can't push them, so then a different muscle has to work to pull the bone back to where it started.
Your skeleton has joints which allow movement when your muscles contract and relax. Some of these joints are very flexible, like your shoulder and hip. Others, like your knee and elbow, move a little less. Others, like your spine and neck, are only able to move a little.
It is important to eat a healthy diet with enough protein to help your muscles grow properly. We find protein in meat, fish, eggs and beans.

Voluntary and involuntary muscles
There are two types of muscles:
Voluntary muscles: These are muscles we can control, like the ones in our arms and legs. When we decide to kick a ball or raise our hand, we are using voluntary muscles.
Involuntary muscles: These are muscles that work without us having to think about it, like the muscles in our heart and stomach. They help us breathe, digest food, and keep our heart beating.

Important words
Contracts – The process when muscles shorten, tighten, or lengthen when moving around.
Involuntary muscles – These are muscles that work without us having to think about it.
Joints – Joints are the parts that connect different bones together and allow for movement.
Muscles – Muscles are like rubber bands that can stretch and contract. They help to keep our bodies upright and support us when we move.
Organs – The heart, lungs and the stomach are all examples of organs.
Protein – A food group used for growth and repair. Foods like meat, fish, eggs and dairy products contain lots of protein.
Tendons – Muscles are attached to our skeleton by tendons.
Tightens –When something becomes more stretched and immovable.
Voluntary muscles – These are muscles we can control, like the ones in our arms and legs.

Activities
Activity 1 - Fill in the gaps
Activity 2 - Muscles quiz
Activity 3 - Make a model arm
New game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space. gameNew game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space
Join Pipette on her epic mission and learn some revolting facts about space along the way.

More on Animals including humans
Find out more by working through a topic
- count7 of 11
- count8 of 11
- count9 of 11
- count10 of 11

