What is light?

Light is a type of energy which is emitted from light sources.
Light sources can either be natural, such as the Sun, or human-made, such as a light bulb.
Light travels in straight lines and is the fastest type of energy, travelling at 186,000 miles per second.
This means that a beam of light could travel 7.5 times around the Earth in in just one second!

Watch: Light travels into our eyes
Watch this video which explains how light travels into our eyes so that we can see things.
Follow light as it travels through your eye and is processed by your brain.
Have you ever wondered how your eyes work?
What's really happening when you see something?
Of course, you can only see something when there's light.
And what is light?
It's energy that zooms around very quickly.
Light bounces or reflects off most objects, but not everything.
When light hits your eye, it actually goes right into it through the opening at the front.
The eye then sends signals to the brain.
That's what we call seeing.
Fascinating facts
When light enters the eye and is focused onto the retina, it is actually upside down. Don't worry though, your clever brain knows this and turns the image the right way around!
Vitamin A is crucial to having a healthy retina. Not having enough Vitamin A can lead to night blindness. Carrots are a good source of Vitamin A but so are lots of other fruits and vegetables too.
The iris changes the size of the pupil. Too much light can really damage our eyes. In bright conditions, the iris reduces the size of the pupil which in turn reduces how much light can enter our eyes. In darker conditions, the iris increases the size of the pupil which in turn increases the amount of light entering our eyes.
The retina in the eye has approximately 120 million rods (cells sensitive to low light) and 6 million cones (cells that provide colour vision).
More than 50% of our brains are devoted to processing visual information and images.
The scallop, a common shellfish in our seas, can have up to 200 eyes with each eye having two retinas.
A healthcare professional who provides eye care is called an optometrist. An ophthalmologist can undertake surgical procedures for eye conditions. Opticians dispense eyeglasses and contact lenses to correct poor vision.
The average person blinks between 15 and 20 times a minute.

How do we see?
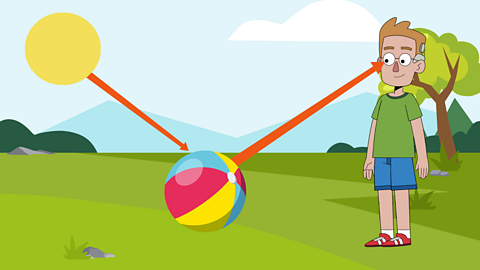
- Light energy is emitted from a light source.
- It travels in a straight line.
- When the light hits an object, it is reflected (bounces off) and travels in straight lines to our eyes.
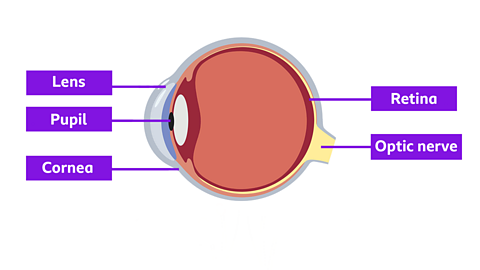
- When light enters the eye, it passes through the cornea, pupils and lens, which focus the light onto the retina.
- In the retina, cells called rods and cones convert the light energy into electrical signals.
- These electrical signals are then sent to the brain through the optic nerve.
- The brain interprets these signals as images.
- If your brain, recognises the image, it recalls its name from your memory, eg “That's a dog!”.

Slideshow: Light and how we detect it

Image caption, Natural light
Light is a type of energy which is emitted from light sources. They can be natural like the light we receive from the Sun during daylight hours.

Image caption, Human-made light
We can also produce human-made light, like torches or headlamps. Light travels in straight lines at 186,000 miles per second.
Image caption, The human eye
The human eye is very complex. When light enters the eye, it passes through the cornea, pupil and lens, which focus the light onto the retina. In the retina, cells called rods and cones convert the light energy into electrical signals which are then sent to the brain through the optic nerve. The brain then interprets these signals as images.
1 of 3
Did you know?
Rods are highly sensitive to light. They are unable to identify colours but are brilliant for helping us to see in the dark.
Cones are less sensitive to light but can distinguish colours. They may not help us see in the dark but they do help us to see the colours of a rainbow and beautiful flowers.
Both are types of photoreceptor, special light-detecting cells found on the retina.
Important words
Cones – A photoreceptor cell found in the retina.
Cornea – The clear protective layer at the front of the eye.
Electrical signals – Electrical signals from the eyes carry information to the brain via nerves.
Lens – The part of the eye that we use to focus.
Light sources – Light sources can either be natural such as the sun or human-made such as a light bulb.
Optic nerve – Made of millions of fibres, the optic nerve sends visual messages to the brain.
Photoreceptor – Cells found in the retina that respond to light.
Pupil – The black circle in the middle of the eye which increases or decreases in size depending on the amount of light.
Retina – The part of the eye that detects light, it is full of photoreceptor cells.
Rods – Photoreceptor cells that are highly sensitive to light but are unable to identify colours.
Activities
Activity 1 – Order it
Activity 2 – Take the quiz
Activity 3 – Label the eye
New game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space. gameNew game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space
Join Pipette on her epic mission and learn some revolting facts about space along the way.

More on Light
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 5
- count4 of 5
- count5 of 5

- count1 of 5

