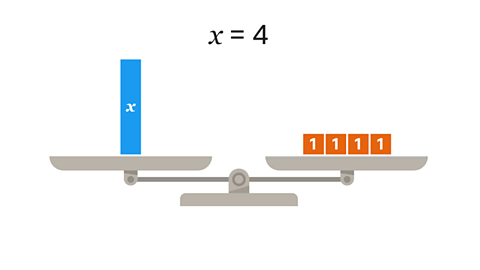
Key points
- A good understanding of how to solve equations with 𝒙 on one side is useful when working with equationA mathematical statement showing that two expressions are equal. The expressions are linked with the symbol = with one unknownA number that we do not know. They are commonly used in algebra, and sometimes referred to as variable and represented by symbols such as 𝒙 or 𝒚 value.
- A set of equations with more than one unknown value are called simultaneousHappening at the same time. equations.
- When there are two unknown values, two equations will be required in order to solve them.
- The two equations cannot be solved on their own. Each one by itself has an infiniteUnlimited, endless number of solutions.

Video
Simultaneous equations can be useful when running a business.
Watch the video to listen to Kim, a textiles designer, talk about how simultaneous equations help her when deciding on how to deliver her products to customers.
Bobby: Hi, Kim.
Kim: Hi, Bobby.
Bobby: Tell me about your fashion business.
Kim: Yes, so we make silk scarves that raise awareness for endangered species and we sell them online.
Bobby: Ah, so when you sell them online and someone buys them, how is it delivered to the customer?
Kim: It normally takes three to five days for delivery and free delivery when you spend over fifty pounds.
Bobby: Oh, that’s good. So it’s free delivery to the customer but it obviously costs you to deliver to them. How do you work out the most cost-effective way of doing this?
Kim: So, I need to compare services. If I have a smaller package, I might use one service and if I have a bigger package, I might use another service.
Bobby: Okay, so if you treat the overall cost and the size of the package as our two variables, then you can compare the two services using simultaneous equations. Based on the answer you get, you’ll know to use Service A for any packages smaller than that, and Service B for any packages larger.
Kim: Yes, absolutely. I need to take considerations into the cost of delivery, the speed of delivery and the cost of packaging.
Bobby: Okay, yeah. So we’re really seeing different unknown variables being applied to a real-life fashion business using simultaneous equations.
Kim: Exactly!
Equations with two unknown variables
One equation with two unknown values will have infiniteUnlimited, endless solutions. This means there is not enough information provided to find the exact solution to the equation.
For example, if two different items are bought together and only the combined cost of them is known, then it is not possible to work out the individual cost of each item.
There are a number of potential solutions to this problem, including solutions that are not integerIntegers are numbers with no fraction or decimal part. They can be positive, negative or zero. 42, 8, and 10000 are examples of integers. values.
Example
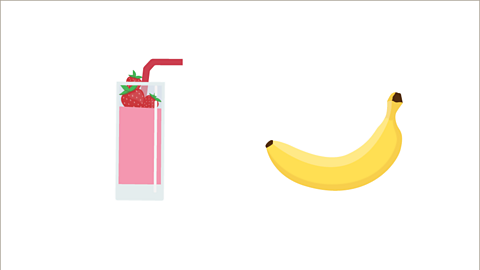
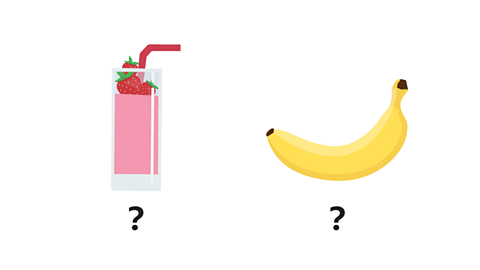
Image caption, The combined cost of a smoothie and a banana is £6. Work out the cost of the banana.

Image caption, The two items could cost the same amount. The smoothie could cost £3 and the banana could also cost £3. This is not the only possible solution.

