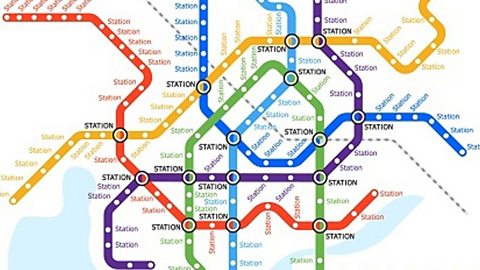
Modelling
Abstraction is the process of separating and filtering out ideas and specific details that are not needed in order to build models that concentrate only on what is needed. When planning a project, think of abstraction as focusing on what is required - not how it is done.
Models created as a result of the process of abstraction help to simplify real-world problems so that programmers can write algorithmA sequence of logical instructions for carrying out a task. In computing, algorithms are needed to design computer programs. and programs that solve those problems more easily. Computers need clear, simple instructions to work properly. To abstract a problem:
get rid of the unimportant parts
focus on the key information
These make the algorithm easier to design and understand.
Example 1 - Abstraction in a routing system
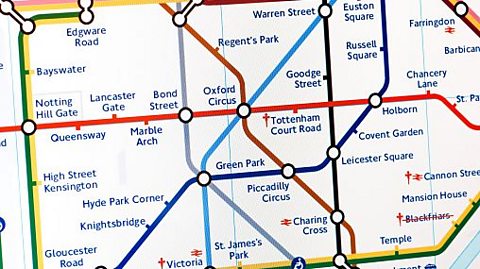
The London underground map is an example of abstraction in the real world. It doesn’t show the buildings, roads or trees - it just shows the station names and the tube lines that people need to be able to get around.
Detail such as timing between stations and routing is not required at this level, as it is an abstraction.

Example 2 – Abstraction in programming
When a customer visits the cinema, the information collected might include: their name, age, seat number, drinks and snacks ordered, time of booking, the ticket design, the cinema staff who served them and their payment method.
To book a ticket the only information that might be required is:
customer name
age (for age restrictions)
seat number
In this example, abstraction is used to only keep what is needed to make the system work.
Structure and modularity
Structured programming is sometimes referred to as modular programming. It involves decomposing a program into manageable chunks to perform individual tasks. The individual tasks can be written as such as functionA section of code that, when programming, can be called by another part of the program with the purpose of returning one single value. or procedures and combined to create a main program. This is known as modularity.
Modularity turns the smaller tasks from decomposition into subroutines. These are separate blocks of code that do one specific job.
The advantages of modularity are:
code is easier to understand
code is easier to test
code is easier to re-use.
Example
This is how the decomposition of a program for users to log into a system might look:
ask for the username and password from the user
check if the user is in the user list
check if the password matches
display Access granted or Access denied.
Analysing requirements
Before a programmer writes a program, it is important to understand exactly what the program needs to do. This means understanding the problem and analysing a set of requirements. This is the first step in solving the problem to find the correct solution.
The requirements are a list of things the program must do and include:
- inputs - the data needed by the program
- processes - what the program must do with the data
- outputs - what the program should tell the user.
The requirements may also include the limitations of the program, the type of user interfaceAn interface allows interaction with a computer system. Modern user interfaces use touch screen technology, with icons to give commands. and any additional rules the program needs to follow.
Example - create a quiz for students
To create a quiz for students, firstly the designer should analyse the requirements of the quiz and identify what is needed to solve the problem (ie to create the quiz.) Then create a plan showing:
- what the program must include
- what data is required and where it comes from
- how the data will be processed
- what the output should look like
- which data structures or algorithms should be used.
Requirements
- The program must display 10 multiple choice questions.
- The user must input their answer.
- The program must check if the answer is correct or not.
- The program must display the total number of correct answers.
- A list of questions and answers is needed.
- A loopA method used in programming to repeat a set of instructions. is needed to repeat the questions.
- A total variable is needed to count the number of correct answers.
More on Systems analysis
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 5

- count4 of 5
- count5 of 5
- count1 of 5