What is electricity?
Electricity is a form of energy.
It is created by generators which can be powered by renewable resources such as wind, solar and hydro-electric or non-renewable resources such as gas, coal and oil.
We measure electrical current in volts (V). Voltage is the ‘push’ which makes electricity flow around a circuit.

Watch: Electrical components
Fran: Ahhh, I almost won that one as well!
Now, our appliances and devices, they all work because of the electrical current that flows into them through a circuit.
An electrical circuit is made of a power source, some electrical conductors, and usually at least one component.
And here I have a few different components. I have a light bulb, our buzzer, and our motor.
Woo hoo!
If I want to have them all in the same circuit, I can do that.
All I need to do is wire them all together, and hopefully this should work.
Yay!
Now, if I want to be able to switch them on and off, I can just break the circuit, like this.
Or I could use one of these - a switch, and this completes or breaks the circuit when you press it.
Let's put it in our circuit and see how it works.
If I switch it on, all the components are working.
So, let's see what my investigator has found out about electrical components.
Child: The 4.5-volt bulb in this circuit is being lit up by a 1.5-volt battery.
I'm going to see if adding more 1.5-volt batteries if it will make the bulb shine brighter.
First, I need to measure the brightness of the bulb, so I can record my findings. 271.6.
Now, I have another 1.5-volt battery, let's add it in.
And I'll measure that to see if it's any brighter. 436.6.
Now, I'm going to add a third battery in, and see if it makes it any brighter. 906.9.
I think we found that increasing the number of batteries made the bulb shine brighter.
Fran: So, remember, how you connect your electrical components in your circuit can make a huge difference.
What are components?
Components are simply the ‘building blocks’ of circuits. Electrical circuits are made up of components.
In an electrical circuit there will be these components:

- A power source
This can be a battery, a generator or an electrical socket. In a battery, the flow of electricity moves from the positive terminal (+) around the circuit to the negative terminal (-) of the battery. - A conductor
This is a material that allows electricity to flow through it, including metals such as copper, aluminium and silver. Wires are usually made from copper. - A load
These are devices that consume electrical energy and perform a function, such as light bulbs, motors and buzzers. Bulbs glow with light and buzzers make a sound when electricity passes through them.
There may also be:
- A switch
This is a device that can control the flow of electricity in a circuit. When the switch is open, the circuit is broken and electricity is unable to flow. When the switch is closed, the circuit is complete and electricity can flow around in an endless circle.

Watch: How a circuit works
Everything you own that uses electricity will have an electric circuit. These circuits are made up of different electrical components.
Learn how an electric circuit works.
VOICEOVER:
The battery pushes electricity along the wires from the positive terminal, through the bulb, back to the negative terminal of the battery making a circuit.
Electricity can travel easily through the metal wires in the circuit.
To turn out the light we need to break the circuit. We can do this by putting in a switch. It doesn't matter where in the circuit you put the switch – the effect is the same.
The bulb glows because electricity flows through the thin wire inside the bulb called a filament and makes it hot.
When the bulb gets old, the wire will eventually break, breaking the circuit and therefore no electricity can flow.
Time to change the bulb!
Fascinating facts

Electricity can travel close to the speed of light at almost 180,000 miles per second.
During a thunderstorm, lightning is formed by natural static electricity.
In 1752 the American scientist Benjamin Franklin conducted experiments with a kite during a thunderstorm to prove that lightning was a form of electricity. He had to take many precautions to avoid suffering an electric shock!
Hydropower is the use of fast-flowing water to produce electricity. The electricity produced is known as hydroelectricity.
Currently, the Three Gorges Dam, China is the largest power generator in the world. It produces hydroelectricity from a 2,335 metre long dam across the Yangtze River.
We can see some electrical components in our everyday life, from light switches to power lines.
Voltage is marked on cells and electrical components such as bulbs and kettles.
Nerve cells in our body use electricity to pass signals to our muscles.

The battery
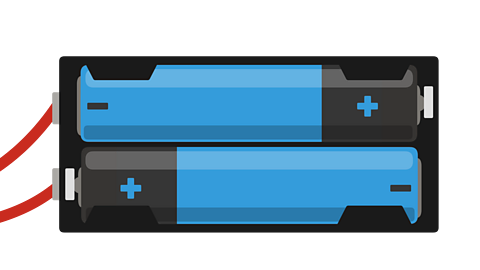
A circuit always starts with a power source, such as a battery. A flow of electricity moves from the positive pole to the negative pole of the battery.
The flow of electricity is pushed by the battery, through the wires to the other components in the circuit. This makes a complete electric circuit.

Switches, bulbs, buzzers and voltage
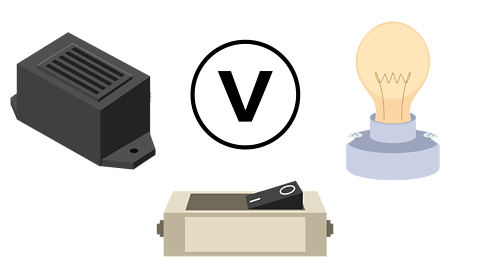
A switch breaks the circuit and the flow of electricity stops. A switch can be used anywhere in a circuit to stop the flow of electricity through a component.
Bulbs glow and buzzers sound when electricity passes through them.
Voltage (V) is the ‘push’ which makes the electricity flow around a circuit. Circuits with lots of components need more voltage because they need more electrical energy to be pushed to them. The more batteries there are the higher voltage will be which means that bulbs will be brighter and buzzers will be louder.

Why is voltage important?

Circuits with lots of components need more voltage because they need more electrical energy to be pushed to them.
To increase the voltage of a circuit, we can either increase the number of batteries, use a battery with a larger voltage, or reduce the number of components in the circuit.
The higher the voltage, the brighter the bulbs and the louder the buzzers. The lower the voltage, the dimmer the bulbs and the quieter the buzzers.

Important words
Components – The ‘building blocks’ of circuits, electrical circuits are made up of components.
Electricity – Electricity is the flow of tiny particles called electrons and protons. It is created by generators which can be powered by gas, coal, oil, wind or solar.
Energy – Energy is what provides the power to helps things work or move.
Generators – Devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Non-renewable – Energy that cannot be replaced within a human lifetime, this includes fossil fuels such as oil, natural gas and coal.
Renewable – Natural energy that we can re-use, this includes solar power, hydroenergy (water), geothermal power (heat) and wind power.
Voltage – The ‘push’ which makes electricity flow around a circuit.
Volts – The strength of a current in an electrical circuit is measured in volts (V).
Activities
Activity 1 – Find the components
Activity 2 – Components quiz
Activity 3 – Draw a circuit

You may need a pen and paper for this activity.
- Draw a diagram of a circuit with three bulbs and three batteries.
- Cover two of the batteries. What would happen to the bulbs?
- Uncover the batteries and cover two bulbs. What would happen to the single bulb?

Where can should you place a switch in this circuit?
You can place a switch anywhere in the circuit and it will have the same effect.
Activity 4 – Build a circuit
New game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space. gameNew game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space
Join Pipette on her epic mission and learn some revolting facts about space along the way.

More on Electricity
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 6

- count2 of 6

- count3 of 6

- count4 of 6

