How shadows are formed

We are surrounded by sources of light.
The Sun is our main source of natural light but we also get light from artificial sources such as ceiling lights, lamps, torches, candles and even electronic devices like phones and televisions.
Light travels in straight lines and will keep going until it is blocked by an opaque object, which does not let any light pass through it.
light cannot pass through the object, and cannot bend around it, so it bounces back off the object.
As the light cannot get to the space behind the object this creates a dark area called a shadow.

Not all shadows are the same size or shape.
The size and shape of the shadow matches the size and shape of the object that is blocking the light (as long as the light is pointing straight at the object).
A person will make a person shaped shadow, and a giraffe will make a giraffe shaped shadow! But there are other things that affect the size of a shadow.
Watch: Light and shadows
FRAN: A shadow is created when an object blocks the light from a light source.
Let me show you.
This torch is lighting up this board here.
And if I put my toy astronaut in front of the light… then we get a shadow. And this is because light travels in straight lines.
So, when the light reaches the astronaut, it can't go around the astronaut, and it can't go through it.
So instead, it blocks the light.
And behind the astronaut there is no light, and so we have a shadow.
And this works for many objects. We can use my hand, or we can use this toy spider, and the same happens.
But do you know what? I hate spiders!
So, let's check in with one of my investigators to see what they've found out about shadows.
INVESTIGATOR: I'm making shadow puppets! The light shines into the theatre.
I can put my puppets here to block the light and make shadows!
The sun is also a light source.
When the sun's light hits you, your body creates a shadow on the ground or wall behind you.
FRAN: Do you know what I really liked?
How you made the puppets look bigger and smaller by moving their position.
And I can do that too, by moving this object - this spider - closer to the light, then it blocks more light, so makes a bigger shadow.
And then if I move this object further away from the light, it blocks less light and makes the shadow smaller.
And it even works if I move the light source but not the object, look! It gets bigger and smaller.
Have you ever seen your shadow when it's all spread out in a pattern?
Well, that happens when there is more than one light source pointing at an object, and it creates multiple shadows.
So we have one light source and two light sources.
And look, multiple shadows!
Now that is cool!
Watch: Shadows around the world
Watch how light and objects work together to create shadows.
Have a think about the different sizes of the shadows in the video.
- Why are some shadows bigger than others?
- Do any shadows change in size?
- Larger objects produce larger shadows. This is because it is blocking more of the light. If the light source is close to the shadow, this also leads to a larger shadow.
- Some shadows, like the palm trees, change in size. This is because the distance from the light sources changes.
What did you find out?
Shadows are changed by:
- The size of the object.
- Whether the light source is moving or still.
- How close the object is to the light.
- How high the light source is.
Fascinating facts

Sundials were first used to tell the time thousands of years ago. Many people still have them in their gardens today.
Half the world is always in shadow because the Sun's light can only reach the side of the Earth which is facing it.
If the object is further away from the light source, the shadow is smaller.
Some objects, such as glass, are transparent and don't make a shadow. Light can shine through them. Some light shines through translucent objects, such as a balloon or sheet of wax paper.
Light travelling through space is usually in a sharper focus, as it doesn't travel through an atmosphere.
When a shadow is cast by the Earth onto the Moon, it is called a lunar eclipse.
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, blocking the Sun's light and forming a shadow.
Shadows are generally longer in the winter as the position of the Sun is lower in the sky.

How do shadows change?
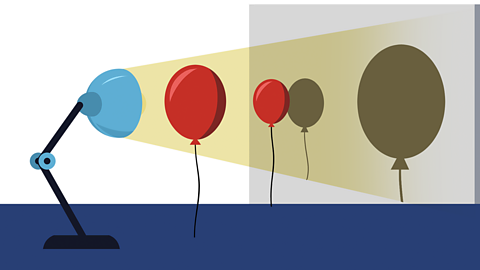
The size of the object
If the same light source was shining on two objects from the same distance away, a bigger object would create a larger shadow and a smaller object would create a smaller shadow.
If an object changes size when the light is shining on it, such as with a balloon inflating, then the shadow will change size too.


