Key points
- Ceramics are made from soft substances, which when heated become hard and brittle.
- Ceramics have many uses which can be linked to their properties.
- Some uses are clearly visible, such as coffee mugs, but other uses are less visible, such as in car engines.
The following items are commonly found in a kitchen:
- mug
- carrier bag
- plate
- bowl
Think about the materials they are made from and their properties and decide which item is the odd one out.
The carrier bag is the odd one out.
The mug, plate and bowl are likely to be made from china (porcelain) which is a ceramic. Carrier bags are made from paper, plastic or fabric.
Ceramics
ceramicA material formed from a soft substance that is heated to make a hard material. are materials which are hard and durable. They are made by baking a starting material in a very hot oven called a kiln. The temperature of kilns is adjustable for firing different clays and can reach temperatures of over 1300 °C.

The starting materials are soft and malleable, meaning they can be shaped. Clay is an example of a starting material.
These soft materials are shaped and then heated to make harder materials which we call ceramics.
These new hard ceramic materials have a fixed shape and cannot be bent.

There are three stages in the firing process.
Water that is in the clay evaporationWhen a liquid turns into a gas at temperatures below its boiling point. as the material is heated up.
chemical reactionWhen chemical bonds are broken and made between atoms, so that new substances (compounds or elements) are made. occur changing the composition of the material.
Some of the substances in the clay melt and when the ceramic is cooled these harden.


Did you know?
Human beings have been making ceramics for over 20,000 years. A ceramic artefact of a statuette of a woman was dated as early as 28,000 BC.

What is done to soft materials like clay to change them into ceramics?
Soft materials are heated to make them into a harder ceramic material, like the material used in flower pots.

Uses of ceramics
Ceramics have a wide range of uses, linked to their propertiesThe properties of a substance are the qualities and characteristics of a substance that describe and identify it.Common properties of ceramics include:
- hardness
- strong under compression
- brittleSomething which is brittle is easily broken or shattered. meaning they can shatter when struck
- heat resistant
1. Structural uses
Ceramic materials are strong, so they can be used for structural products. For example, bricks are ceramic materials made by baking moulded clay.

Advantages of bricks include:
- they are hard so don’t scratch easily
- they are strong under compression, meaning houses aren’t crushed under their own weight
However, a disadvantage is:
- bricks are brittle, meaning they can break if handled carelessly during construction

2. Ceramics in the kitchen and bathroom
Ceramics can be made into almost any shape, and glazed to give them a non-porousA non-porous substance does not allow liquids into it. The liquid stays on the surface. surface. This makes them useful for purposes where hygiene is important, because liquids containing microbes cannot soak into the ceramic and spread diseases.
For example, everything from cooking dishes to toilets is made from ceramics.
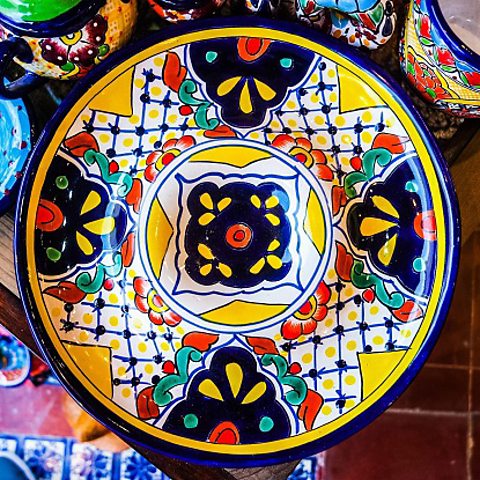

Advantages of using ceramics in the kitchen and bathroom include:
- the starting clay materials are malleableCapable of being hammered or pressed into a new shape without breaking. so can be made into different shapes
- ceramics are heat-resistantA heat resistant substance can be heated to high temperatures without breaking. so won’t break in the oven
However, a disadvantage is:
- ceramics are brittle, meaning ceramics such as plates tend to break when dropped

Ceramics can also be painted with colourful glazes to make artistic and decorative items such as teacups and ornaments.
3. Technical uses
Ceramics are useful engineering materials as they are light and can be heated.
For example, a honeycomb shaped ceramic structure is used to support the metals which speed up the chemical reactions in catalytic converterA device which when fitted to a car exhaust can change harmful nitrogen monoxide and carbon monoxide into nitrogen and carbon dioxide., which are found in car exhaust systems.
Advantages of ceramics in engineering include:
- they have a low densityA measure of how heavy something is compared to its size. Measured in units of mass per unit of volume (e.g. g/cm3). which means they are light compared to their size
- ceramics are heat resistant so can be heated to high temperatures without breaking

Did you know?
The turbine blades of jet engines are coated in a specially engineered ceramic.
This is because ceramics are thermal insulators, meaning they stop the turbines from overheating when they spin thousands of times per minute.

4. Decorative uses
Terracotta is an example of a ceramic material which is used for decorative purposes. It is heated to lower temperatures and left unglazed so the colour of the clay is visible. It has often been used in sculptures.
The Terracotta Army is a collection of terracotta sculptures made to protect the first Emperor of China in the afterlife.

Ceramic tiles are used on the outside of several reusable space craft. Which properties of ceramics makes them ideal for this use?
- heat resistance
- poor heat conductivity
- low density
A space craft can get very hot when it's falling through the Earth’s atmosphere. Ceramics are also low-density materials which help to keep a space craft within its weight limits.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Materials
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 3

- count3 of 3
