Key points
Starch is a type of carbohydrates These are mainly sugar and starches which provide your body with energy. Foods like bread, pasta, rice and potatoes contain lots of carbohydrates.. Its molecules contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
Iodine solution is used to test for starch.
The digestion of starch makes glucoseA sugar produced by plants in photosynthesis and used by all living organisms to release energy during respiration..
Video - Starch in cooking
A case study video explaining how starch molecules react in cooking.
We cook rice every day in the restaurant. We cook maybe around 15 kilos. So, I'm going to show you what happens when you don't wash rice. You'll see just how starchy it is. It will rise above the water and it will be completely white, and that's what makes the rice really sticky.
I need to add just enough water to cover the rice. Before I light the stove, I'm just going to give the rice a swirl and this helps to bring all the starch up. And you can see that the water has changed colour and it's become white.
The rice has been cooking for a while now, but you can see just how starchy it is.
How is starch useful?
Starch is a type of carbohydrate. Its molecules are made up of large numbers of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Starch is a white solid at room temperature, and does not dissolve in cold water.
Most plants, including rice, potatoes and wheat, store their energy as starch. This explains why these foods – and anything made from wheat flour – are high in starch.
You can use iodine to test foods for starch. If starch is present, the orange-yellow iodine solution becomes blue-black.
Starch has many uses. Your body digests starch to make glucose, which is a vital energy source for every cell. Food companies use starch to thicken processed foods, and to make sweeteners. Scientists are investigating the effects of these sweeteners on health.
A rotating model of a starch molecule.
Polymerisation of starch
Starch is an example of a natural polymer. A polymer is a long and repeating chain of the same molecule stuck together. Starch is a long-chain polymer of glucose molecules joined together.
As the plant adds one glucose molecule to the starch polymer, one molecule of water is released. You can see this mechanism in the video opposite. Plants create starch polymers, for example in grains of wheat, to store the glucose made by photosynthesis.
A model of the polymerisation of starch.
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

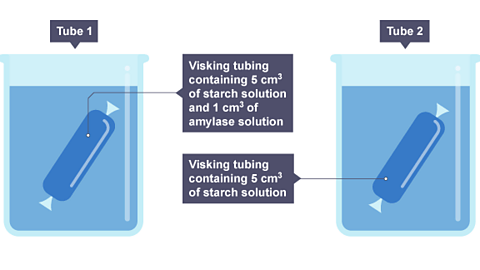
More on Nutrition, digestion and excretion
Find out more by working through a topic
- count13 of 15
- count14 of 15
- count15 of 15

- count1 of 15