Key points
- Construction kits allow for quick and easy assembly, but they are limited by the components available in the kit.
- Working models can be custom-built to precise specifications, but they are time-consuming to create and mistakes can be costly.
- Virtual models (CAD/CAM) eliminate material costs and allow for easy modifications, but they require training in CAD/CAM software.
What are mechanical kits?
- Construction Kits (like Meccano or Lego Technic): These offer quick assembly and testing of ideas. Users can easily modify designs and see immediate results. The advantage is that users can experiment safely and quickly, while the main disadvantage is that the components are limited to what's in the kit, and the final product might not perfectly match the design intentions.
- Working models: these are custom-built using resistant materials like wood, metal, or plastic. The advantage is that users can create exactly what they envision and learn practical manufacturing skills. However, working models can take longer to make, require more skill, and mistakes can be costly in terms of materials and time.

- Virtual models (CAD/CAM ): using software to design and test mechanisms offers the advantage of zero material cost and easy modification. Users can simulate movement and spot problems before building. The disadvantage is that users don't get hands-on experience with physical materials and might miss practical construction challenges. In addition, users need to undergo training in computer aided design (CAD)The process of creating a 2D or 3D design using computer software./computer aided manufacture (CAM)The manufacture of a part or product from a computer aided design (CAD) using computer-controlled machinery, such as a 3D printer.software to be able to use it properly.

How to adhere to mechanical safety
When building and using mechanical systems, users need to understand several key safety aspects:
- Moving parts protection: all rotating parts need proper guards to prevent entanglement or injury. This includes covering gears, belts, and pulleys.
- Stability: ensuring the base is secure and the mechanism is properly mounted to prevent tipping or collapse during operation.
- Material selection: using appropriate materials that can withstand the forces involved without breaking or failing.
- Operational safety: understanding safe operating procedures, including startup, shutdown, and emergency stops.

What are mechanical components?
Wheel and axle
This fundamental mechanism consists of a wheel fixed to a central shaft. It's used to reduce effort in rotary motion, like in a door handle or steering wheel.
Gears
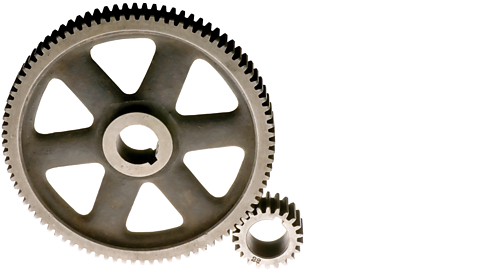
These toothed wheels transmit rotary motion and can change speed, direction, and force. Different types (spur, bevel, worm) serve different purposes in machines.

Cams and followers
These mechanisms convert rotary motion to Reciprocating motionA repetitive up-and-down or back-and-forth linear motion . The follower's shape (flat, knife, roller) affects the motion quality.
Levers

These simple machines amplify force or change its direction.
There are three classes of levers and some applications include scissors (first class), wheelbarrows (second class) or fishing rods (third class).

Belts and pulleys

These transfer rotary motion between parallel shafts and can change speed and direction. Examples include bike gears and conveyor systems.

Shafts

These transmit rotary motion and TorqueA measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis between components.
Their diameter and material affect their strength and performance.

Test yourself
More on Mechanical control systems
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 5

- count5 of 5
