Key points
- Distillation is a separation technique used to separate a solventThe liquid in a solution which dissolves the solute. For example, the solvent in sea water is water. from a mixtureWhen two or more compounds or elements are present without being chemically bonded together.. For example, water can be separated from salt solutionA mixture made when a solute (usually a solid) dissolves into a solvent (a liquid). Sea water is a solution of salt dissolved into water. by distillation.
- Distillation involves boiling the mixture and then condensing the gas to produce a liquid.
What two processes occur in the water cycle to turn sea water into rain water?
Evaporation and condensation.
Water evaporates from the surface of the sea. The salt gets left behind in the sea. Then, the water vapour in the clouds cools and condenses to form rain.
Video
Watch this video to find out how distillationA separation technique which separates the solvent from a mixture, (usually a solution or two liquids with different boiling points). Distillation involves heating the mixture to boil off one of the parts and then condensing the vapour. can be used to separate water from a salt solution.
While you're watching, write down or draw the pieces of apparatus (equipment) that are used during distillation.
Salt is a substance that dissolves easily in water, to make a salt water solution. This is a mixture. We can separate the salt and the water from the salt water solution using distillation.
In here, all of the salt and water particles are mixed up.
To separate the mixture and collect the solvent, we need to make the water change state.
And to do that in the lab we can use something like this.
The salt water solution goes into the flask.
This part is a water-cooled condenser. There’s a hollow tube through the middle, and a sleeve around the outside. When we connect the bottom part to the tap, it fills with cold water, which flows out the top. That helps to keep it nice and cool around the central tube.
We’ll put the Bunsen burner under here and a cylinder to collect the water formed as the water vapour condenses.
And then watch and wait.
When we heat the salt water solution, the particles in the liquid are whizzing around very quickly.
At the solution’s boiling point, the high energy water molecules break free of the liquid surface, forming water vapour.
The water vapour travels up out of the flask, and down into the water-cooled condenser. It’s much cooler here, so the water particles slow down and condense, turning back into a liquid which drips slowly down the tube, and into the cylinder.
After we’ve removed all the water from the solution, there’s only salt left behind and this is pure water.
This process of distillation is used in the chemical industry to separate mixtures of liquids with different boiling points. Like getting petrol and diesel from crude oil, the mixture drilled out of the ground.
What is the name of the piece of apparatus that cools down the hot gas after the mixture has been heated?
Condenser.
What is distillation?

Distillation is a separation technique used to separate liquid (the solvent) from a mixture and keep the liquid part. Distillation involves boiling the solution and then condensingWhen a gas turns into a liquid, transferring energy to its surroundings. the vapourA gas formed when a liquid evaporates or boils. back into a liquid by cooling it down.
For example, dirty water can be distilled to produce pure water, which is safe to drink.

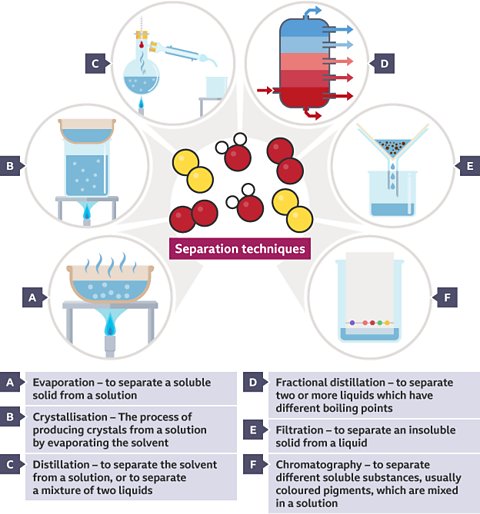
Distillation is just one separation technique. Find out about two others - evaporation and filtration - in these guides.
Which two changes of state occur during distillation?
Boiling (liquid to gas), and then condensing (gas to liquid).
Distilling a salt solution
A salt solution (salt water) can be distilled into pure water which we can drink.
This is done by following these steps:
- The salt solution is placed into a flask and heated until it boils.
- The water turns into a gas but the salt stays behind in the flask.
- The steam passes into the condenserA piece of apparatus used in distillation, which uses cold water to cool down a vapour (gas) and turn it into a liquid, which is called the distillate. . The condenser is a tube which is surrounded by a layer of cold water. This cools the steam, which turns it back into a liquid.
- The distillateThe liquid which is produced from distillation. When sea water is distilled, the distillate is pure water. is pure water.
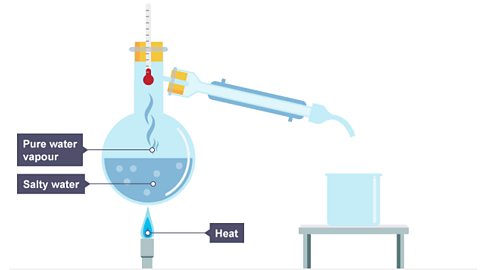
Image caption, Salt solution is heated.
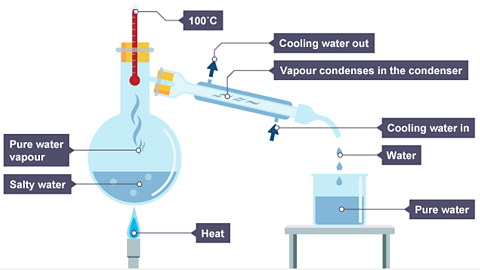
Image caption, Water evaporates and its vapour rises. The water vapour passes into the condenser, where it cools and condenses. Liquid water drips into a beaker.
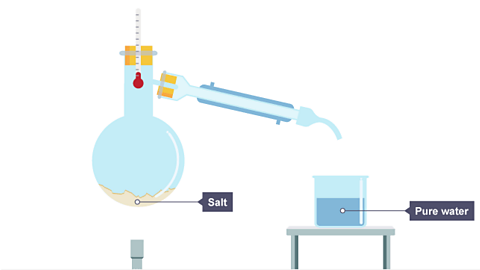
Image caption, All the water has evaporated from the salt solution, leaving the salt behind.
1 of 3

