Key points
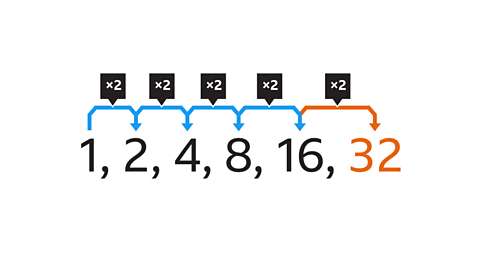
A number pattern is a series of numbers that follow a specific rule. Examples include: odd numbers, even numbers, square numbers and multiples.
A good knowledge of arithmetic and geometric sequences is essential to understanding other types of sequenceA sequence is a set of numbers that follow a certain rule. For example, 3, 5, 7, 9… is a sequence starting with 3 and increasing by 2 each time..
- Each number in a sequence is called a term.
- A sequence which increases or decreases by the same amount each time is called a linear sequenceA set of numbers (terms) in which the next term is found by adding or subtracting the same number each time..
- The term-to-termA term-to-term rule is a rule that allows you to find the next number in a maths sequence, if you know the previous numbers (or terms). of a sequence describes how to get from one term to the next.
- There are other types of sequence that follow a rule, but increase or decrease by a different amount each time.

Finding missing terms in a non-linear sequence
Linear sequences increase or decrease by the same amount each time.
Not all sequences are linear. The term-to-term differences may not be the same and the next term is not always obvious.
There is often a pattern between the differences, rather than the terms, which helps to predict the next number in the sequence.
Example

Image caption, What is the next term in the sequence?
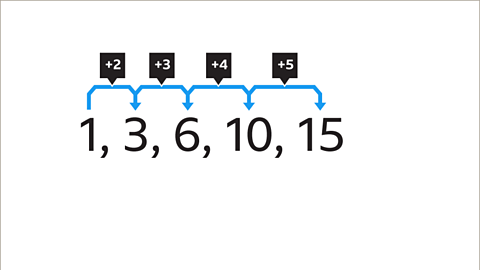
Image caption, The first step is to look at the difference between each pair of numbers in the sequence to find the term-to-term rule. The difference between each pair of terms is a different amount each time. 3 – 1 = 2, 6 - 3 = 3, 10 – 6 = 4 and 15 – 10 = 5
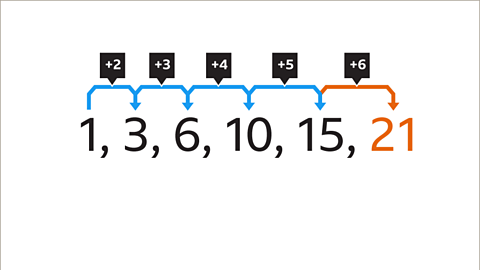
Image caption, While the sequence is not linear, there is a pattern between the difference of each pair of terms. If the pattern continues, then the next difference will be +6, meaning that the next term is 21 (15 + 6).
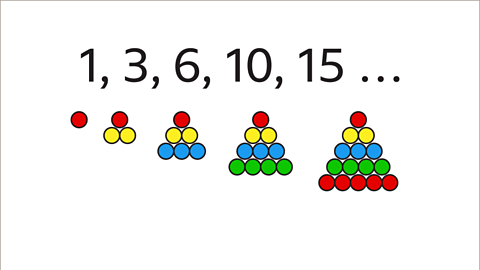
Image caption, Some sequences have special names. This is a sequence of triangular numbers. The name can be understood by looking at diagrams of triangles made of dots. The triangle has one dot on the first row, two on the second row, three on the third row, and four on the fourth row, and so on.
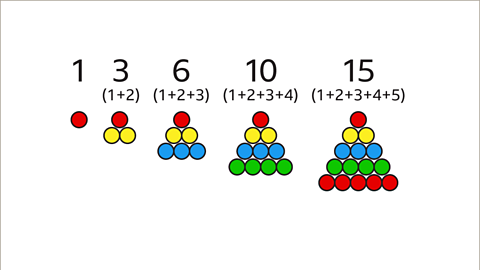
Image caption, The number of dots arranged in a triangular formation is the same as the number in the sequence. This creates the name triangular numbers.
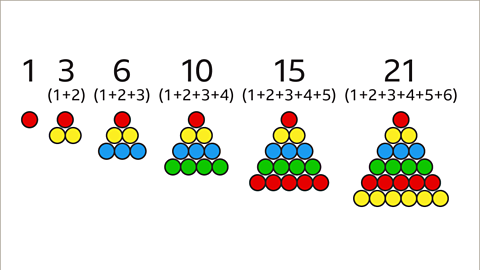
Image caption, The sixth diagram in the sequence will use the existing 15 dots and place 6 more dots underneath to create a bigger triangle. Now there are 21 dots required in total to make the triangle.
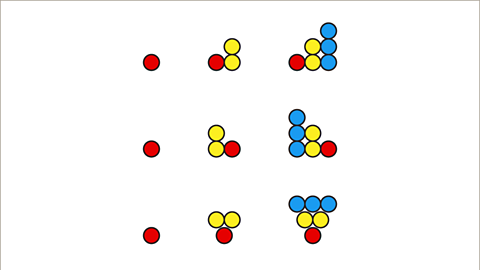
Image caption, The triangular formation can be arranged in different ways but still use the same number of dots each time.
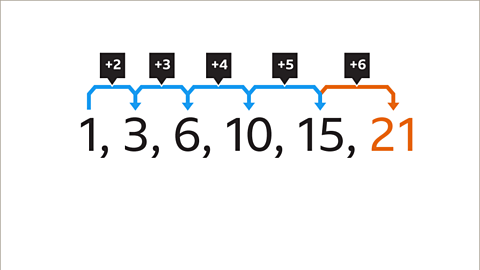
Image caption, Looking at the difference between consecutive terms can also reveal the pattern. The difference between each term is increasing in ones. 3 – 1 = 2, 6 – 3 = 3, 10 – 6 = 4, and 15 – 10 = 5. The next difference will be 6. Therefore, the next number in the sequence is 21 (15 + 6).
1 of 8
Question
What is the next term in this sequence?

