Blood
The composition of blood
Blood transports materials and distributes heat around the body. It also helps to protect against disease. Blood contains blood plasmaThe liquid part of the blood containing useful things like glucose, amino acids, minerals, vitamins (nutrients) and hormones, as well as waste materials such as urea., which is a liquid that cells and cell fragments are suspended in:
Plasma is a straw-coloured liquid that makes up just over half the volume of blood.
Types of blood cell and cell fragments:
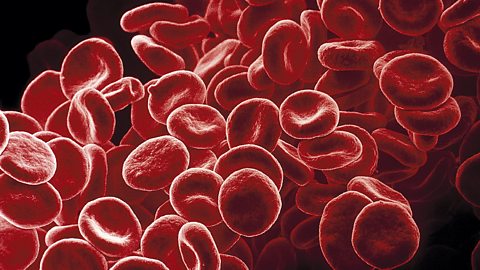
- red blood cells
- white blood cells
- platelets
This table explains the functions of various blood components.
| Component | Function(s) |
| Plasma | Transporting carbon dioxide, digested food molecules, urea and hormones; distributing heat |
| Red blood cells | Transporting oxygen |
| White blood cells | Ingesting pathogens and producing antibodies |
| Platelets | Involved in blood clotting |
| Component | Plasma |
|---|---|
| Function(s) | Transporting carbon dioxide, digested food molecules, urea and hormones; distributing heat |
| Component | Red blood cells |
|---|---|
| Function(s) | Transporting oxygen |
| Component | White blood cells |
|---|---|
| Function(s) | Ingesting pathogens and producing antibodies |
| Component | Platelets |
|---|---|
| Function(s) | Involved in blood clotting |
Red blood cells
Red blood cells transport the oxygen required for aerobic respirationRespiration that requires oxygen. in body cells.
They must be able to absorb oxygenGaseous element making up about 20% of the air, which is needed by living organisms for respiration. in the lungs, pass through narrow blood capillaryTiny blood vessels with walls one-cell thick where exchange of materials occurs., and release this oxygen to respireTo engage in respiration, the energy-producing process inside living cells. cells.
Red blood cells have adaptations that enable them to carry a maximum amount of oxygen. They contain the proteinOrganic compound made up of amino acid molecules. One of the three main food groups, proteins are needed by the body for cell growth and repair.haemoglobinThe red protein found in red blood cells that transports oxygen round the body., which gives them their red colour.
\( \text{haemoglobin} + {oxygen} \xrightarrow {at~the~lungs} \text{oxyhaemoglobin}\)
\( \text{haemoglobin} + {oxygen} \xleftarrow {at~the~cells} \text{oxyhaemoglobin}\)
Haemoglobin can combine reversibly with oxygen. This is important - it means that it can combine with oxygen as blood passes through the lungs, and release the oxygen when it reaches the cells.
- They have no nucleusThe nucleus controls what happens inside the cell. Chromosomes are structures found in the nucleus of most cells. The plural of nucleus is nuclei. - they lose it during their development - so they can pack in more haemoglobin.
- They are small and flexible so that they can fit through narrow blood capillaries.
- They have a biconcave shape - they are the shape of a disc that is curved inwards on both sides - to maximise their surface area for oxygen absorption.
- They are thin, so there is only a short distance for the oxygen to diffuse to reach the centre of the cell.