Did you know?
Drinking water in the UK is not produced by distilling sea water. The process uses lots of energy, making it expensive and potentially polluting. The remaining waste salt can damage ocean ecosystems.


When a solution made from salt dissolved in water is distilled, the temperature reading on the thermometer will be 100°C.
Why is this?
100°C is the boiling point of the water.
Distillation of two liquids
Some mixtures contain more than one liquid. If there are two different liquids with different boilingWhen a liquid turns into a gas as it absorbs energy from the surroundings. points, they can also be separated using distillation.

For example, sanitising sprays for disinfecting surfaces contain ethanol and water.
Ethanol boils at 78°C, whereas water boils at 100°C. A mixture of ethanol, water and salt can be separated using fractional distillation A separation technique used to separate a mixture of liquids with different boiling points. This can be applied when there are more than two liquids or if two mixed liquids have boiling points which are too close for simple distillation..

Water and ethanol can be separated using distillation by following these steps:
- Heat the mixture in a flask until the gas above the mixture is 78°C. The ethanol boils and can be re-captured using a condenserA piece of apparatus used in distillation, which uses cold water to cool down a vapour (gas) and turn it into a liquid, which is called the distillate. in the same way as the water in the salt water example.
- Keep the temperature at 78°C until the liquid ethanol coming from the condenser stops or slows down to almost nothing.
- The water will remain in the original flask.

Crude oil
Fractional distillation is a technique also used in the chemical industry to obtain petrol and diesel from crude oil (a fossil fuel).
Crude oil is a mixture of lots of different liquids (fractions) and we can use their different boiling pointThe temperature at which a pure substance boils from a liquid into a gas. For example, the boiling point of pure water is 100°C. The boiling point is also the temperature at which a gas will condense into a liquid. to separate them into more useful substances.
Fractional distillation can be used if the boiling points of two mixed liquids are similar. In these cases, the boiling points would be too close for simple distillation.

Fractional distillation still relies on different boiling points, but is able to accommodate much closer boiling points whilst maintaining the purity of the products. Simple distillation would risk both liquids evaporating, meaning the distillate would still be a mixture.
Which technique would be used to separate a mixture of the solid solute potassium bromide dissolved into water?
Distillation.
There is no need to use fractional distillation, as the mixture contains only one liquid.
Working scientifically
Working safely in the lab
When working with apparatus it is essential that you are aware of the hazards and take appropriate precautions to minimise the risk to yourself and others.
Below is a list of hazards in the distillation process. How might we reduce the risk of each one?
- Knocking over glassware – risk of broken glass and cuts
- Hot liquids – risk of spillage and scalds
- Bunsen burner flame – risk of burns or fire
- Heater – risk of burns
- Flammable liquids (e.g. ethanol) – risk of fire
Here are some possible answers to each one:
| Hazard | Risk | Risk reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Knocking over glassware | Broken glass and cuts | Keep apparatus away from the edge of the table and make sure it is as stable as possible. For example, by resting the glassware on a flat surface. |
| Hot liquids | Spillage and scalds | Keep apparatus away from the edge and remain standing during the experiment. Remember to tuck seats in so they aren't in the way if you need to move away from spillages quickly. |
| Bunsen burner flames | Burns or fire | Secure any ties or lanyards and tie back long hair. Also make sure the Bunsen burner is on a safety flame to increase its visibility when not being used. |
| Heater | Burns | Only handle the heater by the outer casing. Where possible, avoid handling the heater once it is switched on. Give the heater time to cool after it is switched off. |
| Flammable liquids (e.g. ethanol) | Fire | Make sure flammable items are never near naked flames or sources of heat. Use extra care when handling to avoid accidental spillage. |

Often a level of risk remains but we must be aware and take steps to minimise it.
Sometimes experiments that are more hazardous are only done by specially trained scientists.
Find out more about working safely in science.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Pure and impure substances
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 7

- count4 of 7

- count5 of 7

- count6 of 7