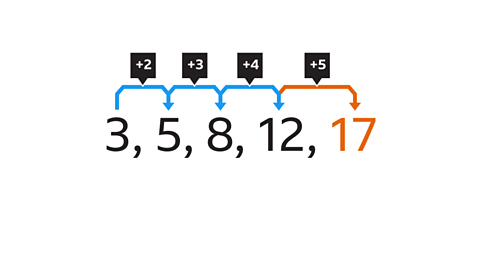
The difference between each term in the sequence increases by 1 each time.
5 – 3 = 2
8 – 5 = 3
12 – 8 = 4
The difference between the next 2 terms will be 5
12 + 5 = 17
The next term in the sequence is 17
Finding the next term in a quadratic sequence
quadratic sequenceA quadratic sequence is a list of numbers with a definite pattern. They can be identified by the fact that the differences between the terms are not equal, but the second differences between terms are equal. involve square numberA number that can be written as the product of two equal numbers. Eg, 100 is a square number as it is the result of 10 × 10.
They can be identified by the fact that the differences between the terms are not equal.
However, the difference between the differences (known as the second difference) is equal.
The term-to-term rule and the second difference can be used to find the next number in a quadratic sequence.
Examples
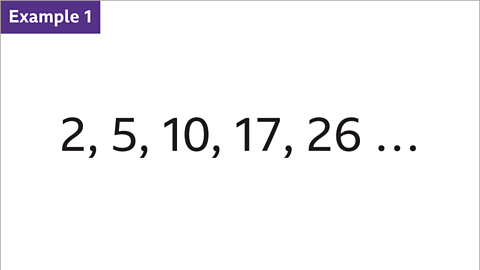
Image caption, What is the next term in this sequence?
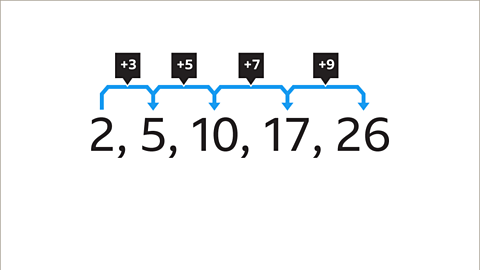
Image caption, The first difference between the terms is not the same each time. However, there is a pattern between the first differences. Each difference increases by 2
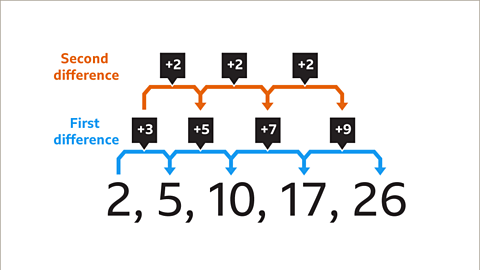
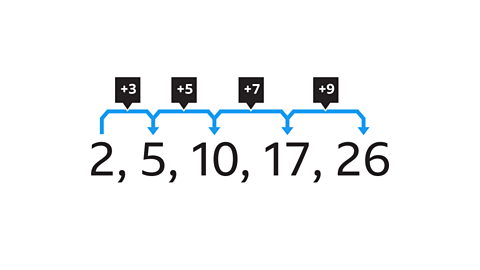
Image caption, +3, +5, +7, +9 are the first differences. +2, +2, +2 are the second differences. The second difference is 2. This means that the sequence is quadratic.
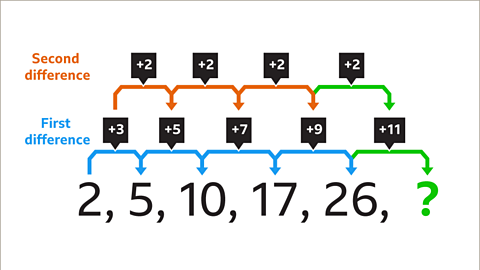
Image caption, Continue this pattern of differences to find the next number in the sequence.
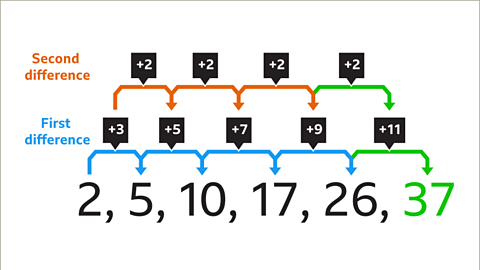
Image caption, The first difference will increase by 2 each time. The difference between the fifth and the sixth term will be +11. The next term of the sequence is 26 + 11 = 37. The sequence involves square numbers as each term is one more than a square number.

