What do you know?
What is climate?
Climate refers to the average atmosphericAssociated with the air above our heads. The atmosphere is the air that we breathe and the place where our weather happens. conditions, such as temperatureHow warm or cool something or someone is. Air temperature is usually measured in degrees Celsius (°C). and precipitationAny moisture that falls from the clouds, such as snow, rain, hail and sleet., for a given place over a period of time.
Key points
- Climate change refers to changes in the Earth's average temperature. These changes occur naturally over time, but most scientists think that human behaviour is increasing the amount of greenhouse gasThe gases responsible for global warming and climate change - carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons). in the atmosphere, which is causing more rapid changes to the climate.
- Evidence for climate change can come from tree ring analysis, ice core samples, and observations of changes in ice cover.
- Climate change can be managed bymitigationTaking steps to reduce the severity of something. For example, climate change mitigation involves limiting or preventing greenhouse gas emissions. andadaptationTaking steps to change or adjust something. For example learning to live with climate change.. Mitigation means reducing greenhouse gasemissionsA potentially harmful gas that is produced and sent out into the air, for example carbon dioxide., and adaptation is learning to live with the effects of a warmer planet.
Game - HIC climate change
Play a Planet Planners mission and help a high-income country take steps to manage climate change.
You can also play the full game
What is climate change?
Climate change refers to changes in the Earth's average temperature. Climate change occurs naturally through things like volcanic eruptions, changes in the Earth’s orbitThe curved path of an object around a star. For example, the Earth orbits the Sun. and variations in the Sun’s energy.
In recent years, temperatures have been increasing more rapidly than in the past. Global temperatures are around 1 °C higher than they were around 100 years ago. An Intergovernmental Panel on Climate ChangeA body of the United Nations that was set up in 1988. The IPCC carry out research relating to climate change. report of 2023 says that global warming of 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels is very likely during the 21st century. To avoid this, greenhouse gas emissions must be at least halved.
Greenhouse gases
Most scientists agree that human behaviour is causing this increase in temperature. Humans are increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxideA gas that is naturally present in the atmosphere and a greenhouse gas. Trees absorb carbon dioxide and humans breathe it out. and methaneA gas that is naturally present in the atmosphere. The decay of natural materials in landfills and marshes create methane., within the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases can be released by human activity, such as:
- burning of fossil fuelA natural fuel such as coal, oil or gas found within the Earth’s crust. Fossil fuels are formed from the remains of living organisms., which releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- deforestationThe removal of trees. This is sometimes done to make land for farming, roads or settlement., as trees absorb carbon dioxide and store carbon.
- food waste, which creates methane when it breaks down.
Carbon dioxide emissionsA potentially harmful gas that is produced and sent out into the air, for example carbon dioxide. from fossil fuel combustion and industry are now more than three times higher than they were in 1965. Greenhouse gases absorbTo take something in, gradually. For example plants absorb carbon dioxide. any heat that is reflected from the Earth. A greater concentration of greenhouse gases means that more heat is absorbed and so the planet warms up.
What is the greenhouse effect?
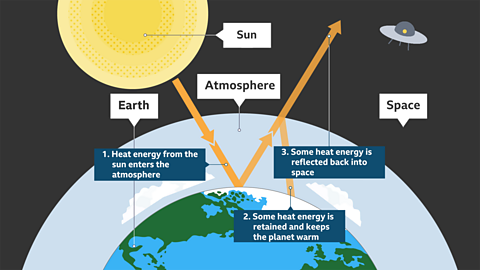
Image caption, The greenhouse effect is a natural process that keeps the planet warm. Without it, humans would not be able to live on Earth.
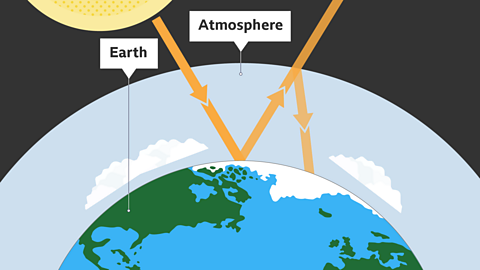
Image caption, Energy from the Sun warms the Earth’s surface. The Earth emits some of this heat back out into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, then absorb some of this heat, which helps to keep the planet warm.

Image caption, Humans have been increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This is through activities like burning fossil fuels, deforestation and creating food waste.

Image caption, A greater concentration of greenhouse gases leads to a warmer planet. This could mean that some places will struggle to grow food, some places will disappear under rising sea levels and some countries will experience more tropical diseases.

Image caption, Climate change can be managed by limiting or preventing the amount of greenhouse gases that we produce. If we don’t do this, we must learn to live with the effects of climate change.
1 of 5
Question
Why is it important that the Earth has some greenhouse gases?
Greenhouse gases help to keep the planet warm. Without them, humans would not be able to live on Earth.
Evidence for climate change
There is clear evidence that climate change is taking place. This includes tree ring analysis, ice core samples, and measurements of ice cover.
Tree rings

The rings found within a tree trunk can show how old the tree is and what the climate was like during the life of the tree. Some trees can live for thousands of years. Very old trees can give information about past climates.

Ice core samples

Ice cores are drilled out ofice sheetA large layer of ice covering the land. or glacierA large mass of ice, slowly moving downhill through gravity.. The tiny air bubbles within the ice contain gases found in the atmosphere in the past. Ice cores from Antarctica have provided information about the climate from as far back as 800,000 years ago.

