What are the key points about electromagnetic waves and radar?
Regions of the electromagnetic spectrumThe different types of electromagnetic radiation, arranged in order of frequency or wavelength..
Uses and dangers of electromagnetic waveA transverse wave caused by oscillations in an electromagnetic field. waves.
radarThe letters in the word radar stand for Radio Detection And Ranging. Radar is a detection system which uses radio waves to determine the location and speed of aircraft and other objects..
What are the common properties of electromagnetic waves?
electromagnetic waveA transverse wave caused by oscillations in an electromagnetic field. are members of a family of waves with common properties called the electromagnetic spectrumThe different types of electromagnetic radiation, arranged in order of frequency or wavelength..
All electromagnetic waves:
are transverse wave A wave that moves in a direction at right angles to the way in which the particles are vibrating.;
can travel through a vacuumA volume/ region of space that contains no matter.;
travel at exactly the same speed in a vacuum, the speed of light, 300,000,000 m/s.
Like all waves, electromagnetic waves:
transfer energy from one place to another;
can be reflected;
can be refractionProcess by which a wave changes speed and sometimes direction upon entering a denser or less dense medium, eg a light ray changes direction when refracted by a lens..
Differences
Each type of wave in the electromagnetic spectrum has different:
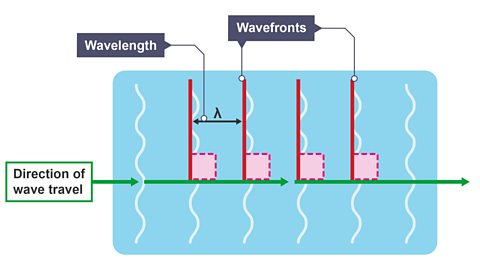
wavelengthThe length of a single wave, measured from one wave peak to the next.;
frequencyThe number of waves produced each second. The unit of frequency is hertz (Hz)..
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of wavelengthThe length of a single wave, measured from one wave peak to the next..
The types of radiation that occur in different parts of the spectrum have different uses and dangers - depending on their wavelength and frequencyThe number of waves produced each second. The unit of frequency is hertz (Hz)..
There are seven members of electromagnetic family.
The order of electromagnetic waves in the spectrum is shown in the table below.
They are arranged in order of decreasing wavelength (and increasing frequency):
| Energy | Frequency | Wavelength | Radiation type | Typical wavelength in m | Typical use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lowest | Lowest | Longest | Radio waves | 1 | Communication such as: • TV and radio • mobile phones • radar • Wi-Fi • Bluetooth |
| microwaves | 1 x 10-2 | Fast cooking of food and satellite communication | |||
| Infrared | 1 x 10-4 | Heat transfer by radiation: • electric heaters • cooking by grilling • night vision equipment • TV remote control • burglar alarms | |||
| Visible light | 4 x 10-7 to 7 x 10-7 | • seeing • photography • optical fibre communication | |||
| Ultraviolet | 1 x 10-8 | • Sunbeds, which make vitamin D in the skin and can be used to treat some skin conditions • detecting forged bank notes • hardening some types of dental filling • nightclubs and bowling alleys to make clothes glow | |||
| X-rays | 1 x 10-10 | • medical images of bones • airport baggage scanners | |||
| Highest | Highest | Shortest | Gamma radiation | 1 x 10-12 | • killing cancer cells • sterilising medical equipment • killing bacteria to prolong shelf life of fruit |
Radio waves have the lowest frequencies and longest wavelengths, while gamma waves have the highest frequencies and shortest wavelengths.
All of these waves travel at the same speed in a vacuum, which is the speed of light or about 300,000,000 m/s (metres per second).
Key fact
It is important to remember the order of the seven regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The following sentence might help: Rats and Mice In Venice Use eXtra Gondolas.
What are the hazards of electromagnetic radiation?
Over-exposure to certain types of electromagnetic radiation can be harmful.
The higher the frequencyThe number of waves produced each second. The unit of frequency is hertz (Hz). of the radiation, the more energy it carries and the more damage it is likely to cause to the body.
Radio waves can cause a very small rise in the temperature of the human body - of up to 0.2oC. Some people claim the very low frequency radio waves from overhead power cables and mobile phone base stations near their homes has affected their health, although this has not been reliably proven.
Microwaves can cause internal heating of body tissues. The microwaves are absorbed by water molecules and vibrate vigorously, causing a rise in temperature.
Infrared radiation is felt as heat and causes skin to burn.
Visible light from a laser which is very intense can damage the retina at the back of the eye.
Ultraviolet can damage skin cells and lead to skin cancer and damage the eyes, it can cause skin to age prematurely.
