Key points

- The densityAll substances are made of particles. Density is a measure of how close together particles are. Closely packed particles have a higher density than particles that are spread out. of an object or substance is its massHow much matter is contained in an object. It is similar to weight, but weight is affected by gravity. An object mass cannot change but its weight can depend on where it is measured. divided by its volumeThe amount of space occupied by a 3D shape, measured in cubic units, such as cm³, mm³ and m³. May also be referred to as capacity.:
Density = Mass ÷ Volume
The units of density depend on the units used for mass and volume, but are usually g/cm³ (if mass is measured in g and volume in cm³).
The more DenseAn object where a large amount of mass is in a given volume. The particles are crowded together. a substance is, the heavier it feels.
Using the formula Density = Mass ÷ Volume makes it possible to compare the density of objects with different magnitudeThe size of an object. of volume and mass.

How to compare solids and liquids
Substances can be compared using density:
- If two liquids that are mixed have a different density then the least dense liquid would float to the top.
- Different types of wood have a different density. A hardwood has a greater density and would feel heavier than a softwood.
- Objects that are more dense take up less space than the same mass of a less dense material. For example, a metric unitsUnit of measurement in the metric system. Metric units include metre, centimetre, millimetre, kilometre. tonne of feathers would take up a far greater volume of space compared to a metric tonne of bricks.
Examples

Image caption, When different liquids are mixed together in the same container, their densities will affect what then happens. It will depend on the density of the each of the liquids. If the liquids are different colours it is easier to see the physical effect of density.

Image caption, A small amount of five different liquids are added to one container: vegetable oil, water, washing up liquid, maple syrup and honey.

Image caption, The liquid which is the most dense (honey) sinks to the bottom of the container. The liquid which is the least dense (vegetable oil) floats to the top of the container. The different colours of the liquids make it easier to see the effect of density.
Image caption, Solids have different densities too. Two metal bars, one made from aluminium and the other from copper, are the same size and therefore have the same volume. If the two bars were picked up, one would feel heavier, because it has a greater density.
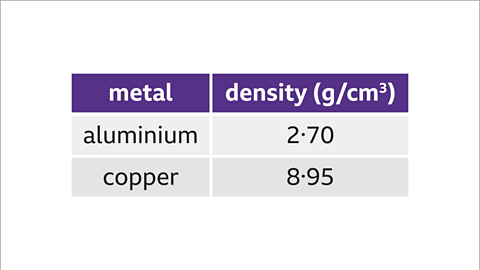
Image caption, The density of aluminium is 2.70g/cm³. The density of copper is 8.95g/cm³. Copper has the greater density. If the two bars are the same size then the one made from copper would feel heavier.
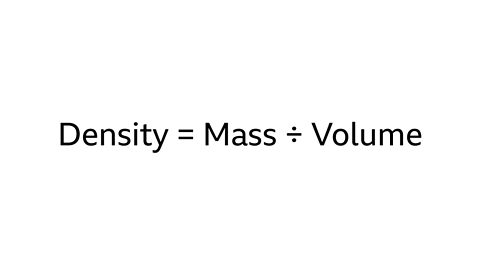
Image caption, Density = Mass ÷ Volume. There are many units of mass and volume covering many different magnitudes. As a result there is a large number of units that describe density, a common one being g/cm³. If the densities of two different substances are given in the same units then it is possible to compare their relative densities.
1 of 6
Question
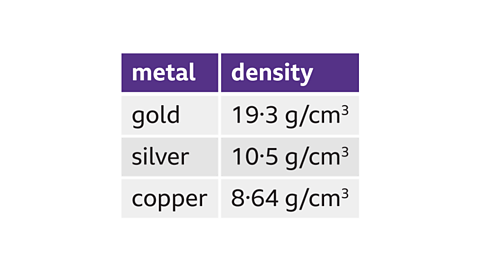
Record these three precious metals in terms of their densityAll substances are made of particles. Density is a measure of how close together particles are. Closely packed particles have a higher density than particles that are spread out., from greatest density to lowest density.
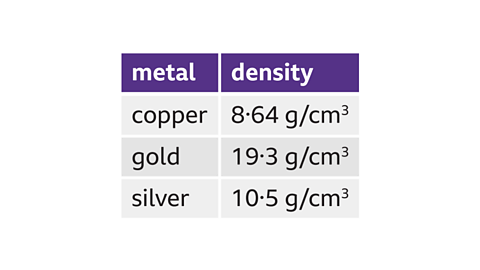
Gold has the greatest density of 19.3 g/cm³.
Silver comes second, with a density of 10.5 g/cm³.
Copper has the lowest density of 8.64 g/cm³.
How to work out density
Density is the mass per unit volumeThe amount of space occupied by a 3D shape, measured in cubic units, such as cm³, mm³ and m³. May also be referred to as capacity.. It can be measured in several ways:
A common way to calculate the density of any solid, liquid or gas is to divide its massA measure of the amount of matter an object is made out of. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg). in grams (g) by its volume in cubic centimetres (cm³).
If the object is large, then the density would be calculated by dividing the mass in kilograms (kg) by its volume in cubic metres: Density = Mass ÷ Volume.
The units for density will result from the units provided for the mass and the volume.
Example
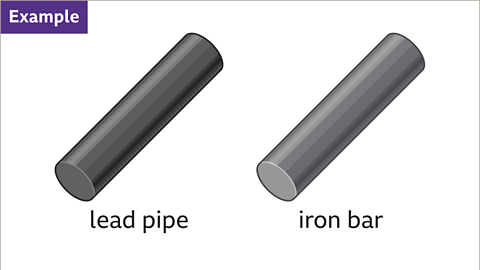
Image caption, Calculate the density of these different types of metals.

