Key points
- There are different ways to complete a calculation using long multiplication.
- The areaA measure of the size of any plane surface or 2D shape. Area is measured in square units, for example, square centimetres or square metres: cm² or m². method is also known as the grid method.
- The area method can be useful when multiplying large numbers together.
- Using an arrayAn array in maths is an arrangement of objects, numbers or pictures in columns or rows. or grid model can help to see the relationship between multiplication and division.
For example:
5 x 8 = 40
8 x 5 = 40
40 ÷ 5 = 8
40 ÷ 8 = 5
Visual representations of multiplication
- An arrayAn array in maths is an arrangement of objects, numbers or pictures in columns or rows. is a rectangular arrangement to represent multiplication. This can be drawn as a rectangle made up of squares or dots in rows and columns.
- The number in each row multiplied by the number in each column equals the total number.
- An array can help to illustrate different factsThe word 'fact’ is related to the instant recall of knowledge about a number. A multiplication fact for 20 could be 4 x 5. A division fact for 20 could be 20 ÷ 5 = 4 involving multiplication and division. It can also help to demonstrate that multiplication is commutativeAn operation is commutative if the order does not matter. Multiplication and addition are commutative, eg 4 × 3 = 3 × 4 and 4 + 3 = 3 + 4 .
- The distributive lawThe distributive law says that multiplying a number by a group of numbers added together is the same as doing each multiplication separately. Eg, 3 × (2 + 4) = 3 × 2 + 3 × 4 means that more complicated multiplication calculations can be broken down into smaller chunks by partitionTo split a number into component parts. Eg, the two-digit number 38 can be partitioned into 30 + 8 or 19 + 19 bigger numbers. Eg, 15 x 3 is the same as 10 x 3 + 5 x 3. Both equal 45. 15 has been partitioned into 10 and 5
- Using a visual representation of multiplication can be useful to look at before moving onto the area method for multiplication.
Example: visual representation

Image caption, What does this representation show?
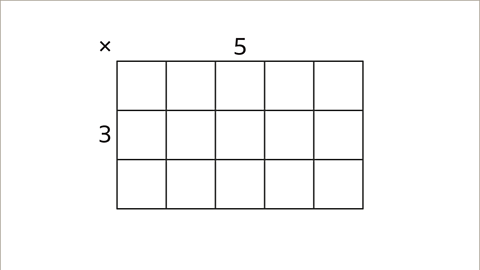
Image caption, This array model provides a lot of information. Count the squares – there are 15 in total. The array is 5 by 3 which shows that 5 x 3 = 15
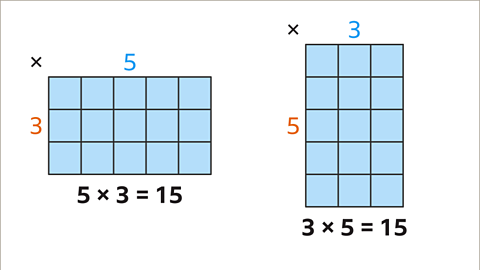
Image caption, The array can be shown as 5 groups of 3 showing that 5 x 3 = 15. Or it could be shown as 3 groups of 5 showing that 3 x 5 = 15. This demonstrates that multiplication is commutative.
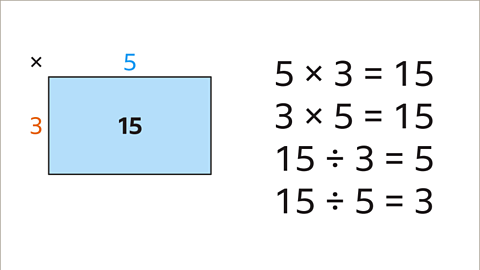
Image caption, Representing the array as a grid can be helpful when dealing with large integer values. This means each array square does not have to be drawn. This area model representation highlights 4 multiplication and division facts.