Whether the light source is moving or still
If both the light source and the object stay still then the shadow will stay still too.
But if the light source begins to move then the shadow will change, either by changing the direction in which the shadow is pointing (it will always be behind the object, on the opposite side that the light source is) or by changing the length or width of the shadow.
You can see this by looking at the shadow of a tree throughout the day as the Sun moves across the sky.

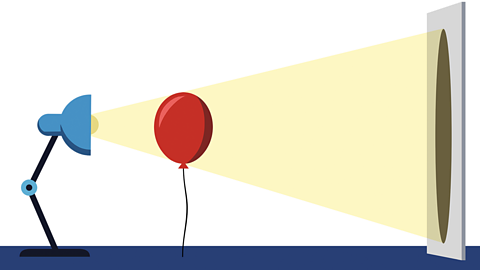
How close the object is to the light
If an object is close to the light source then it will create a bigger shadow.
This is because the object is blocking more of the light. If the light source is further away then it will create a smaller shadow because it is blocking less of the light.

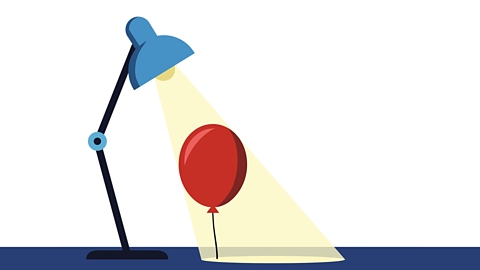
How high the light source is
if the light source is close to the ground and pointing to the side of the object then this will create a long shadow that comes out of the opposite side of the object.
As the light source moves higher the shadow will become shorter and shorter until the light source is high up and pointing straight down onto the object, where there will be no shadow at all that you can see.
This is shown when the Sun rises, travels overhead and sets at the end of a day; the shadows will be longest in the morning and evening, and shortest at midday.

Light and shadows

Image caption, A sundial
The Sun appears to move across the sky, forming shadows that change position throughout the day. However, it is not the Sun moving but our Earth rotating that causes the shadows to change. We can tell the time by looking at the shadows.

Image caption, Shadow puppet
You can use light to cast a shadow of your hands on a wall. You can move your hands to make different shapes and the shadow will make an image. You can make things using your hands like a dog, a cat or even a rabbit.

Image caption, Glass bottles
Glass is translucent which means that it allows light to pass through it, but objects on the other side will not be clearly seen.
1 of 3

Did you know?
If an object is opaque like a person then this will create a dark black shadow because no light can pass through at all.
If an object is translucent then the shadow will be much paler and be more grey than black because some light is passing through.
If an object is transparent, like a window or a glass it won’t make a clear shadow at all as the light can travel through it.

Important words
Light – Beams that can be seen by the human eye. Light travels in straight lines and will keep going until it is blocked by a solid object.
Opaque – Opaque means something that does not allow light to pass through it and cannot be seen through.
Translucent – Translucent means the material will allow some light to pass through it but objects on the other side will not be clearly seen.
Transparent – If an object or material is transparent, it means light completely passes through it, and you can see clearly through it.
Shadow – A shadow forms when an opaque or non-transparent object blocks light from passing through it and reaching a surface on the other side.
Activities
Activity 1 – Identifying the parts of a shadow
Activity 2 – Shadows quiz
Activity 3 – Shadow experiment
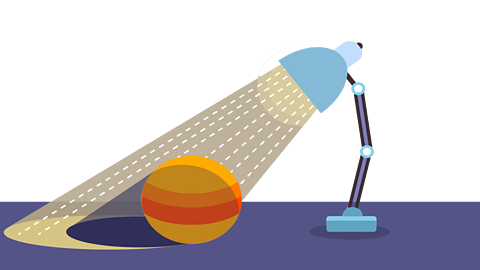
- Choose an opaque object which will make a shadow.
- Move the object nearer or further away from a light source.
- Measure the length of the different shadows.
You could record your findings in a table like this.
| Object | Distance from light source | Length of shadow |
|---|---|---|
| tennis ball | 5cm | |
| 10cm | ||
| 15cm | ||
| 20cm | ||
| 25cm |
- Try it with a different object.
- What did you notice? Did you change the size of the shadow?

New game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space. gameNew game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space
Join Pipette on her epic mission and learn some revolting facts about space along the way.

More on Light
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 3

- count2 of 3