Image caption, Either item could cost more than the other, but still total the same amount when added together. For example, the smoothie could cost £4 and the banana could cost £2. Add the two amounts: £4 + £2 = £6

Image caption, The cost of each item may not be an integer value. The smoothie could be £2.50 and the banana could be £3.50. Take care when checking solutions that are not integer values. £2.50 + £3.50 = £6
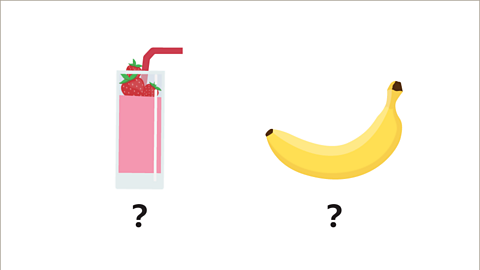
Image caption, An equation with two unknown values will have an infinite number of solutions. The unknown values are the cost of the smoothie and the cost of the banana. When there are two unknown values, then two equations will be required to work them out.
1 of 5
Solving a simultaneous equation
- One equationA mathematical statement showing that two expressions are equal. The expressions are linked with the symbol = with two unknownA number that we do not know. They are commonly used in algebra, and sometimes referred to as variable and represented by symbols such as 𝒙 or 𝒚 values will have an infiniteUnlimited, endless number of solutions.
- If a second equation is introduced, then it is possible to solve the problem and find the value of both variableA quantity that can take on a range of values. .
- Two equations with the same solutions are called simultaneousHappening at the same time. equations.
- Comparing the two equations often leads to one variable being eliminated, meaning the value of the remaining variable can be calculated.
- The other variable can be calculated using substituteIn algebra substitute means to replace a letter (or variable) with a number..
Example

Image caption, The total cost of a smoothie and a banana is £6. The cost of a strawberry smoothie and two bananas is £8.50. Work out how much each item costs.

Image caption, Compare the two sets of items. Look at what is the same and what is different.

Image caption, Each set of items contains a smoothie and a banana. The second set has one extra banana and costs £2.50 more than the first. Calculate £8.50 - £6

Image caption, A banana costs £2.50

Image caption, The first set of one smoothie and one banana costs £6. The cost of the banana is £2.50. Substitute the price of the banana into the equation. Smoothie + £2.50 = £6
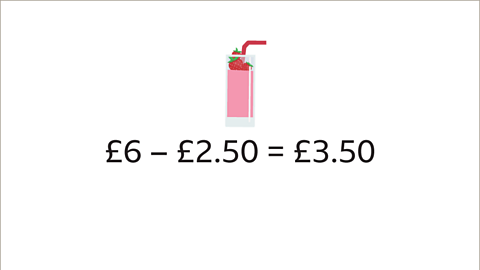
Image caption, Calculate the price of the smoothie using subtraction. £6 - £2.50 = £3.50

Image caption, Check solutions work for both equations by substituting the values, so £3.50 + £2.50 = £6 and £3.50 + £2.50 + £2.50 = £8.50
1 of 7
Question
Two smoothies and two bananas cost £11
Two smoothies and three bananas cost £14
What is the price of a banana?

The second set of items contains one additional banana.
The second set costs an additional £3. £14 - £11 = £3
The price of a banana is £3

Representing the problem using a bar model
- A bar modelOne or more rectangular bars drawn to represent information. can be used to represent a problem, instead of drawing or using images for each object.
- Using images helps to identify the structure of the mathematical problem, however a bar model can be drawn more quickly, especially if the problem involves a larger number of items.
- The representation of a bar model can be used in other mathematical contexts.
Example