Image caption, The volume and mass of each object is needed to compare the density of the two different metals. The lead pipe has a mass of 2268 grams and a volume of 200 cm³. The iron bar has a mass of 3537 grams and volume of 450 cm³.
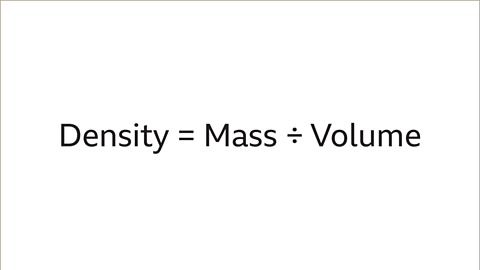
Image caption, The formula of Density = Mass ÷ Volume must be used to calculate the density of each type of metal.
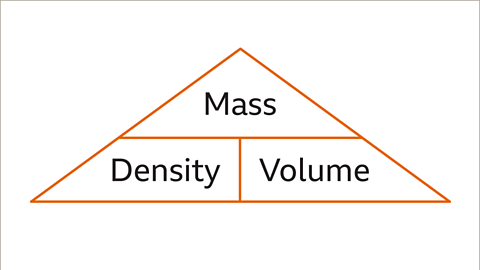
Image caption, The Mass, Density, Volume triangle can be used to help remember the formula.
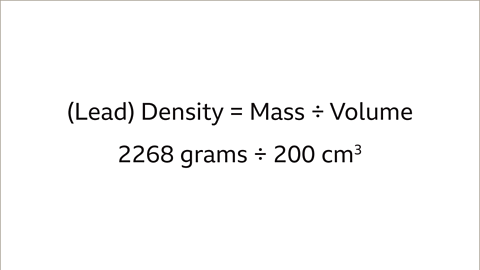
Image caption, The density of the lead pipe is 2268 grams ÷ 200 cm³ = 11.34 g/cm³.
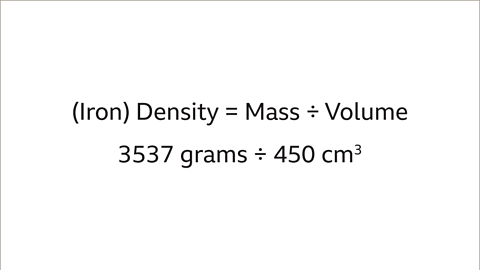
Image caption, The density of the iron bar is 3537 grams ÷ 450 cm3 = 7.86 g/cm³.

Image caption, Lead has a greater density than iron. The density of the lead is 11.34 g/cm³. The density of the iron is 7.86 g/cm³. If a block of lead and a block of iron were the same size then the lead would have a larger mass than the iron, which means that the lead would be heavier.
1 of 7
Question
What is the density of a gold necklace that has a mass of 57 grams and a volume of 3 cm³?

Density = Mass ÷ Volume
57 grams divided by 3 cm³ is 19 grams/cm³.
The density of the gold necklace is 19g/cm³.
Practise your understanding of density
Quiz
Practise your knowledge of using density in maths with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Measurement
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 4
- count2 of 4