Ice cover

Ice sheets and glaciers change in size in response to global temperatures. More than 80 per cent of the snow on Mount Kilimanjaro has melted since 1912 and according to NASA, Antarctic ice is melting at an average rate of 150 billion tonnes every year.

Question
How can ice core samples tell us about past climates?
Ice cores contain tiny air bubbles. Scientists can look at the gases trapped within these bubbles to discover what past climates were like.
Impacts of climate change

Climate change is causing global temperatures to increase and average sea levels to rise. Scientists suggest that the impacts of higher temperatures and rising sea levels could include:
- a change to the location of the Earth’s climate beltPlaces with similar atmospheric conditions that run in a line from east to west around the globe. For example, tropical climates lie in a belt around the Equator., which would make it difficult for some countries to grow food.
- flooding of coastalThe area where land meets the sea or ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or sea. and Low-lyingLand that is at or near sea level.communityA group of people living in a particular place..
- the spread of tropical diseaseIllnesses that relate to tropical areas. Malaria is a tropical disease as it is found in warm, wet climates., like malariaA disease spread by mosquito bites in tropical climates. Malaria is curable but can be life-threatening., to places that are further north and south.

Video: Rising sea levels
Watch this video to find out how climate change is affecting rising sea levels in the Solomon Islands.
ADE ADEPITAN: Hi, I’m Ade. I’m in the Solomon Islands out in the Pacific Ocean and these islands are beautiful but they’re under threat because of rising sea levels which puts them on the front line of climate change.
ADE ADEPITAN: The Solomon Islands are one of the most heavily forested countries in the world.
ADE ADEPITAN: Finally I’ve seen some signs of life. We’ve been on this boat for about half an hour, maybe more, and this is the first person I’ve seen. How you doing?
ADE ADEPITAN: The population here is small and most people live off the land or the sea.
ADE ADEPITAN: I think this is where we’re headed to, we’ve got a load of houses right on the water, all built on stilts.
ADE ADEPITAN: I’ve come to a village called Kia to pick up Gladys Habu.
GLADYS: Hello.
ADE ADEPITAN: Hey Gladys, How are you? Welcome on board.
ADE ADEPITAN: Gladys wanted to take me to a nearby island called Kale. It was one of her favourite places to visit as a child.
GLADYS: So this is a photo that I took. My grandparents actually lived here. Some of my best childhood memories were here at Kale. So that is unfortunately what’s left of Kale island.
ADE ADEPITAN: Is this it? Wow. So ten years ago, that looked like this?
GLADYS: Yeah. It was so beautiful, so thick with forest.
ADE ADEPITAN: And it’s gone! That’s astonishing.
ADE ADEPITAN: Kale used to cover 50,000 square metres, but as sea levels have risen, Kale has disappeared.
GLADYS: It’s quite devastating, I remember I would have to walk around with mum and dad with me because we’d lose our way if we go on our own. That’s how big Kale was.
ADE ADEPITAN: I just can’t imagine that, I can’t imagine that there was a dense forest over there and now all we can see is seawater.
ADE ADEPITAN: Kale is one of the first islands in the world to disappear beneath the waves because of climate change. And as the sea level continues to rise, Gladys’ village is now under threat.
GLADYS: We used to have our house just in front there but the tide’s just coming up higher and higher each year. It’s really hard, it’s become a daily challenge for all of us.
ADE ADEPITAN: Beaches have disappeared, and houses are falling into the sea.
GLADYS: Our country doesn’t contribute much to the emission of greenhouse gases and global warming and yet we are the ones facing this and it’s not something we brought upon ourselves, this is something that people from the Western countries did to us and we are facing the consequences of their own doings, so I feel for my people because we can’t afford this and this is all we have.
ADE ADEPITAN: The Solomon Islands produce less than one hundredth of one per cent of global greenhouse gases. But along with other low-lying Pacific islands, they’re paying the highest price.
Game - LIC climate change
Play a Planet Planners mission and help a low-income country take steps to manage climate change.
You can also play the full game
Managing climate change
Climate change can be managed by:
- Mitigation – limiting or preventing greenhouse gas emissions. Examples of this are renewable energyEnergy that can be replaced as quickly as it is used. For example, there is a continuous supply of wind which makes it a renewable form of energy., such as solar panelA panel designed to convert the heat from the sun to heat water or generate electricity., and new technology, such as electric vehicleMethods of transport that run off a rechargeable battery rather than traditional fuels, such as petrol or diesel. .
- Adaptation – learning to live with climate change. Examples of this include building flood defenceStructures put in place to stop flooding. Dams are a flood defence. to protect against rising sea levels, and developing new crops that are drought-resistantSomething that is able to cope with very low levels of water. For example, drought-resistant crops can grow in areas with very little rainfall..
Question
Name one climate change adaptation strategy.
Any of the following are examples of climate change adaptation strategies.
- building flood defences to protect coastal areas from rising sea levels.
- the use of drought-resistant crops.
Climate change scepticSomeone who questions or doubts something. For example, many people are sceptics about the theory that aliens exist. are people who have doubts about whether climate change is happening or whether attempts to manage climate change will work.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Play Planet Planners on Roblox! gamePlay Planet Planners on Roblox!
Explore global locations, solve real-life challenges and make the big decisions that shape the future.

More on Weather and climate
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 4

- count2 of 4

- count3 of 4


