What are the key learning points?
refractionProcess by which a wave changes speed and sometimes direction upon entering a denser or less dense medium, eg a light ray changes direction when refracted by a lens. from a more dense medium (e.g. glass) to a less dense one (e.g. air).
Measuring the critical angleThe critical angle is the angle of incidence in the dense medium when the angle of refraction in the less dense medium is 90°. using a semi-circular glass block.
Conditions for total internal reflectionWhen the angle of incidence in the dense medium is greater than the critical angle, all the light is reflected and none is refracted..
Applications of TIR in industry and medicine.
What is total internal reflection (TIR)?
When a light ray reaches the boundary between two transparent materials it may be refracted.
If the light is leaving the more dense medium, the ray should refract away from the normalA construction line drawn at 90° to the surface. as it emerges.
However, if this would refract the ray at more than 90° from the normal, the refraction is not possible.
In this situation, the ray is reflected inside the more dense medium, following the law of reflectionThe law of reflection states that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence or i=r..
This is called Total Internal Reflection (TIR).
The angle of incidence when the angle of refraction is 90°, is called the critical angle.
Total internal reflection only occurs when:
light travels from a more dense medium to a less dense medium e.g. from glass to air.
the in the more dense medium is greater than the critical angle.
if the angle of refractionThe angle between the normal and the refracted ray. in the air is 90°, the angle of incidence in the glass is called the critical angle.
if the angle of incidence in the glass is greater than the critical angle, total internal reflectionWhen the angle of incidence in the dense medium is greater than the critical angle, all the light is reflected and none is refracted. occurs.
The diagram below shows the light refracting from glass into air.
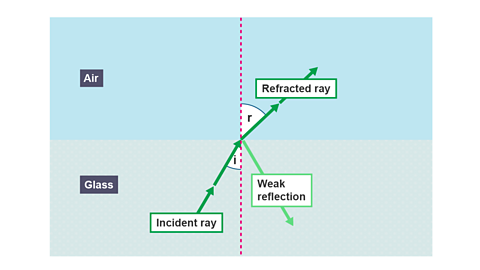
Image caption, Light refracting from a more dense medium (glass) into a less dense medium (air)
As the angle of incidence in the glass is less than the critical angle, most of the light is refracted. A small amount of the light is reflected inside the glass. For light travelling from glass into air, the angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence.
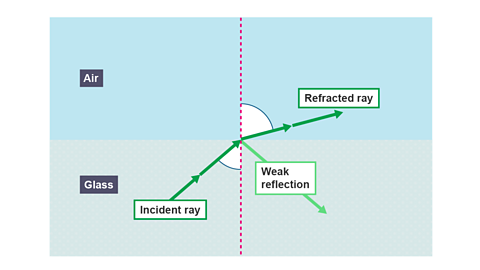
Image caption, Light refracting from a more dense medium (glass) into a less dense medium (air)
As the angle of incidence increases, the angle of refraction also increases.
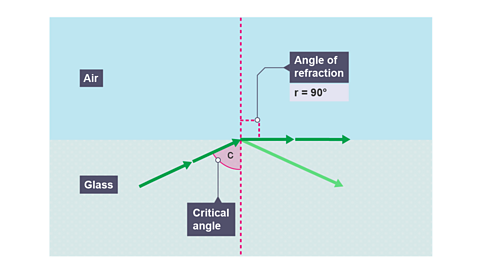
Image caption, Light refracting from a more dense medium (glass) into a less dense medium (air)
When the angle of refraction is exactly 90°, then the angle of incidence is called the critical angle C.
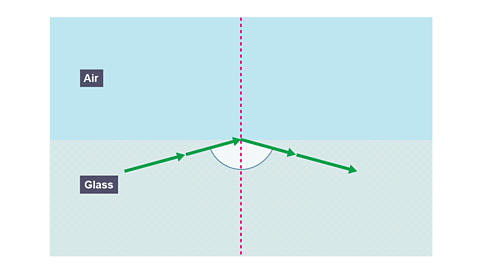
Image caption, Light refracting from a more dense medium (glass) into a less dense medium (air)
When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle: none of the light is refracted; the light is totally internally reflected, and the law of reflection is obeyed, i = r.
