What are the key learning points about velocity and acceleration?
Velocity is measure of how much displacement changes with time.
Acceleration is a measure of how much the velocity changes with time.
Both velocity and acceleration are vectorA physical quantity that has both magnitude (size) and direction. Eg force, velocity, displacement, acceleration. quantities.
What is velocity? (Higher tier only)
The only difference between velocityThe rate of change of displacement. The distance travelled in one second in a specified direction. Measured in m/s. and speed is that velocity has a direction, and so is a vector quantity.
Average velocity = \(\frac{\text{total~displacement}}{\text{total~time}}\)
v = \(\frac{\text{disp}}{\text{t}}\)
displacementA distance measured in a specified direction. is the distance moved in a straight line, in a given direction, from the starting point.
Displacement is a vector quantity as it has size and direction.
Question
If a car travels 24 m east in 3 seconds, what is its velocity?
Answer
Displacement = 24 m east.
Velocity = displacement ÷ time.
Velocity = 24 m ÷ 3 s = 8 m/s east.
The velocity of the car is 8 m/s east.
Worked example:
A plane flies 400 m east from point A in 20 s.
The plane then flies 300 m south to point B in 30 s.
The average speed and average velocity of the plane is calculated using:
Average speed = \(\frac{\text{total distance}}{\text{total time}}\) = \(\frac{\text{(400 + 300)}}{\text{(20 + 30)}}\) = \(\frac{\text{700 m}}{\text{50 s}}\) = 14 m/s
Average velocity = \(\frac{\text{total displacement}}{\text{total time}}\) = \(\frac{\text{500 m}}{\text{50 s}}\) = 10 m/s (in the direction from A to B).
Question
You walk all the way around the house in the diagram in 20 seconds.
a) What is your speed?
b) What is your velocity?
Answer
a) speed = distance travelled ÷ time taken
distance moved = 10 m + 10 m + 10 m + 10 m = 40 m.
Speed = 40 m ÷ 20 s = 2 m/s.
Your speed is 2 m/s.
b) Velocity = displacement ÷ time
displacememt = 0 (Your displacement is nothing. You have ended up at your original position. No net distance in a straight line has been made between the start and end point.)
velocity = 0 m ÷ 20 s = 0 m/s.
Your velocity is zero.
How to work out average velocity (Higher tier only)
If the initial velocity (u) and final velocity (v) are known, the average velocity can be calculated using the equation:
Average velocity = \(\frac{\text{initial velocity + final velocity}}{\text{2}}\)
This can be written as:
Average velocity = \(\frac{\text{u + v}}{\text{2}}\)
Question
A school bus is travelling at 4 m/s.
Its velocity then increases to 12 m/s.
Calculate the average velocity of the bus over the journey.
Answer
Final velocity = 12 m/s.
Initial velocity = 4 m/s.
Average velocity = \(\frac{\text{initial velocity + final velocity}}{\text{2}}\)
= (4 m/s + 12 m/s) ÷ 2 = 16m/s ÷ 2 = 8 m/s.
The average velocity of the bus is 8 m/s.
Key fact
Average velocity = \(\frac{\text{displacement}}{\text{time}}\)
Average velocity = \( \frac{\text{initial velocity + final velocity}}{\text{2}} \)
You decide which equation to use, depending on the quantities given in the question.
How to calculate the rate of change of speed
When speed changes, the rate of change of speed can be calculated using the equation:
Rate of change of speed = \(\frac{\text{final speed – initial speed}}{\text{time taken}}\)
Rocos = \(\frac{\text{v - u}}{\text{t}}\)
Rate of change of speed is a scalar quantity and it is measured in m/s2.
Rate of change of speed is the scalar equivalent of accelerationThe rate of change of velocity. It is measured in metres per second squared (m/s²). Acceleration = change of velocity ÷ time taken..
Question
Find the rate of change of speed of an athlete, if she starts from rest (0 m/s) and she reaches a speed of 6 m/s in 12 seconds.
Answer
Final velocity v = 6 m/s.
Initial velocity u = 0 m/s (initially at rest).
The (final velocity – initial velocity) is (6 m/s – 0 m/s) = 6 m/s.
The rate of change of speed is (final velocity – initial velocity) ÷ time, which is 6 m/s ÷ 12 s = 0.5 m/s2.
The rate of change of speed of the athlete is 0.5 m/s2.
This means every second, their speed increases by 0.5 m/s.
What is acceleration? (Higher tier only)
When an object changes velocity, it accelerationThe rate of change of velocity. It is measured in metres per second squared (m/s²). Acceleration = change of velocity ÷ time taken..
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity.
Acceleration is the change in velocity per second and is measured in m/s2.
Acceleration is a vector quantity because it has size and direction.
The relationship between acceleration, change in velocity and the time taken is given by the equation:
acceleration = \(\frac{\text{(final velocity – initial velocity)}}{\text{time taken}}\)
This can be written as:
a = \(\frac{\text{v - u}}{\text{t}}\)
v = final velocity and u = initial velocity
v - u = the change in velocity.
When objects are dropped from rest on Earth, they accelerate towards the ground at a rate of 10 m/s2.
If an object has an acceleration of 10 m/s2 it means that the velocity of the object changes by 10 m/s every second.
