What is geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy is a type of renewable energy that uses the Earth’s natural heat to heat homes and businesses or generate electricity.
In this article you can learn about:
- What geothermal energy is
- How it can be used to generate electricity
- Where in the world geothermal energy is used
- What the advantage and disadvantages of geothermal energy are
This resource is suitable for energy and sustainability topics for primary school learners.
Video - Geothermal energy
In this short video, find out how geothermal energy works and what the advantages and disadvantages of geothermal energy are.
Meet Geothermal power, Geo for short.
He's not really at home in Scotland.
He's an extreme kind of guy.
He likes a bit of danger.
He's happiest in places with earthquakes and volcanos – where tectonic plates meet.
Tectonic plates are giant slabs of solid rock that make up the Earth's crust.
The plates sit on top of boiling hot magma (melted rocks to you and me), called the Earth’s mantle.
The plates sort of float about on the magma, moving to and fro, sliding into each other and sometimes causing natural disasters on the surface.
But it's not all bad, because the gaps in between the plates, called fault lines, sometimes let a wee bit of magma squeeze through.
And that magma heats up natural underground reservoirs, or big pools of water.
You know when you see a kettle boiling, with all the steam coming out the top? Well, they're like that. Definitely keep your hands off!
And this is where Geo comes back in: hi Geo. Yes, yes you are radical.
Geo's excited because this is basically hot water - for free!
And hot water is great for making electricity.
Geothermal power plants draw steam from the reservoirs to the surface.
The kinetic energy from the steam turns the turbines and generators turn this energy into electricity. The steam cools and becomes water again.
Then it's piped back underground to the reservoir where it will heat up and be used again.
This is great news for countries like Iceland, New Zealand or Indonesia, because they're on the fault lines of tectonic plates, so their power plants provide a constant, renewable and reliable source of electricity.
Countries like Scotland can't build Geothermal power plants because they're not on fault lines.
But Geo can help us out in Scotland just a wee bit with ground source heat pumps.
Ground source heat pumps push fluid through a loop of pipes underground.
Heat from the ground warms the fluid which flows up into your house, and through a heat exchanger where it heats up household water.
Sorry Geo. I know hot washing-up water isn’t very extreme.
But it is very useful!
Geothermal power plants
Geothermal power plants are built where there are underground reservoirs of water around fault lines in the Earth’s tectonic plates.
The gaps between the plates allow magma to heat up the water.
Learn what tectonic plates and fault lines are here: Tectonic movement

Image caption, Geothermal power plants use the power of the Earth's natural heat to generate electricity.
(Bart Pro / Alamy Stock Photo)
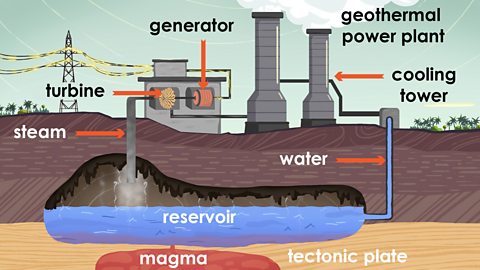
Image caption, Underground reservoirs of water are heated by magma, producing steam that rises and is channelled into the power plant.
The steam then turns turbines, which turn generators, generating electricity. The steam is then cooled down and returned to the reservoir.