Image caption, One smoothie and one banana cost £6.50. One smoothie and three bananas cost £13.50. Work out the price of a smoothie.
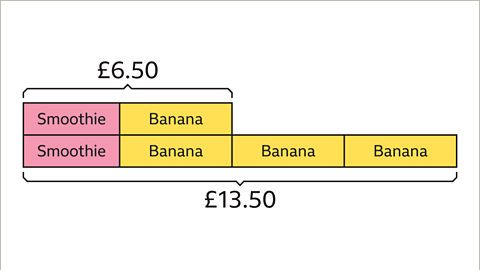
Image caption, This information can be represented as a bar model rather than using images for the different items. The first set of items is represented by the bar at the top. The second set of items is represented by the bottom bar. The bar model helps identify what is the same and what is different.
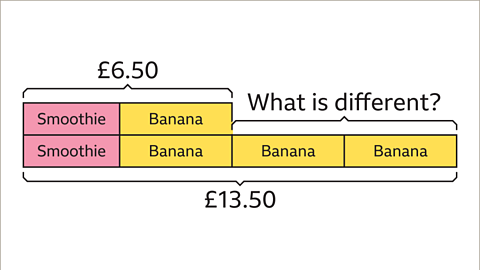
Image caption, Each set of items contains one smoothie and one banana. The difference is that the second set of items has two extra bananas.
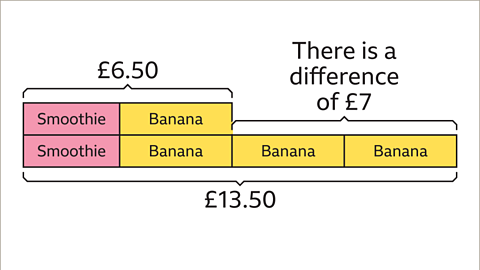
Image caption, The extra two bananas cost £7 (£13.50 - £6.50 = £7)

Image caption, If two bananas cost £7, each banana costs £3.50. Adding the price of each banana to the bar model makes it simpler to work out the price of the smoothie.

Image caption, Using the first set of items, one smoothie and one banana cost £6.50. £6.50 - £3.30 = £3. Each smoothie costs £3

Image caption, It is important to check that solutions work for both equations by substituting the values. The first set included one smoothie and one banana. £3 + £3.50 = £6.50

Image caption, The second set included one smoothie and three bananas. £3 + £3.50 + £3.50 + £3.50 = £13.50. The solution works for both equations.
1 of 8
Question
Two cups of tea and two cups of coffee cost £10 in total.
Two cups of tea and one cup of coffee cost £7
What is the price of one cup of tea?
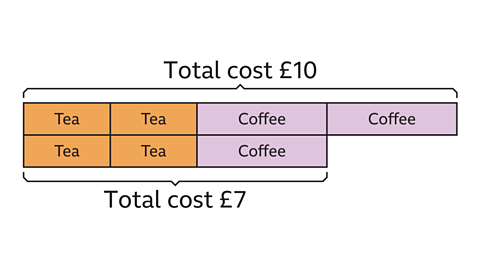
The extra cup of coffee increases the cost by £3
Two cups of tea and one cup of coffee cost £7
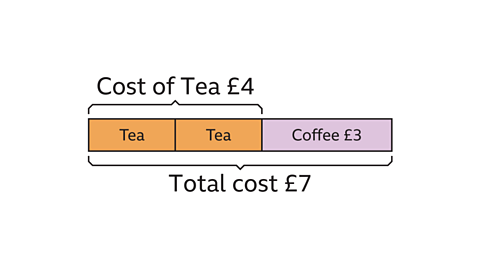
Therefore, two cups of tea cost £4
One cup of tea costs £2
It is important to check solutions work for both equations by substituting the values.
Two cups of tea and two cups of coffee cost £2 + £2 + £3 + £3 = £10
Two cups of tea and one cup of coffee cost £2 + £2 + £3 = £7
The solution works for both equations.
Practise solving simultaneous equations
Practise solving simultaneous equations with this quiz. You may need a pen and paper to help you work out your answers.
Quiz
Real-life maths

Simultaneous equations can be used by athletes, for example when calculating the best routes for running or cycling training.
They can create a mathematical expression that takes into account the distance and average speed for different parts of the route they plan to take. Equations can be used to set different goals, such as maximising time for building endurance, or speed for best performance.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Equations
Find out more by working through a topic
- count6 of 7
- count7 of 7

- count1 of 7

- count2 of 7