Image caption, What is the next term in this sequence?
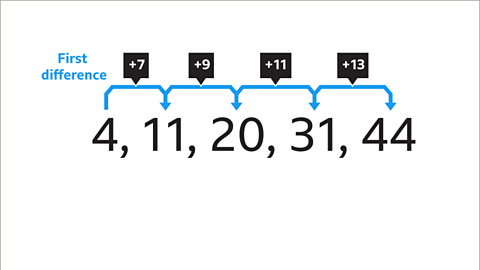
Image caption, The first difference between the terms is not the same each time. However, there is a pattern between the first differences. Each difference increases by 2 each time.
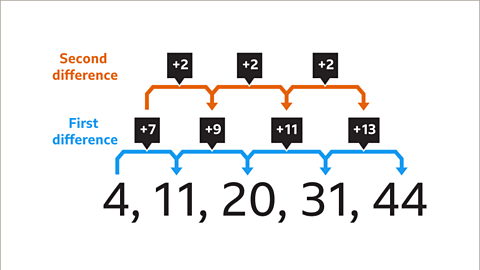
Image caption, The second difference is +2. 9 – 7 = 2, 11 – 9 = 2 and 13- 11 = 2. +7, +9, +11, +13 are the first differences. +2, +2, +2 are the second differences. The second difference is 2. This means that the sequence is quadratic.
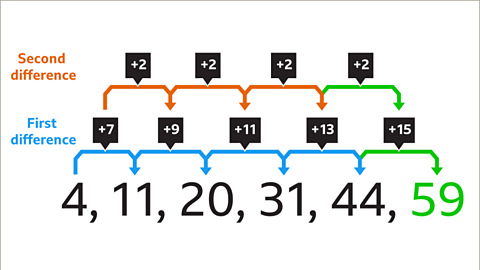
Image caption, The difference between the fifth and the sixth term will be +15. Continue this pattern of differences to find the next term in the sequence. The sixth number in the sequence is 59, because 44 + 15 = 59
1 of 9
Question
What is the next term in this sequence?

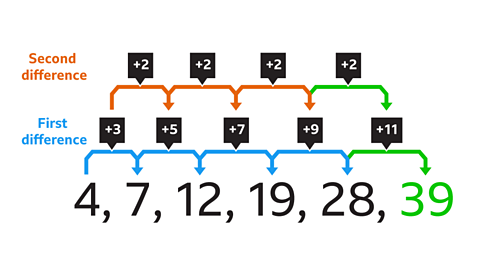
The first difference between each pair of terms changes each time.
The differences are +3, +5, +7, +9
The second difference is +2
The difference between the fifth and sixth term will be 9 + 2 = 11
The next number will be 28 + 11 = 39
Practise other sequences
Quiz
Practise recognising and finding terms in other sequences with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you with your answers.
Real-life maths

Non-linear sequences can be seen in nature.
The number of petals on many flowers and the branches of trees grow in a ‘Fibonacci sequence’.
This is a naturally occurring pattern where the previous two numbers are added together to create the next number in the sequence (0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34…).
Some flowers have 3 petals, others have 5 petals, others 8 petals, and so on.
Fibonacci numbers can be pictured as a spiral, which can also be seen in hurricanes, seashells and the pattern of sunflower seeds.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Patterns and sequences
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 4