Let's learn what light is and how it travels.
Watch and learn
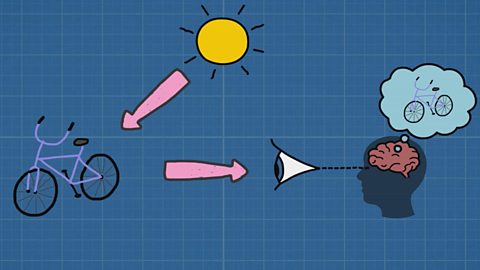
What is light energy and how can it help us see things?
Everything we can see is because of how our eyes detect the light around us.
Title: Light
Light is a form of energy. When we say light, we mean the energy that we can detect with our eyes. When light enters our eyes, our brain interprets this into images we can ‘see’.
The light from the Sun looks white but it is actually a combination of many different colours of light. We can see this by splitting the sunlight using this glass prism.
The colours are the same as a rainbow. This is because a rainbow is created in a similar way. Water droplets in the air split the white sunlight into different colours to make a rainbow.
We use the term ‘spectrum’ to describe the colours of sunlight arranged in order. The objects and colours we can see are created by light shining on them and different colours being reflected back and into our eyes.
This T-shirt is white because all the colours of light reflect off it. This T-shirt is red because only red light is reflected off it. All the other colours of light are absorbed. The T-shirt is black because all the different colours are absorbed by it, Very little light is reflected back, so it appears very dark.
All light travels in straight lines. But when light travels through different materials, such as water and air, the light slightly changes direction. We call this refraction.
Above the water, the light reflecting off this pencil is travelling straight into our eyes. When the light from the pencil passes from the water to the air it is refracted, causing the pencil to look bent.
When light changes direction, the image you see can be changed in unusual ways.
What is light?

Light is a form of energy. It can come from many sources, for example:
- the Sun
- light bulbs
- lightning
- candles
- glow sticks.
Some animals, such as fireflies and glow-worms, are also light sources. They make their own light to attract mates to breed with.

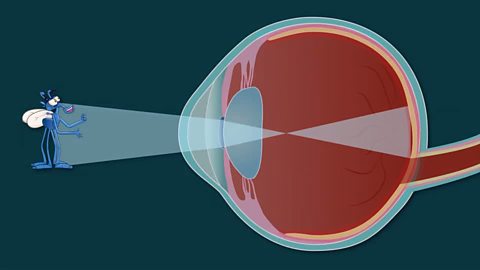
How do we see light?
light reflects off things and enters our eye through the pupil.
it passes through the lens which focuses the light onto the retina in the back of the eye.
from here, light sensors transform the light hitting them to electrical signals that travel through the optic nerve to the brain.
the brain interprets these signals into images of what we can see.
This is how we 'see'.
How does the human eye work? revision-guideHow does the human eye work?
Learn more about how the eyes and brain work together to help people see.
What is energy? revision-guideWhat is energy?
Find out where energy comes from and what the main types of energy are.

What colour is light?
Daylight from the Sun might look like it's white but light is made up of many colours. We call this full range the Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again..
We can see the full colour spectrumThe range of different colours seen when white light is split up. in a rainbow.
What is a rainbow?

A rainbow is formed when sunlight bends when it enters raindrops. This splits white light into the different visible colours that are then reflected back out of the raindrops.
We can split white light into a spectrum of colours using glass prisms or the reflective side of a CD.
What is a rainbow? revision-guideWhat is a rainbow?
Find out more about rainbows.

Why do we see different colours?
Different surfaces reflect different parts of the spectrum.
For example:

A red object absorbs every colour in the colour spectrum apart from red, which it reflects.

A yellow object absorbs every colour in the colour spectrum apart from yellow, which it reflects.
What do you think happens with a blue object?
A blue object absorbs every colour in the colour spectrumapart from blue, which it reflects.

Black is a little different. A black object absorbs all the colours of the colour spectrum so it doesn’t reflect any colour.
Most objects we think of as black aren't truly black. They are more usually very dark colours that reflect a little bit of light.
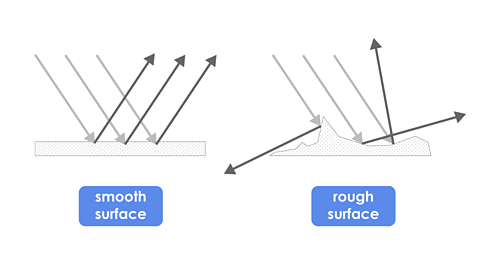
How does light travel?
Light travels in straight lines from the source.
It reflects off objects in straight lines as well. This is how a smooth, shiny mirror reverses what you see.
When light reflects off a rough surface it goes in different directions so you don’t get a sharp reflection.
Think about how different a reflection is in still water compared to water that has waves or ripples.

Light reflecting off this still water makes the house look like it's sitting on a mirror.

Reflections on rippled water usually looked twisted and distorted.
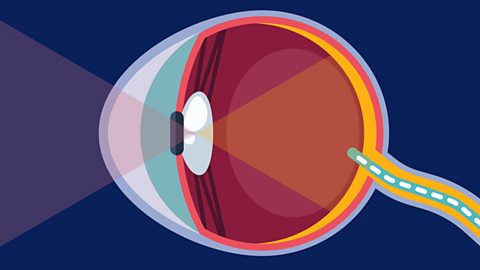
Why do things look weird in water?

Light travels in straight lines until it passes from one material to another, for example from air to water or water to air.
When this happens, the light is refractionThe process of light changing speed when it travels from one material to another. This can cause the light to bend or change direction., which means it changes speed. This can change the direction of the light, causing objects underwater to look bent or like they don't line up properly.

How fast does light travel?
Light travels incredibly fast. In fact it’s the fastest moving thing in the universe – nearly 300,000 km in 1 second!
It is so fast that it can travel 7 ½ times the length of the Equator in one second!

Astronomers use light years to measure really big objects and long distances in the Universe.
Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is over 100,000 light years across. That means if you could travel at the speed of light, it would take you 100,000 years to get from one side to the other!


Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – The form of energy that allows us to see objects around us.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – Anything (natural or artificial) that produces light.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – The range of different colours seen when white light is split up.
Sorry, something went wrongCheck your connection, refresh the page and try again. – The process of light changing speed as it travels through different materials. This can cause it to change direction.
Activity

Try this light experiment!
You will need:
a coin
a glass filled with water
a paper straw or pencil
Fill the glass with water and experiment with how this changes how the coin, straws and pencils look.
Watch this video to find out what to do!
Video
Quiz
Do you want to find out how much you've learned about light? Try our fun quiz!
More on Light and sound
Find out more by working through a topic
- count7 of 10

- count8 of 10

- count9 of 10
- count10 of 10
