Key Points
energyEnergy can be stored and transferred. Energy is a conserved quantity. can transfer by heating from a hotter region to a cooler region.
The temperature of the hotter region decreases. The temperature of the cooler region increases.
Heating can occur by conductionEnergy transfer by heating through a material due to collisions between particles., radiation or convection.
Hot versus cold
The hotter an object, the more energy it has in its thermal energy storeThere is more energy in the thermal energy store if a substance is hotter..
The average speed of particles in a hot substance is greater than in a cold substance.
Temperature is how hot a substance is. Temperature is commonly measured in degrees Celsius (°C) using a thermometer.
Temperature depends on the average speed of the particles in a substance.

Example - a hot cup of tea cools down
Temperature
The cup of tea has an initial temperature of 80°C and cools to a temperature of 30°C . energyEnergy can be stored and transferred. Energy is a conserved quantity. has transferred to the surroundings.
Thermal energy store
Hot tea has more energy in its thermal energy storeThere is more energy in the thermal energy store if a substance is hotter. than cold tea. As the tea cooled, the average speed of the particles in the tea reduced.
This energy didn’t disappear - it transferred to the surroundings.
Energy has transferred from the thermal energy store of the tea to the thermal energy store of the surroundings.

Thermal equilibrium
If there is a difference in temperature between two objects, energy transfers by heating from the hotter object to the cooler one.
The greater difference in temperature, the faster the energy is transferred.

Example 1 - eating an ice lolly on a hot day
energyEnergy can be stored and transferred. Energy is a conserved quantity. is transferred by heating from the hot surroundings to the cold lolly. This causes the lolly to warm up.


Example 2 - drinking a hot coffee on a cold day
Energy is transferred by heating from the hot coffee to the cold surroundings. This causes the coffee to cool down.

When the objects reach the same temperature as the surrounding environment, the energy transfer will stop.
When the objects are at the same temperature, they are in thermal equilibriumA situation where two objects are at the same temperature and there is no overall transfer of energy by heating between them..
Energy transfer
Energy is transferred by heating due to:
radiation
conduction
convection
Video - Radiation, conduction and convection
Watch the video to find out more about radiation, conduction and convection.
SPEAKER ONE: The sun’s energy is carried to Earth by radiation. As electromagnetic waves, to be precise. Like a giant radiator, the sun is the major source of heat energy here on Earth.
Heat flow by radiation doesn’t need anything to travel through. It doesn’t need particles of air, liquid or anything solid. It can travel through nothing at all. So this is how the sun’s energy travels through the vacuum of space.
Having reached the Earth by radiation, this energy may be absorbed by the Earth’s surface, as well as by things on it and they warm up. The energy flows and spreads through these things in one of two ways – either by conduction or convection.
When heat is transferred through a solid, like this knife that is out in the sun, this kind of energy flow is called conduction. The particles inside metals are especially good at conducting heat. When these tightly packed particles are heated, they gain more energy, vibrate more quickly and the heat energy is swiftly passed along from one particle to another.
YOUNG PERSON: Ah, that’s hot!
SPEAKER ONE: By touching the hot metal object, the heat energy flows once again, very quickly from the handle to Orianne’s skin.
The more energy there is, the hotter it feels. Heat flows because there is a difference in temperature. It always transfers from warmer objects or places (here, the knife) to cooler one’s to Rishil or Orianne’s skin.
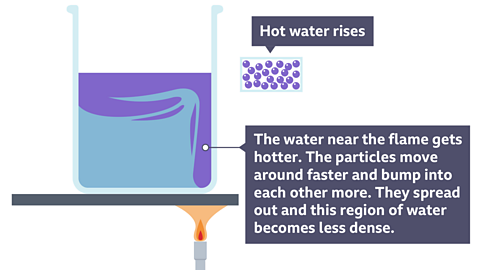
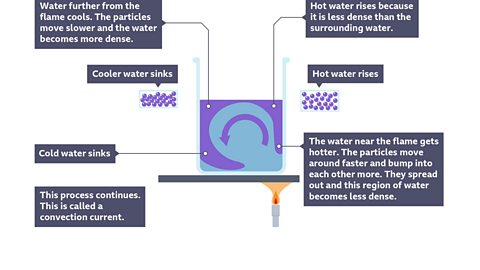
The third way that heat is transferred is by convection. Convection is how heat energy travels in moving currents through liquids and gasses. The molecules actually move away from the source of heat, carrying energy with them.
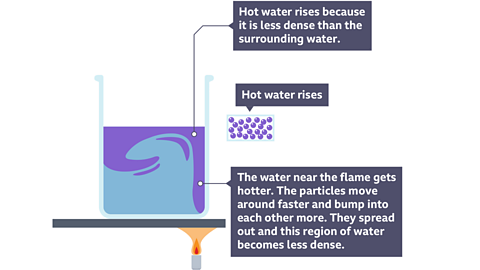
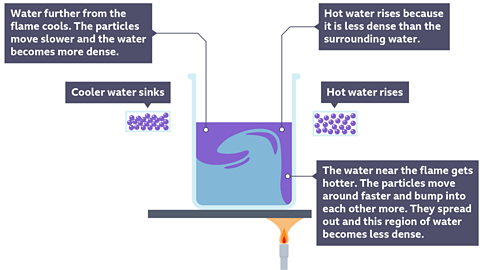
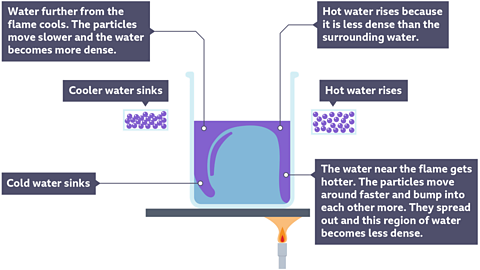
When a glass of water is placed on hot sand, heat will be transferred through the water by convection. When the particles of water in the bottom of the glass heat up, they move more quickly, spread out and become less densely packed together than the cooler particles around them.
They rise up thought denser and cooler water to the top of the glass and this cooler water sinks to the bottom where it also gets heated up. This movement sets up a convection current and eventually all of the liquid is heated up to the same temperature.
Radiation