Click through to view the velocity of a ball dropped from rest
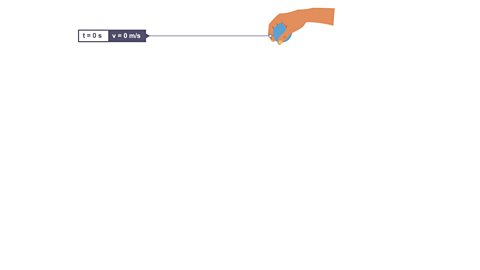
Image caption, 1. The ball is at rest. Time (t) is 0 seconds. Velocity (v) is 0 m/s.
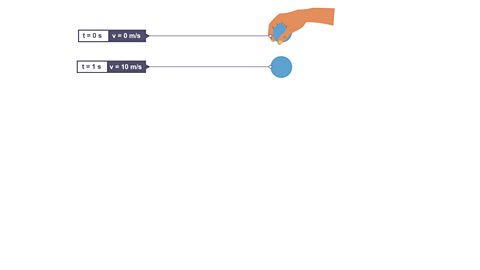
Image caption, 2. The ball is dropped. At time (t) 1 s, the velocity is 10 m/s.
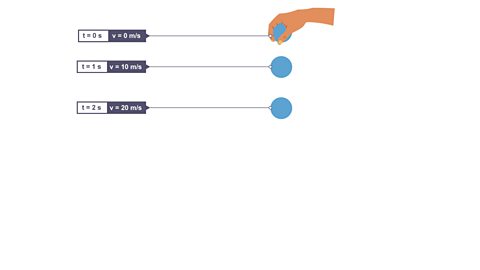
Image caption, 3. At time (t) 2 s, the ball's velocity (v) increases to 20 m/s.
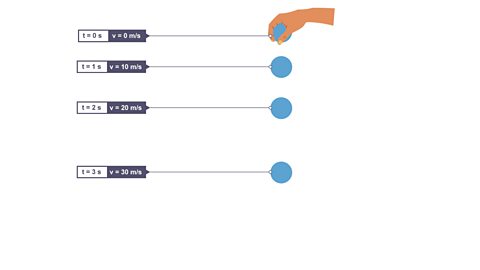
Image caption, 4. At time (t) 3 s, the ball's velocity (v) increases to 30 m/s.
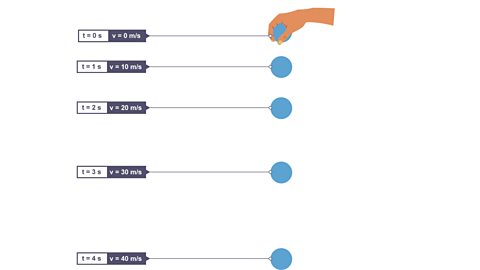
Image caption, 5. At time (t) 4 s, the ball's velocity (v) increases to 40 m/s.
1 of 5
Question
Find the acceleration of a car, if it starts at 10 m/s and it reaches 30 m/s in 4 seconds.
Answer
Final velocity v = 30 m/s.
Initial velocity u = 10 m/s.
The (final velocity – initial velocity) is (30 m/s – 10 m/s)
= 20 m/s.
The acceleration is (final velocity v – initial velocity u) ÷ time, which is 20 m/s ÷ 4 s = 5 m/s2.
The acceleration of the car is 5 m/s2
Question
Find the acceleration of the car, if it starts at 20 m/s and slows down to 12 m/s in 2 seconds.
Answer
Final velocity v = 12 m/s.
Initial velocity u = 20 m/s.
The (final velocity – initial velocity) is (12 m/s – 20 m/s)
= -8 m/s.
The acceleration is the (final velocity – initial velocity) ÷ time, which is -8 m/s ÷ 2 s = -4 m/s2.
The car has an acceleration of -4 m/s2.
A negative acceleration is called a retardation.
A minus sign means that the car is slowing down by 4 m/s every second.
Question
A car can accelerate from 22 m/s to 30 m/s in 4 seconds.
Calculate the acceleration of the car.
Answer
Final velocity v = 30 m/s.
Initial velocity u = 22 m/s.
The change in velocity = (v-u) = (30 m/s – 22 m/s)
= 8 m/s.
a = (v – u) ÷ t = 8 m/s ÷ 4 s = 2 m/s2.
The acceleration of the car is 2 m/s2.
Question
A motorcycle goes from rest (0 m/s) to 40 m/s in 8 seconds.
Calculate the acceleration.
Answer
Final velocity v = 40 m/s.
Initial velocity u = 0 m/s.
The final velocity – initial velocity = (v – u) = (40 m/s – 0 m/s).
= 40 m/s.
The acceleration = (final velocity – initial velocity ) ÷ time = 40 m/s ÷ 8 s = 5 m/s2.
The acceleration of the motorcycle is 5 m/s2.
Question
While riding his bike, Jacob brakes and slows from 11 m/s to 3 m/s in 2 seconds.
Calculate Jacob’s acceleration.
Answer
Final velocity v = 3 m/s.
Initial velocity u = 11 m/s.
The (final velocity – initial velocity) = (v – u) = (3 m/s – 11 m/s)
= -8 m/s.
The acceleration = (v – u) ÷ t = -8 m/s ÷ 2 s = -4 m/s2.
Jacob has an acceleration of -4 m/s2 (or a retardation of 4 m/s2).
Test your knowledge
More on Unit 1: Motion
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 4
- count4 of 4
- count1 of 4