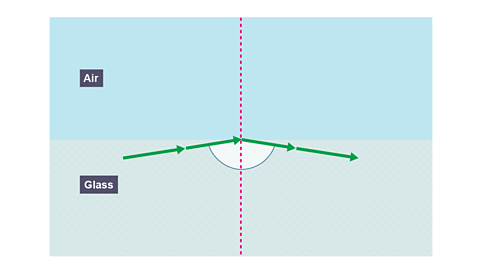
Image caption, Light refracting from a more dense medium (glass) into a less dense medium (air)
When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle: none of the light is refracted; the light is totally internally reflected, and the law of reflection is obeyed, i = r.
1 of 5
How to measure the critical angle experimentally
Investigate experimentally the critical angle and the conditions under which total internal reflectionWhen the angle of incidence in the dense medium is greater than the critical angle, all the light is reflected and none is refracted. occurs within a semi-circular glass block.
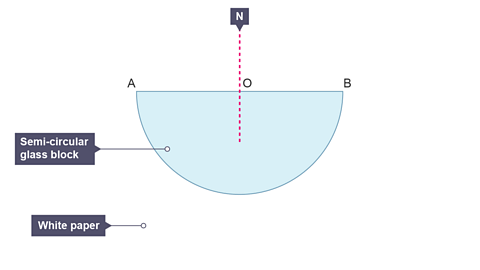
Image caption, 1. On a sheet of white paper, draw around a semi-circular glass block. Remove the glass block. Locate the centre of the side AB, mark the position O and, using a protractor, draw a normal. Label the normal, N. Replace the glass block carefully on its outline.
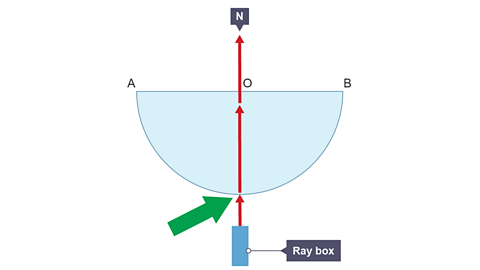
Image caption, 2. Connect a ray box to a low voltage power supply. Direct ray of light into the block through the curved surface along the normal at O. Observe that the ray does not change direction on entering the block. This is why a semicircular block is used.
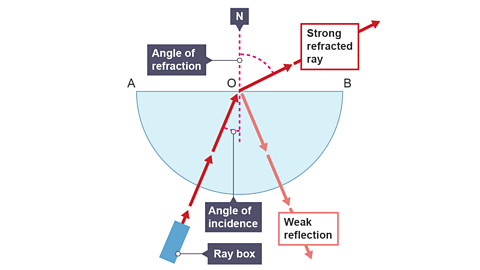
Image caption, 3. Increase the angle of incidence so that the angle of incidence at O should be about 15°. Observe the refracted ray – away from the normal into air. Note that there is also a weak reflected ray inside the glass block.
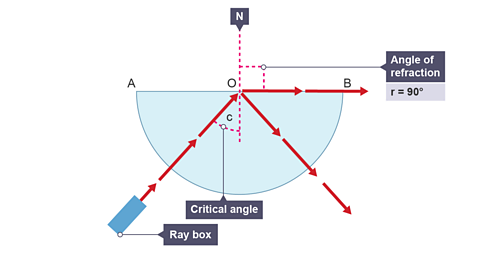
Image caption, 4. Slowly increase the angle of incidence, until the angle of refraction is 90°. The angle of incidence in the glass block is the critical angle C. Note that there is still a reflected ray inside the glass block but it is stronger now.
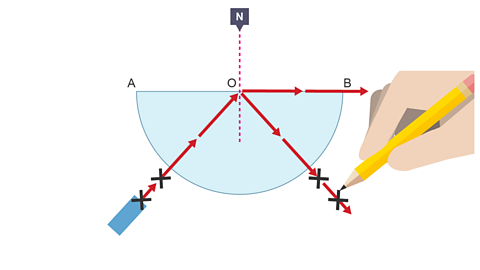
Image caption, 5. Mark the position of the incident ray with two pencil Xs.
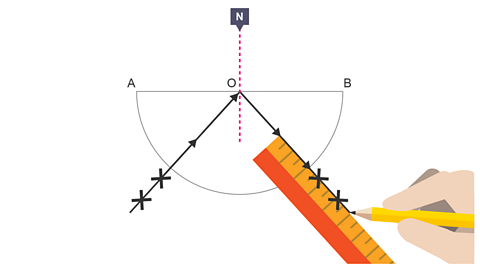
Image caption, 6. Remove the glass block. Use a ruler and a pencil to join the Xs to O.