All objects transfer energy to their surroundings by infrared radiationElectromagnetic wave emitted from a hot object. . The hotter the object, the more infrared radiation it emits.
Infrared radiation is a type of electromagnetic wave. Unlike conduction and convection, there are no particles involved. This means that energy can be transferred by radiation when there are no particles, like the vacuum of space.
Radiation is why we feel the warmth of the Sun.

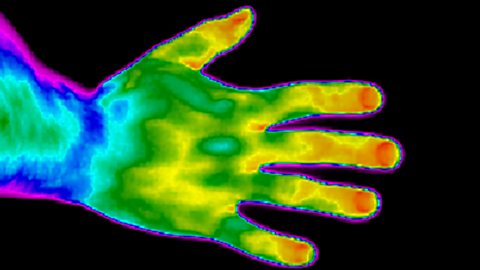
Thermal imaging cameras detect the amount of infrared radiation emitted by an object.
The camera produces an image like this one of the hand.
The blue and purple areas represent cooler areas. These emit less infrared radiation.
The yellow and orange areas represent hotter areas. These emit lots of infrared radiation.

Conduction
Conduction is where energy is transferred by the vibrating particles in a substance. The energy is transferred from a hotter region to a cooler region.
Conduction happens fastest in solids because the particles are close together.
Materials which transfer energy easily from a hot area to a cooler area by conduction are called conductorA material which allows electrical current to flow through it easily, eg copper or gold.. Metals are very good conductors.
Have a look through this slideshow to understand more about metals as conductors.
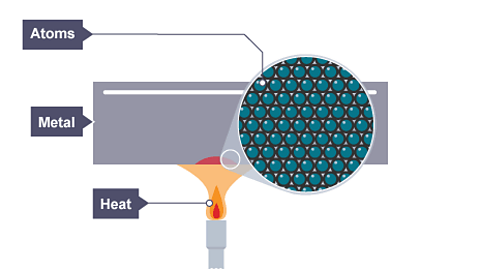
Image caption, The cool metal starts to be heated
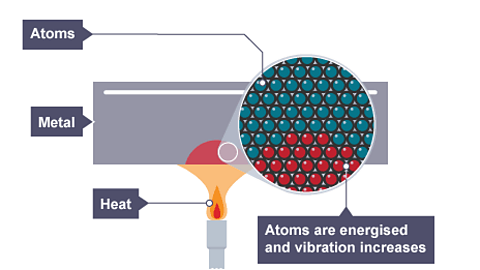
Image caption, As the metal warms conduction starts
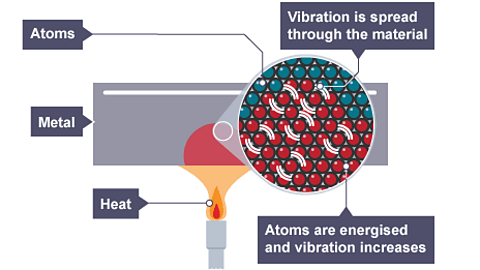
Image caption, Energy transfer by conduction continues through the metal
1 of 3
Materials which do not transfer energy easily from a hotter area to a cooler area are called insulatorA material that does not allow current to flow through it easily, eg wood or glass. . Air and plastics are good insulators.
The best insulator is a vacuum. Conduction cannot occur if there are no particles.
Convection
A fluid is a substance that can flow. Both liquids and gases are fluids.
The particles in a fluid can move around from one place to another.
Look through the slideshow to understand more about the stages of convection.
1 of 5
Insulation

