Electrical circuits

Designers can make useful products that include electrical componentA device in an electric circuit, such as a battery, switch or lamp..
They allow a product to have lights, sound and movement. However for these components to work, they need to be in an electric circuitAn electric circuit contains a power source and devices, which are connected together in a loop using wires.
An electrical circuit is a loop through which an electric currentThe flow of electricity through a wire or circuit. can flow.
It consists of:
a power source – such as a battery or a generator
wires – which allow electric current to flow through them
components – devices such as switches, bulbs, or motors

Video: What is a circuit?
Watch this video to discover how circuits work and how they can be represented in simple diagrams.
For electricity to flow, everything needs to be connected in a big ring. It’s called a circuit.
For example, the lights in most houses and flats are part of a circuit controlled by the consumer unit, where power enters the house.
We can see how circuits work, and represent them with some simple diagrams, using basic electrical components like these.
You start with a cell, or combination of cells. These could be batteries, solar panels, or a power supply connected to the mains - anything that can provide power to our circuit.
A wire from the cell can then be connected to a component like a bulb.
And to complete the circuit you need to connect it back to the other side of the cell.
Ah! There we go!
You can put all kinds of other components in the circuit, to be powered by the cell.
Like a motor.
Or you can even put in a switch that can temporarily break the circuit.
How are circuits powered?
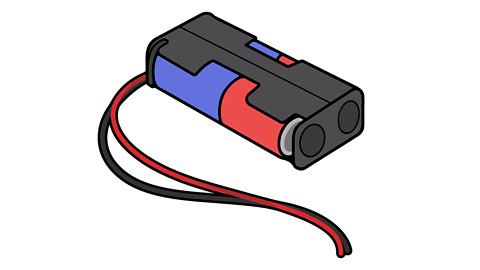
All circuits need a power source to work.
Some products use mains electricity, so they need to be plugged in.
Others use batteries, this means they can be taken anywhere but the battery will run out of power over time.
There are other types of power sources too, such as solar panels, which use energy from the Sun.
The flow of electricity is ‘pushed’ by the power source, through the wires, around the parts of the circuit.

What is a component?
A component is a device in an electric circuit, such as a battery, switch or lamp which allows electricity to pass through it. Each component makes something happen using electricity.
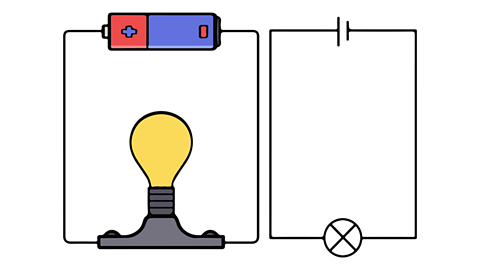
The picture above shows a circuit with a bulb and a battery cell in. The diagram next to it shows the symbols for each of these components.
How much power does a circuit need?

Voltage (V) is the ‘push’ which makes the electricity flow around a circuit. Circuits with lots of components need more voltage because they need more electrical energy pushed to them. The more batteries, a higher voltage means bulbs will be brighter and buzzers will be louder.
Circuits with lots of components need more voltage.
The more batteries in a circuit, the higher the voltage which means bulbs will be brighter and buzzers will be louder.
When voltage is lower, bulbs will be less bright and buzzers will be quieter.

How do we turn devices on and off?
Electricity will only travel around a circuit that is complete.
When a switch is open (off), there is a gap in the circuit. Electricity cannot travel around it and a components in the circuit will turn off.
When a switch is closed (on), the circuit is complete. Electricity can travel around it and components in the circuit will turn on.
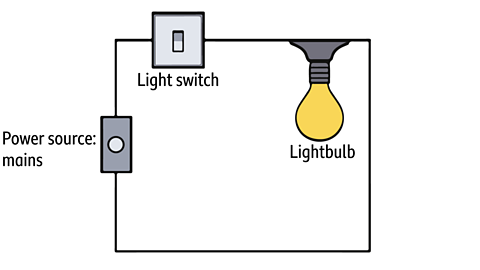
Electrical circuits in the home
Find out about some electrical circuits and their components.
Drawing circuit diagrams
When designing a product that uses an electrical circuit you can draw a circuit diagram to record and share your plan with others.
To draw circuit diagrams, we use simple symbols to represent the different components.
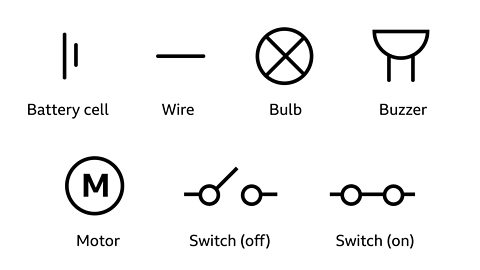
To find out more about how to draw circuit diagrams take a look at this KS2 Circuit symbols article.
Key words
| Electric circuit | An electric circuit contains a power source and devices, which are connected together in a loop using wires. |
| Electrical component | A device in an electric circuit, such as a battery, switch or lamp. |
| Electric current | The flow of electricity through a wire or circuit. |
| Voltage (V) | A measurement of the strength of an electric current. Circuits with lots of components need more voltage. |
Quiz
Can you remember what you've learnt about circuits? Find out by taking this quiz.
Play BBC Bitesize educational games! gamePlay BBC Bitesize educational games!
Fun, interactive games for children aged 4-11, with maths, English, science, history and many more subjects.

More on Electrical systems and computer control
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 3

- count3 of 3