Image caption, This grid representation shows that 15 x 3 = 45

Image caption, Partitioning numbers is useful when multiplying using the grid method. Larger numbers can be partitioned to make them easier to calculate. Eg, 15 can be partitioned into 10 and 5
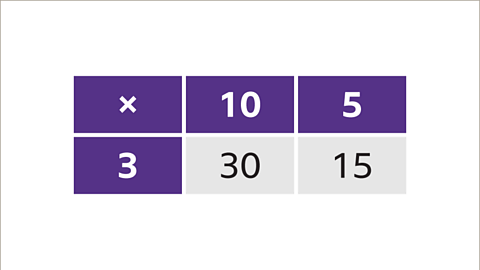
Image caption, This grid has been highlighted to demonstrate the distributive law. The distributive law can help to break the calculation into more manageable chunks. 15 has been partitioned into 10 + 5. 15 x 3 is the same as 10 x 3 + 5 x 3. Both make 45
1 of 7
How to multiply using the area method
- Draw a rectangle.
- partitionTo split a number into component parts. Eg, the two-digit number 38 can be partitioned into 30 + 8 or 19 + 19 each number in the calculation.
- Multiply the value in each column by the value in each row.
- Add up all the totals within the grid.
- The total is the answer to the multiplication.
Remember that multiplication and addition are both commutativeAn operation is commutative if the order does not matter. Multiplication and addition are commutative, eg 4 × 3 = 3 × 4 and 4 + 3 = 3 + 4 . The order in which you complete the grid or add up the totals does not matter. The outcome will be the same.
Example: 79 x 23
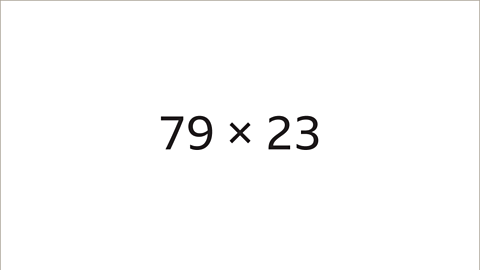
Image caption, Calculate 79 x 23 using the area method.

Image caption, Partition the numbers into tens and units. 79 is split into 70 and 9. 23 is split into 20 and 3. Draw a separate row and column for each partitioned number.
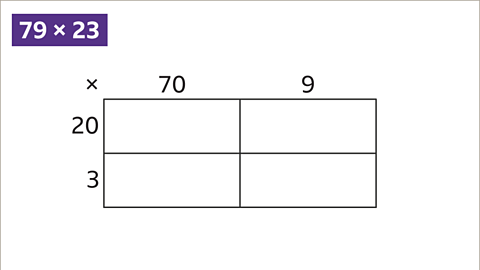
Image caption, Multiply each column and row with each other to get 4 numbers.
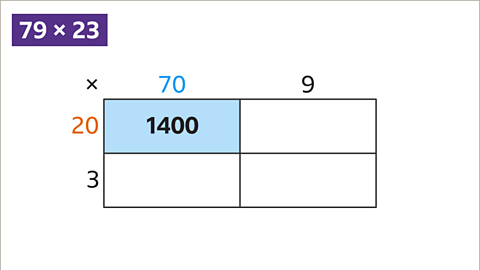
Image caption, This rectangle gives the answer to 20 x 70. 20 x 70 = 1400
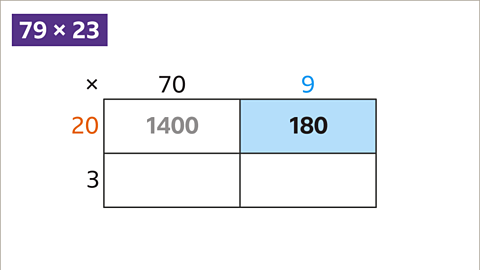
Image caption, This rectangle gives the answer to 20 x 9. 20 x 9 = 180
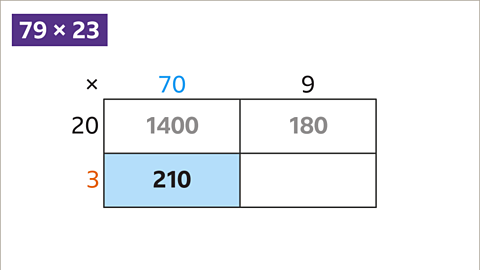
Image caption, This rectangle gives the answer to 3 x 70. 3 x 70 = 210

Image caption, This rectangle gives the answer to 3 x 9. 3 x 9 = 27

Image caption, Add the 4 numbers in the grid together to get the total. 1400 + 180 + 210 + 27 = 1817

Image caption, Multiplication is commutative. This means that the four sections of the grid can be completed in any order. Addition is also commutative so the four values can be added together in any order. The outcome will be the same.
1 of 9
Question
What multiplication sum does the grid represent?

The calculation represents 45 x 39
45 has been partitioned into 40 and 5
39 has been partitioned into 30 and 9
Practise multiplying using the area method
Try this quiz to practise multiplying using the area method. You may want to use a pen and paper to help with your workings out.
Quiz
Real-world maths
Long multiplication is used regularly in daily life. Using the area method breaks the stages into more manageable steps and is less likely to lead to place value errors.

It is important that tradespeople have the right number of materials to complete the job they are working on. For example, a painter may use the area method to calculate the total surface area of a house they are decorating.
The same painter might use the area method to calculate the cost of the raw materials needed. Eg, 12 tins of paint are required which cost £14 per tin, so they would need to calculate 12 x 14

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Place value
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 5

- count4 of 5