Image caption, Geothermal energy plant and Blue Lagoon Leisure Park, Iceland
Geothermal energy currently supplies 70% of Iceland's energy. Most of it is used to heat water that keeps houses, streets and even open air swimming pools warm in all weathers. (robertharding / Alamy Stock Photo)
1 of 3
In a geothermal power plant:
The steam created from the heat of the water is drawn up to the surface.
The kinetic energyEnergy that an object possesses because of its movement. A ball being thrown through the air has kinetic energy because it is moving. When water moves this is also an example of kinetic energy. from the steam turns turbineA turbine is a machine that turns the movement of liquid or gas into energy that can be used. In a simple turbine water or air push against turbine blades and spin them round. The spinning blades turn a long pole called a shaft. The shaft can then turn other pieces of machinery, such as a generator that is used to produce electricity. in the power plant.
The generatorA machine that is used to make electricity. When the generator head is turned, this energy is converted to electrical energy. then turn this energy into electricity.
The mantleThe largest part of the Earth’s interior and lies between the Earth’s core and the Earth’s crust. It is extremely hot and is mostly made up of molten rock. cools the steam and it becomes water again and then the water is piped back into the reservoir where the process can start again.
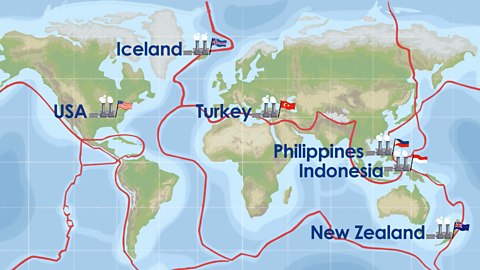
Where are geothermal power plants?
Most geothermal power plants are located in parts of the world that sit on fault linesLong cracks in the Earth’s crust. These cracks form gaps between huge slabs of rocks called tectonic plates. Earthquakes and volcanoes occur most along fault lines. between tectonic plates. They have lots of volcanic activity and the Earth's crust is thinner, which helps create the conditions needed to capture geothermal energy more easily.
Countries like Iceland, New Zealand and Indonesia can use geothermal energy because they are on these fault lines.
Geothermal energy in the UK
Geothermal power plants work best in places where there are fault lines between tectonic plates and less drilling is needed to reach underground stores of hot water.
Building geothermal plants in the UK could work but would be more expensive to set up. Pipes might have to stretch hundreds of metres or more underground to reach sources of hot water.
Two projects in Scotland (in Shettleston in east Glasgow and Lumphinnans in Fife) already work in a similar way. Instead of drilling new pipes, each use the heat from water in abandoned mines to heat a small number of homes.
Ground source heat pumps
Countries like Scotland can also benefit from geothermal energy by using ground source heat pumps. These use shallow underground pipes to warm water that can then be used to help heat buildings.
The lower you go underground, the warmer the ground is, so pumping fluid through underground pipes can heat it up. We can use this to provide central heating and hot water for our homes.
This is another example of geothermal energy.
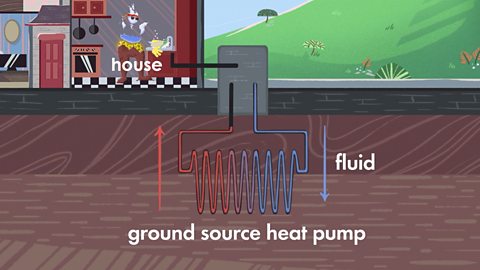
Image caption, In Scotland you can use ground source heat pumps to power central heating and provide hot water for our homes.

Image caption, Most ground source heat pumps use horizontal pipes that are buried in trenches two metres or more underground. (Adam Murphy / Alamy Stock Photo)
1 of 2
The advantages and disadvantages of geothermal electricity
Advantages of geothermal electricity
Geothermal power is more environmentally friendly than the use of fossil fuels and its carbon footprint is low.
It is a source of renewable energy that will not run out. The hot reservoirs within the Earth are naturally refilled, making it both renewable and sustainable.
There are a lot of geothermal sources we haven't yet explored so there is a lot more energy to find and use.
Learn about the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy: What is renewable and non-renewable energy?
Disadvantages of geothermal electricity
Geothermal power plants can't be built everywhere. They are easiest to set up near fault lines, and become more expensive and difficult to set up the further down you have to drill to reach hot water.
Greenhouse gases can be released from underground during drilling into the ground to build geothermal power plants. These gases are released into the atmosphere naturally but this happens more quickly near geothermal plants.
Building geothermal power plants (which involves digging into the Earth) can trigger earthquakes.
Find out what causes earthquakes with Isla and Connor: Tectonic Movement: Earthquakes

Key words about geothermal electricity
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – The surface layer of the Earth. It covers the whole planet, both land and sea. It is made of rocks and minerals and can be anywhere between 1.5 to 70 km thick.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – Large slabs of solid rock that form the Earth’s crust. They are like the pieces of a large jigsaw puzzle that fit together and are separated by fault lines. Tectonic plates slowly float around on a thick layer of hot, molten rock called the mantle. The movement of tectonic plates can create mountains and seas or cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – Long cracks in the Earth’s crust. These cracks form gaps between huge slabs of rocks called tectonic plates. Earthquakes and volcanoes occur most along fault lines.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – The thickest layer of the Earth’s interior. It lies between the Earth’s core and the Earth’s crust. It is extremely hot and is mostly made up of molten rock.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – Molten rock that is located deep below the Earth’s surface. Magma can escape when deep cracks in the Earth's crust appear or when volcanoes erupt. Magma that reaches the Earth's surface is called lava.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – An event that happens as a result of natural processes. A natural disaster cannot be caused by humans. Volcanoes, earthquakes and tsunamis are examples of natural disasters that can be caused by the movement of the tectonic plates.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – A turbine is a machine that turns the movement of liquid or gas into energy that can be used. In a simple turbine water or air push against turbine blades and spin them round. The spinning blades turn a long pole called a shaft. The shaft can then turn other pieces of machinery, such as a generator that is used to produce electricity.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – A machine that is used to make electricity. When the generator head is turned, this energy is converted to electrical energy.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – A large tower that is used to cool the steam, turning it back to water, which is then returned to the reservoir.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Challenge

Find countries that could most easily use geothermal energy
Find two maps online: a map of the world and a map of the world’s fault lines.
Use the maps to find countries that have the most potential to create power using geothermal energy.
Pick two or three countries : Do they currently have geothermal power plants? If they do, what is this energy is used for?
Tectonic movement. mapTectonic movement
Explore where tectonic plates and fault lines are with Isla and Connor.

More on Sustainability
Find out more by working through a topic
- count7 of 16

- count8 of 16

- count9 of 16

- count10 of 16