Insulation is used to reduce unwanted thermal energy storeThere is more energy in the thermal energy store if a substance is hotter. transfers and maintain the temperature of an object.
For example, an insulated picnic bag can keep your lunch cooler for longer. It can also keep hot food hotter for longer.

Reducing conduction, radiation and convection
The table shows how conduction, radiation and convection transfer energy and how to reduce the method of energy transfer.
| How is energy transferred? | How can we reduce the method of energy transfer? | |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation | Energy is transferred by an electromagnetic wave. | Use shiny white or silver surfaces. |
| Conduction | Particles collide with each other. Conduction can occur between objects if they are touching. | Use insulators. |
| Convection | Hotter fluid is less dense than colder fluid so it rises. Energy is transferred by the moving fluid. | Stop the fluid from circulating. |
Everyday examples
Look at these examples to understand how conduction, radiation and convection can be reduced in a range familiar objects and places.

Insulated coffee cups
Insulated coffee cups have two layers. There is a gap between the two layers to reduce conduction.
The cup also has a lid. This reduces convection by trapping the hot gases inside the cup.
The inside of the cups are usually a shiny white surface. This reflects infrared radiation.


Cooking pan handles
Cooking pans are made of metal. Energy is transferred to the food by conduction through the metal base and sides of the pan.
Some pans have metal handles and some have plastic handles.

Which of the two pans in the photo is safer to hold when frying food?
The pan with the plastic handle is safer to hold. Plastic is an insulator. Your hand will not get hot.
Flasks
Flasks come in many different colours and are used to hold either hot or cold drinks. The colour of the flask is important.

Choose the shiny white flask to keep your water cold. It transfers less energy by radiation. A shiny white surface is a poor absorber of infrared radiation and therefore helps keep a cold drink cold.
The shiny white flask is also the right choice to keep a hot drink hot. It transfers less energy by radiation. A shiny white surface is a poor emitter of infrared radiation and therefore helps keep a hot drink hot.

Examples in the home
There are many different examples of insulation used within the home to stop it getting too hot in the summer or too cold in the winter. Look through the slideshow to explore more.

Image caption, There is insulation in the walls and roofs of houses. This is a wool-like material. Air is trapped between the fibres. Air is a poor conductor so reduces energy transferred by conduction. The air cannot easily circulate therefore convection is reduced.

Image caption, Sometimes this insulation is also coated in a reflective material. This reduces energy transfer by radiation.

Image caption, Double glazed windows have two panes of glass rather than one. A thin layer of air is trapped between the two panes of glass. The trapped air reduces both conduction and convection. Air is a gas and gases are insulators. This reduces the energy being transferred by conduction. The air is trapped in a narrow gap between the two panes of glass so it can’t circulate and this reduces convection.

Image caption, Carpets and curtains are other types of insulation as they trap cold air.
1 of 4
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Teaching resources
Are you a physics teacher looking for more resources to engage your students? In this series of short films, daredevil science geek Greg Foot is prepared to attempt anything to find your students the answers to some of life's weirder questions.
BBC Bitesize for Teachers has thousands of free, curriculum-linked resources to help deliver lessons - all arranged by subject and age group.
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Energy
Find out more by working through a topic
- count6 of 7

- count7 of 7

- count1 of 7
- count2 of 7