White blood cells
There are several main types of white blood cell.
Phagocytes
About 70 per cent of white blood cells are phagocytesCells, such as white blood cells, that engulf and absorb waste material, harmful microorganisms, or other foreign bodies in the bloodstream and tissues.. Phagocytes engulf and destroy unwanted microorganisms that enter the blood, by the process of phagocytosisThe process of the ingestion of bacteria or other material by phagocytes.. They are part of the body's immune systemThe body's defence system against entry of any foreign body, including pathogens and agents such as pollen grains. The role of the immune system is to prevent disease..
Lymphocytes
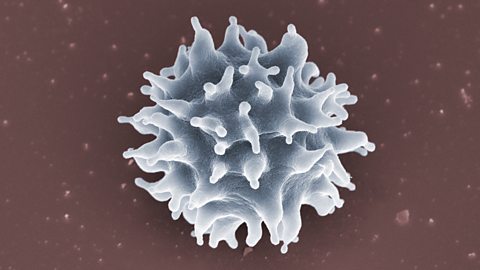
Lymphocytes make up about 25 per cent of white blood cells. They are also part of the body's immune system. Lymphocytes produce soluble proteins called antibodyA protein produced by the immune system in humans (and other animals) that attacks foreign organisms (antigens) that get into the body. when a foreign body such as a microorganism enters the body.
Platelets
Platelets are cell fragments produced by giant cells in the bone marrowSoft tissue found inside bones that produces new blood cells..
Platelets stop bleeding in two main ways:
- they have proteinOrganic compound made up of amino acid molecules. One of the three main food groups, proteins are needed by the body for cell growth and repair. on their surface that enable them to stick to breaks in a blood vessel and clump together
- they secrete proteins that result in a series of chemical reactions that make blood clot, which plugs a wound.
Blood products
Blood products are components of blood that are given to a patient by blood transfusionWhen people are given blood via a drip.. They include:
- red blood cells
- platelets
- plasma
- antibodies
Blood products are produced from blood from blood donorA person or organism providing an organ or tissue for transplant..
Blood products can then be given to patients depending on their needs. Patients rarely receive transfusions of whole blood in modern medicine.
Blood products are screened for:
- infectious agents such as HIV
- their blood group
- the presence of certain antibodies
Blood for transfusion must be compatible with that of the patient's blood, for instance, their blood group. Before a transfusion, white blood cells are often removed to reduce the risk of infections or immune reactions.
Looking at blood cells
Many types of blood cell are 10 μm in size or less. You will need high power to examine them.
The slides will have been stained to show the cells, and cell features. The micrograph shows many red blood cells and three white blood cells.
An example of a commonly-used stain is Giemsa stain. It aids identification by staining:
- red blood cells pink
- platelets pale pink
- white blood cell cytoplasm pale blue
- white blood cell nuclei magenta