Transformations
Transformations change the size or position of shapes.
The 4 transformations of 2D shapes that you should know are covered in M5, M6 and M7:
- translation – moving a shape in a straight line
- reflection – flipping. a shape to create a mirror image
- rotation – turning a shape
- enlargement – changing the size of a shape by a scale factor
In the exam you may be asked to draw and/or describe transformations.
In Module 8 (M8), there may be questions on any of the transformations work at M5, M6 and M7 as well as:
- enlargement using a negative scale factor
- combined translations
Enlargement with a negative scale factor
An enlargement with a negative scale factor produces an image on the other side of the centre of enlargement. The image appears upside down.
Example
Enlarge triangle G by a scale factor of −2 about the centre (−2, 3).
Solution
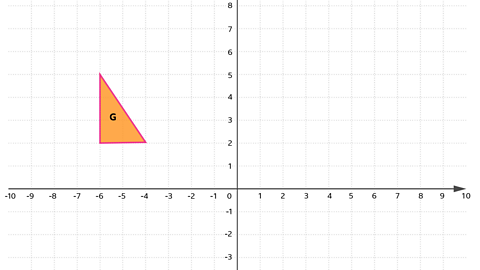
Image caption, Step 1
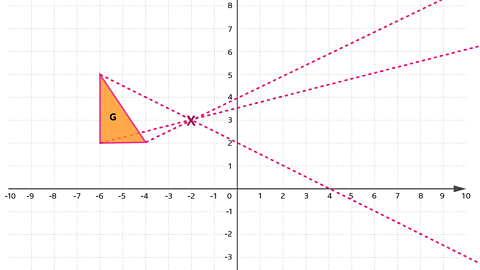
Image caption, Step 2
Plot the centre of enlargement and draw lines from each point on the shape through the centre of enlargement and out the other side
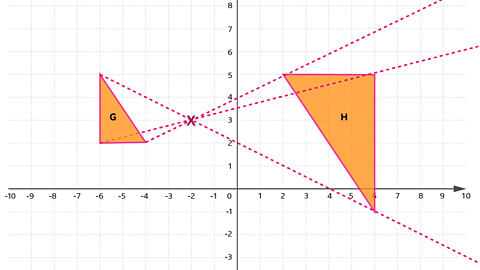
Image caption, Step 3
First, count the horizontal and vertical distances from each point to the centre of enlargement. Double this, and count out the other side of the centre following the dashed lines. From this, plot and join the new points.
1 of 3
The rectangle ABCD has been enlarged by a scale factor of \(–\frac{1}{2}\).
The lengths in rectangle A'B'C'D' are \(\frac{1}{2}\) times as long as rectangle ABCD. The distance from O to A'B'C'D' is half the distance from O to ABCD.
Question
Describe the transformation which maps triangle Q onto triangle P.
Draw from each point on the triangle Q to the corresponding point on triangle P.
The centre of enlargement is where they cross \((-1, 5)\) which is between the two shapes so it must be a negative scale factor.
All of the sides in P are 3 times as long as the sides in Q making the scale factor \(–3\).
Combining transformations
Transformations can be combined by doing one transformation and then another.
Example
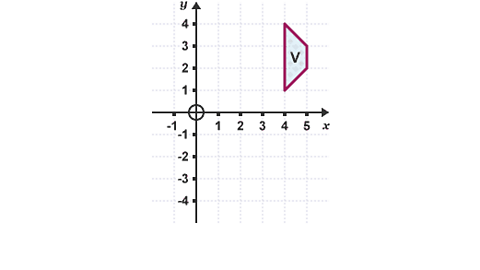
Image caption, Reflect the shape V in the line x = 2, followed by a rotation through 180° about the point (1,0).
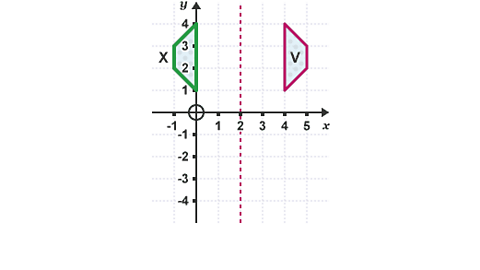
Image caption, Draw the mirror line x = 2. Reflect the shape V in this line and label it X.
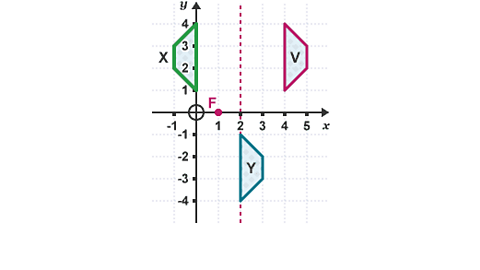
Image caption, Rotate the shape X 180° about the point (1,0). Label this image Y.
1 of 3
Example
Question
Reflect triangle M in the line \(x = –2\) and then rotate the image 90° ACW about the point \((–2, 2)\).
- Draw the final image after the two transformations
- Describe the single transformation that maps the final image back onto triangle M.
Solution
– The single transformation which maps the final image back to M is a reflection in the line \(y = –x\).
Test yourself
Question
Describe a single transformation that is equivalent to a reflection in the \(x\)-axis followed by a reflection in the\(y\)-axis.
First, drawing a diagram will help.
The shape has been rotated 180° about the origin.
More on M8: Geometry and measures
Find out more by working through a topic