X-rays damage cells inside the body. They cause dangerous ionisationProcess by which electrons can be added or removed from an atom to create an ion. and when this happens with moleculeA collection of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. in living cells, the genetic material of a cell, the DNAThe part of the cells of living things that carries information about how they look and function. Everyone’s DNA is different, except identical twins who share the same DNA. is damaged. This can lead to cancer. This is why doctors and dentists stand behind protective screens when taking lots of X-rays.
Gamma rays also damage cells inside the body causing dangerous ionisation in living cells which damages DNA. This can lead to cell death and cancer.
Ultraviolet radiation and suntan
Ultraviolet radiation, UV, is found naturally in sunlight.
We cannot see or feel ultraviolet radiation, but our skin responds to UV exposure by turning darker over time.
This is called a sun tan.
This happens as our bodies attempt to reduce the amount of ultraviolet radiation reaching deeper skin tissues.
Darker skins absorb more ultraviolet light, so less ultraviolet radiation reaches the deeper tissues.
This is important, because prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation can cause skin cancer and damage to eyes.
It is sensible to wear high protection, UV blocking sunscreen on sunny days to avoid skin cancer.
Overexposure of our eyes to ultraviolet radiation can cause blindness, so we should also wear hats and sunglasses on sunny days.
Example
Radio 1 broadcasts on a frequency of 99.7 MHz.
Calculate the wavelength of Radio 1 waves.
Answer
Radio waves are electromagnetic waves and so their speed in a vacuum = 300,000,000 m/s.
v = f \(\lambda\)
v = 300,000,000 m/s
v = 300,000,000 m/s
f = 99.7 MHz = 99.7 x 106 Hz
300,000,000 m/s = 99.7 x 106 Hz x\(\lambda\)
\(\lambda\) = \(\frac{\text{300,000,000}}{\text{99.7 x 10}^{6}}\)
\(\lambda\) = 3.0 m
The wavelength of Radio 1 waves is 3.0 m.
Question
State three differences between sound waves and electromagnetic waves.
Answer
- Sound waves are longitudinal waveA wave that moves in the same direction (parallel) as the direction in which the particles are vibrating. , electromagnetic waves are transverse wave A wave that moves in a direction at right angles to the way in which the particles are vibrating..
- Sound waves cannot travel through a vacuum, electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuumA volume/ region of space that contains no matter..
- Sound waves travel at 330 m/s through air, electromagnetic waves travel much faster, at 300,000.000 m/s through air.
What is radar?
Ultrasound travels at the speed of sound which is 330 m/s in air.
This is not fast enough to track fast, high-flying aircraft.
For example, an ultrasound pulse would take over 6 seconds to return after reflecting from an aircraft 1 km away.
By that time the aircraft would have moved position significantly.
So, instead of using ultrasound, radio waves are used as they travel at 300,000,000 m/s.
A radio wave echo from the same aircraft would return after 3 millionths of a second. (3µs).
This is why radar is used instead of sonar for aircraft.
Radar stands for Radio Detection And Ranging.
It works in the same way as sonar but with radio waves in place of ultrasound.
A short pulse of radio waves is transmitted and the time it takes for the reflection (the echo) to return is measured.
The distance is calculated using distance = speed x time.
As with sonar, it is important to remember to only use half of the time there and back when calculating the distance.
Example
meteorologistsPeople who study weather. use radar to track a storm.
A pulse of radar is reflected by the storm and returns to the receiver after 3 ms.
- How far away is the storm?
- Why do the meteorologists use radar to track the storm rather than sonar?
Answer
1. How far away is the storm?
Radar uses radio waves which are electromagnetic waves and travel at a speed of 300,000,000 m/s.
Distance = speed x time
Speed = 300,000,000 m/s
Time for the radio waves to travel to the storm and back = \(3 ms = \frac{\text{3}}{\text{1000}}\) = 0.003 s
Time for the radio waves to travel to the storm = \(\frac{\text{0.003 s}}{\text{2}}\) = 0.0015 s
Distance = 300,000,000 m/s x 0.0015 s = 450,000 m = 450 km.
The storm is 450 km away.
2. Why do the meteorologists use radar to track the storm rather than sonar?
The meteorologists uses radar because the distance involved is so large and ultrasound travels relatively slowly at 330 m/s.
It would take sonar too long to travel to the storm and back, during which time the storm would have moved.
This would make it impossible to determine its position accurately.
How much do you know about electromagnetic waves and radar?
More on Unit 2: Waves
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 5

- count2 of 5

- count3 of 5
- count4 of 5