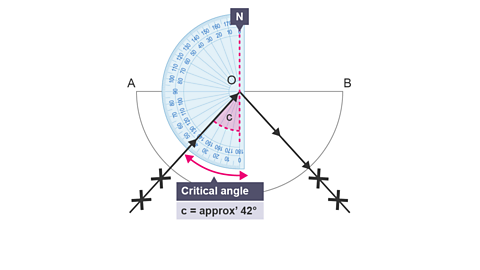
Image caption, 7. Use a protractor to measure the critical angle C. The critical angle in glass is approximately 42°.
1 of 7
What is a totally reflecting prism?
Total internal reflection inside a 45o glass prism.
The critical angleThe critical angle is the angle of incidence in the dense medium when the angle of refraction in the less dense medium is 90°. for the type of glass used to make the prism = 42o.
The ray of light is turned through 90o.
At A the ray of light is incident along the normalA construction line drawn at 90° to the surface. and passes straight through into the glass prism without being bent.
At B the at the glass – air boundary is 45o which is greater than the critical angle. total internal reflectionWhen the angle of incidence in the dense medium is greater than the critical angle, all the light is reflected and none is refracted. occurs, and the angle of reflectionThe angle between the reflected ray and the normal. is 45o.
At C the ray of light is incident again along the normal and passes straight through into air without being bent.
Total internal reflection inside a 90o glass prism
The critical angle for the type of glass used to make the prism = 42o.
The ray of light is turned through 180o.
How do bicycle and car reflectors work?
The red plastic reflector on the back of a bicycle or a car is shaped so that light from the headlight of a car passes straight through the front surface.
The back of the plastic reflector is shaped like a row of 90o prisms.
Total internal reflection occurs.
All the light bounces back and is returned in the direction from which it came.
No matter in which direction the light is incident on the reflector, it always retraces its path.
So, car drivers see the reflection of their own headlights in the reflector.
Periscope
What are the applications of total internal reflection (TIR)?
Optical fibres
total internal reflectionWhen the angle of incidence in the dense medium is greater than the critical angle, all the light is reflected and none is refracted. allows light to be contained and guided along very thin fibres.
Usually made of glass, these are called optical fibres and they have many uses:
Fibre broadband internet sends computer information coded as pulses of light along underground optical fibres.
Doctors can look at the inside of their patients using an endoscope - a long tube which guides light into the patient and then guides the reflected light back out to give an image.
Decorations, like some artificial Christmas trees, carry coloured light to different parts of the decoration and let it shine out in different directions.
An optical fibre is a thin fibre of high-quality glass.
Very little light is absorbed by the glass.
Light getting in at one end undergoes repeated total internal reflection and is trapped inside the glass, even when the fibre is bent.
It emerges at the other end only slightly less bright.
Information such as computer data, telephone calls and video signals can be converted into either visible light pulses or infrared pulses, and transmitted long distances by optical fibres.
This enables long distance communications to occur quickly and cheaply – as glass fibre is much cheaper than a copper wire needed to carry electrical signals.
In addition, optical fibres can carry much more information than a copper cable of the same diameterThe distance across the middle of a circle..

Endoscopes
Optical fibres are also used in endoscopes that allow surgeons to see inside their patients.
A bundle of optical fibres in a tube guides light into the patient and then guides the reflected light back out to give an image.
A surgeon can see on a monitor what is happening inside a patient’s body, in real time.
Optical fibres make keyhole surgery possible because the endoscope also has instruments for cutting and retrieving tissue.
This means the patient doesn’t have to be cut open which reduces scaring and makes recovery quicker and less painful.
Example question
The diagram below shows the path of a ray of red light passing through a glass prism.
Questions
Name the process happening to the ray at the point X.
There is no light emerging from the prism at Y. Name the process happening to the light at Y.
How does the speed of light change, if at all, as (a) it passes point Y and (b) as it passes point Z?
Answers
The process happening to the ray at the point X is refractionProcess by which a wave changes speed and sometimes direction upon entering a denser or less dense medium, eg a light ray changes direction when refracted by a lens..
The process happening to the light at Y is total internal reflectionWhen the angle of incidence in the dense medium is greater than the critical angle, all the light is reflected and none is refracted..
(a) The speed of light does not change when light is reflected so as it passes point Y the speed stays the same (b)The speed of light increases as it passes from a dense medium (glass) into a less dense medium (air) so, as light passes point Z, its speed increases.
Question
A second ray of red light strikes the prism at the point P as shown below.
Continue the path of the second ray, incident at P, through and out of the glass prism.
Answer
Test your knowledge
More on Unit 2: Light
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 3

- count1 of 3