What is a circuit?

A circuit is a closed loop containing various components.
Electrical current flows around the circuit.
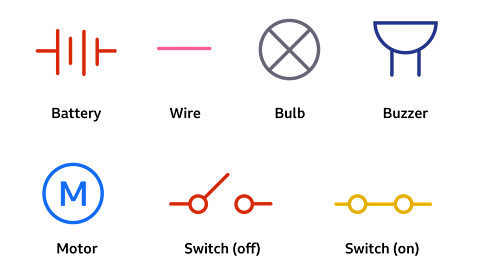
Scientists use symbols to represent the different components in a circuit.
A circuit will always have a battery (cell) as well as other components. Components, such as bulbs, buzzers,switches and motors, need a battery in order to work.

Why do we need symbols?
Symbols are simplified drawings. We use symbols because they are easier to draw and they act as a universal language allowing engineers and scientists from all over the world to discuss and work on circuit projects.
Symbols are used to create circuit diagrams. These diagrams help us visualise and understand how components are connected in a circuit.
Each symbol represents a specific component. Knowing the symbol helps to identify the components in a circuit and understand the role they play.
Video: Constructing an intruder alarm
Follow along and learn how to construct a circuit.
You've got some seriously cool stuff here, Frank.
If we’re putting this Sandwich Intruder Alarm together, we’re going to need a diagram!
Sweet.
Each of these symbols are different electrical parts.
We just need to arrange them in to a circuit!
First we need power, man – this symbol here is a cell, or battery.
That one’s a motor – we don’t need that one.
But that’s a light bulb – we can use that.
Let’s finish off with the buzzer, to make some noise!
But we need the power to flooowww – let’s join it all up with wires.
Don’t forget the switch – we’ll set it up so if someone treads on it, the switch will close, setting off our alarm!
Let’s check it out!
Niiiice…
Frank! Someone’s stealing the sandwich!
Frank!?.. Frank?
Aww man…
Fascinating facts
Electricity is a form of energy.
Batteries work by converting chemical energy into electrical energy.
In a battery, electricity flows from a positive terminal (+) around the circuit to a negative terminal (-). This flow continues indefinitely until the circuit is broken or the battery runs out of chemical energy.
The flow of current in an electrical circuit is measured in amperes or amps (A).
Voltage (V) is the 'push' which makes electricity flow around the circuit.
In a thunder storm, lightning is formed by natural static electricity.
In 1752 the American scientist Benjamin Franklin conducted experiments with a kite during a thunderstorm to prove that lightning was a form of electricity. He had to take many precautions to avoid suffering an electric shock!
Electricity can travel close to the speed of light – almost 186,000 miles per second.

What do the symbols mean?
Important words
Battery – A battery is made up of more than one cell. Cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy.
Circuit – A closed electrical loop containing various components.
Components – The 'building blocks' of circuits, all electrical circuits are made up of components.
Circuit diagrams – Diagrams which help to visualise and understand how components are connected in a circuit.
Symbols – Simplified drawings of electrical components.
Wires – Pieces of flexible conductive metal that can transport electricity.
Activities
Activity 1 – Identify the circuit symbols
Activity 2 – Circuit symbols quiz
Activity 3 – Draw a series circuit

It is really important that wires are drawn as straight lines using a ruler.
When you are drawing a real circuit using symbols, we often show the circuit as a rectangle.
Practise drawing the following series circuits using symbols:
- A simple circuit with a bulb and battery.
- A series circuit where the bulb doesn't light up.
- A circuit with three batteries, a bulb and a buzzer.
Challenge: Can you design a circuit for traffic lights?

Activity 4 – Match the symbols
New game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space. gameNew game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space
Join Pipette on her epic mission and learn some revolting facts about space along the way.

More on Electricity
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 2

