Introduction to catalysts
Key points
- A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction.
- The catalyst is not used up or chemically changed during the reaction.
- Enzymes are catalysts that work inside the cells of living organisms.
Video about catalysts
This flask contains hydrogen peroxide. It’s a compound that breaks down into water and oxygen gas naturally when it is at room temperature.
This is called a decomposition reaction. Decomposition means to be broken down into smaller parts.
So what would you expect to see if a reaction was happening?
Three typical signs that a chemical reaction is happening are: a gas being produced, a change of colour, or a change in temperature. As this sits here, we can’t see any visible reaction.
With hydrogen peroxide, the reaction happens so slowly that it’s difficult to see.
If we want to see the reaction, we need to speed it up. This is where a catalyst comes in. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction.
We have two different catalysts that speed up the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to try: manganese dioxide and an enzyme called catalase, which is found in potatoes. We are using liquidised potato for this test.
Enzymes are natural catalysts. They control how quickly chemical reactions happen inside living things.
In humans, some enzymes help us break down our food during digestion.
When a catalyst is added, it is not used up or chemically changed in the reaction. We can prove this by weighing our catalyst at the beginning and the end of our experiment.
When working with hydrogen peroxide it is important to wear safety glasses and gloves.
With all of our safety equipment on, we’re going to add a small amount of hydrogen peroxide to our flask using a funnel to ensure there is no spillage.
First we’re going to try adding the enzyme catalase to the hydrogen peroxide.
As you can see we do get a small visible reaction here. We can see the white bubbles foaming up around the potato.
But different catalysts will be more effective than others. When we add the manganese dioxide it gives us a much more vigorous reaction. We know a reaction is happening as we can see a gas is being released. In this experiment the gas being released is oxygen. The flask also gets very hot, which is another sign of a chemical reaction.
The hydrogen peroxide has now become water and oxygen. The oxygen was the gas we saw in the bubbles during our reaction and the water turned into steam because of the heat. At the end of our reaction we can also see the manganese dioxide at the bottom of the flask.
And if we filter it out and dry it, we can weigh the manganese dioxide to show that the catalyst has not lost any masss.
The catalyst was not used up in the reaction. In fact the mass here is slightly heavier. This is because there is still a little bit of moisture left on the filter paper.
Have you ever heard the term ‘catalytic converter’? Do you know where they are found, and what they do?
Catalytic converters are found in the exhaust systems of vehicles like cars.
They speed up useful chemical reactions which reduce the pollution released by the vehicle.

What are catalysts?
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reactionWhen chemical bonds are broken and made between atoms, so that new substances (compounds or elements) are made. without being used up or chemically changed.
Catalysts are usually specific to a particular reaction. The best catalyst for one reaction is unlikely to have any effect at all on a different reaction. Different catalysts are needed for different reactions.
Enzymes
biological reactionsChemical reactions that occur inside living organisms. For example, chemical reactions are involved in digestion, and in respiration to release energy from compounds in food. in the cells of living things are sped up by catalysts called enzymes.
Enzymes are biological catalysts. They are important for biological reactions like digestion. Look through this slideshow to learn more about the enzymes involved in digestion.
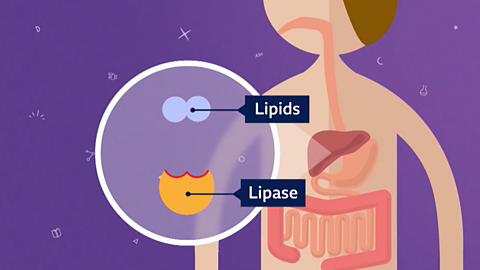
Image caption, 1. Enzymes are catalysts used in biological reactions to speed them up. Lipase is an enzyme (catalyst) used in digestion to break down lipids.
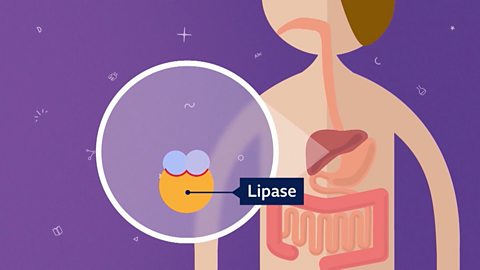
Image caption, 2. Enzymes like lipase have a specific shape. This shape fits into the molecule it will break apart or join together with.
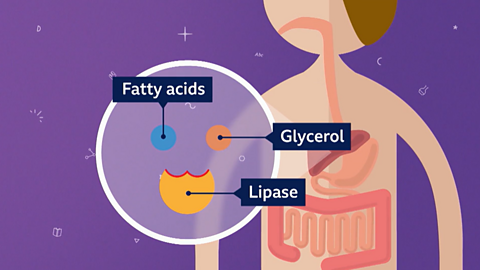
Image caption, 3. The enzyme lipase helps in digestion by breaking down fats and oil (lipids) into fatty acids and glycerol for storage.
1 of 3
Lipase is an enzyme (catalyst) used in digestion to break down fats, also known as lipids. Lipaseenzymes are named after the lipids that they break down.
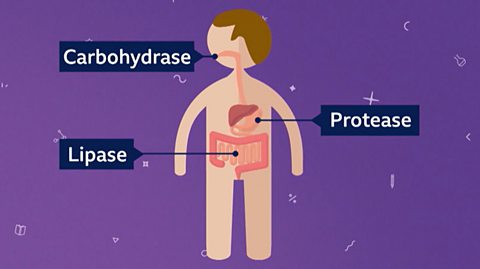
The two other key enzymes used in digestion break downproteins andcarbohydrates.
Can you work out what they're called?
Protease break down proteins and carbohydrase break down carbohydrates. Lipase, carbohydrase and protease are the three key types of enzymes in our digestive system.
Recognising catalysts
Catalysts don’t get used up or chemically changed by the reaction. They will be present at the end of the reaction.
The massA measurement of the amount of matter (stuff) present in an object or a certain amount of a chemical. Mass is measured in kilograms or grams and it remains the same wherever the object is in the universe. of the catalyst at the end of the reaction will be the same as the mass of the catalyst at the start.
The picture shows a reaction with a catalyst. The left hand side shows manganese dioxide (black powder) being added to hydrogen peroxide (colourless liquid) and right hand side shows the end of the reaction. The products are water and oxygen.

Manganese dioxide is a very effective catalyst for this reaction. The bubbles are oxygen.
Notice how all the manganese dioxide powder is still there at the end of the reaction. This means the catalyst has not been used up or changed.
0.2 g of manganese dioxide catalyst is added to the hydrogen peroxide. After the reaction, the catalyst is filtered, washed and dried. It is then weighed. What is the mass of the catalyst after the reaction?
0.2 g – the same mass as before the reaction. Remember - catalysts are not used up or chemically changed during a reaction.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Chemical reactions
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 12

- count5 of 12

- count6 of 12

- count7 of 12
