Key points
- The skeleton allows movement, provides support and protection for vital organs and makes blood cells.
- Skeletal muscles move the bones in the body.
Skeletal and muscular systems
The skeletal system is made from bones and joints.
- The femur bone in the thigh is the longest and strongest bone in the body.
- The smallest bones in the body are called the ossicles in the ear.
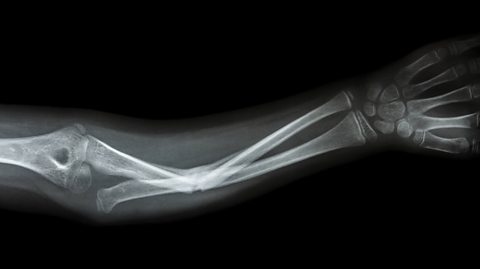
Bone is a living tissue with a blood supply. It is constantly being dissolved and formed and it can repair itself if a bone is broken. Calcium is important for this process.
Bones work with muscles and tendonA strong cord-like tissue which connects muscles to bones. to allow the body to move.

Video
I just went for a run and my whole body feels like jelly. The only thing holding me up at these bones, quite literally, actually.
Your skeleton supports and protects your body. The skull, for example, protects your brain. Important if you like thinking or moving, since your brain sends the signals that control your muscles.
Those signals travel through nerves that run through your spinal cord, which is protected by bones called vertebrae.
Then there's the rib cage and sternum, which protect the heart and lungs. Besides protecting our organs, bones also work together with muscles and tendons to get the body moving.
For example, the humerus, radius and ulna work with your biceps and triceps to curl or extend your arm. Having many joints allows for complex fluid movements so we can do things like kick a ball or throw a javelin.
But personally, I might just use all these muscles, bones and joints to go sit down and catch my breath.
Can you answer these questions based on the video?
1. What does the skull do?
2. What are the three bones in the arm?
Protects the brain.
The humerus, radius and ulna.
Function of the skeleton
The skeleton has four main functions:
- to support the body
- to protect some of the vital organs of the body
- to help the body move
- to make blood cells
Support
The skeleton supports the body.
The spinal cord is surrounded by vertebraeBackbones that surround and protect the spinal cord. Plural: vertebrae, singular: vertebra. Vertebrates are animals with a backbone. Most people are born with 33 of these but adults usually have 24 because some join together naturally as the body grows. Without these bones people would not be able to sit upright. The major bones in the legs are the femur, fibula and tibia. These allow a person to stand upright.
Protection
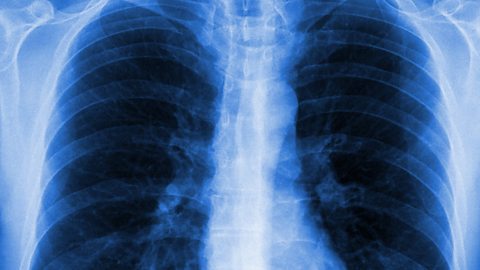
The bones protect the vital organs:
- the skull protects the brain
- the vertebrae protect the spinal cord
- the ribcage protects the heart, lungs and liver

Movement
Some bones in the skeleton are joined rigidly together and cannot move against each other. Bones in the skull are joined in this way. Other bones are joined to each other by flexible joints. The vertebrae have limited movement, but the shoulders, elbows and knees are joints that allow more movement.
Muscles are attached to bones by tendonA strong cord-like tissue which connects muscles to bones. Skeletal muscles contract and relaxMuscles get shorter by contracting and return to their original length when they relax. Muscles pull on bones for movement. to move bones.
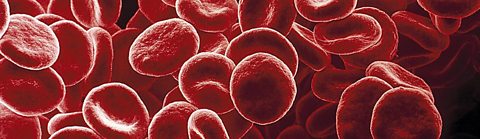
Making blood cells
There are different kinds of blood cells, including:
- Red blood cells, which carry oxygen around the body in the blood
- White blood cells, which are involved in destroying harmful microorganisms in the body
These cells are made in the bone marrowThe spongy material inside your large bones like those in your legs and hips, in which other cells are made. This is soft tissue inside our larger bones which is protected by the hard part of the bone which surrounds it.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Test questions
What are the four main functions of the skeleton?
- To support the body
- To protect some of the vital organs of the body
- To help the body move
- To make blood cells
Write a paragraph to answer the following question. Tap 'Show answer' to see four points you could have included.
Describe how your bones protect your tissues and organs.
- The skull protects the brain.
- The ribcage protects the heart and lungs.
- Vertebrae protect the spinal cord.
- Larger bones protect the bone marrow where blood cells are made.
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Living organisms
Find out more by working through a topic
- count6 of 15

- count7 of 15

- count8 of 15
- count9 of 15
