Finding angles
Intersecting lines are lines that cross each other.
Parallel lines are lines that never cross each other - they keep the same distance apart from each other.
When two lines intersect, the opposite (X) angles are equal.
Parallel lines
On parallel lines, alternate (Z) angles are equal.
On parallel lines, corresponding (F) angles are equal.
On parallel lines, interior © angles add up to \({180}^\circ\).
A short video showing how to find the missing angles on crossing lines when you only know one of the angles.
How to find the missing angles on crossing lines slideshow

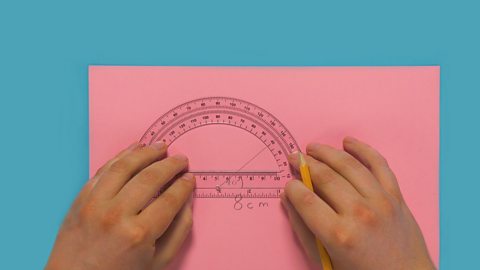
Image caption, Click to see a step-by-step slideshow.

Image caption, WHAT YOU NEED: ruler, pencil and coloured pens.
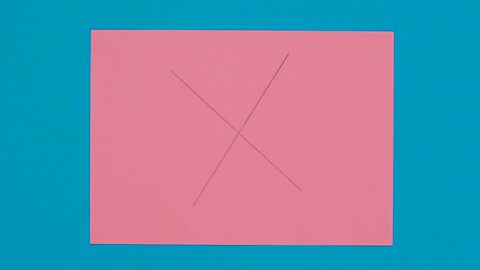
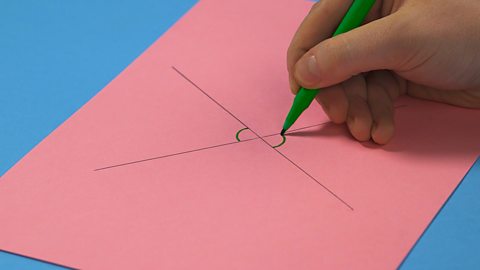
Image caption, STEP 1: Draw two lines which cross on a piece of paper.
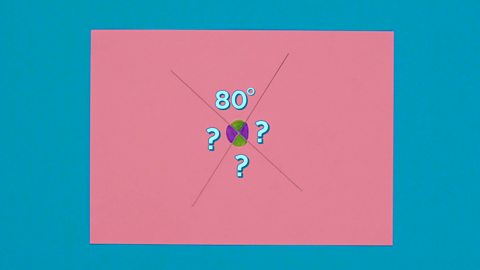
Image caption, STEP 2: Label the angle you know and colour in the angle arc. Colour in the opposite angle in the same colour, and the other two angles in a different colour.
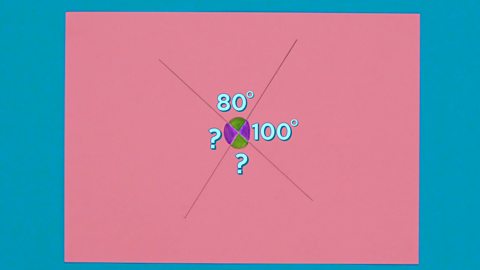
Image caption, STEP 3: The given angle here in green is 80°. The angles on a straight line always add up to 180°, so the purple angle next to it must be 100°.
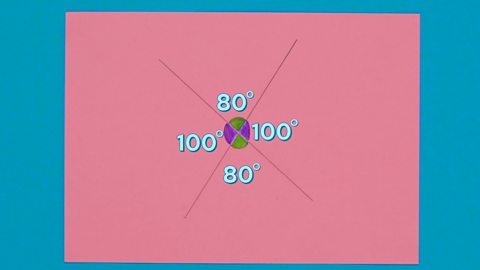
Image caption, STEP 4: Work out the size of the remaining angles. Opposite angles are always equal, so the remaining green and purple angles must be 80° and 100°. All angles around a point will always add up to 360°.
1 of 6
Parallel and equal lines
Parallel lines are marked with arrows.
A line which crosses a pair of parallel lines is called a transversal.
Lines of equal length are marked with dashes.
Question
In the following diagram, DE is parallel to AC, and AB = CB.
a) Find the size of angle \({a}\). Give a reason for your answer.
b) Find the size of angle \({c}\). Give a reason for your answer.
c) Find the size of angle \({b}\). Give a reason for your answer.
d) Find the size of angle \({e}\). Give a reason for your answer.
Answer
a) \(a = 40^{\circ}\) (corresponding angle to angle at point D)
b) \(c = 40^{\circ}\) (AB = CB, therefore angle \({a}\) = angle \({c}\), because it is an isosceles triangle)
c) \(b = 100^{\circ}\) (angles in a triangle add up to \(180^{\circ}\))
d) \(e = 140^{\circ}\) (\({e}\) and \({c}\) are co-interior angles)
Test section
Question 1
What are intersecting lines?
Answer
Intersecting lines are lines that cross each other.
Question 2
What are parallel lines?
Answer
Parallel lines are straight lines that never meet each other.
They keep the same distance apart from each other.
Question 3
Which picture shows alternate angles?
a)
b)
c)
Answer
Alternate angles make a Z shape with parallel lines.
So, the correct answer is a).
a)
Question 4
Which picture shows opposite angles?
a)
b)
c)
Answer
The correct answer is c).
Opposite angles are created when two lines cross.
c)
Question 5
Which picture shows corresponding angles?
a)
b)
c)
Answer
The correct answer is a).
Corresponding angles make an F shape with parallel lines.
a)
Question 6
Which picture shows co-interior angles?
a)
b)
c)
Answer
The correct answer is c).
Co-interior angles make a C shape with parallel lines.
c)
Question 7
What's the size of angle \({q}^\circ\)?
Answer
The sum of angles on a straight line is \({180}^\circ\).
So \({180}^\circ-{130}^\circ={50}^\circ\).
Question 8
What's the size of angle \({p}^\circ\)?
Answer
Opposite angles are equal, so \({p}^\circ={110}^\circ\).
Question 9
What's the size of angle \({r}^\circ\)?
Answer
The sum of angles in a triangle is \({180}^\circ\).
So, using \({p}^\circ={110}^\circ\) and \({q}^\circ={50}^\circ\), \({r}^\circ={180}^\circ-{110}^\circ-{50}^\circ={20}^\circ\).
Question 10
What's the size of angle \({s}^\circ\)?
Answer
Angles on a straight line add up to \({180}^\circ\), so \({q}^\circ={180}^\circ-{130}^\circ={50}^\circ\).
Also, \({s}^\circ\) and \({q}^\circ\) are alternate angles, and are therefore equal.
So, \({s}^\circ\) = \({50}^\circ\).
More on Shape, space and measures
Find out more by working through a topic
- count34 of 50
- count36 of 50