Key points
- Adding and subtracting numbers written in standard form can be carried out by converting to an ordinary (decimal) number format before completing the calculation. The numbers are then changed back into standard formStandard form is a way to write really large or very small numbers. In standard form, numbers are recorded as a number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of ten. This is also called standard index form or scientific notation. .
- Multiplication and division of numbers written in standard form is processed wholly within standard form.
Knowledge of converting numbers into and from standard form will be useful before looking at calculations with standard index form.
How to add and subtract numbers in standard form, with decimals
Adding and subtracting numbers in standard form can be done by working with ordinary (decimal) numbers:
- Write the standard formStandard form is a way to write really large or very small numbers. In standard form, numbers are recorded as a number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of ten. This is also called standard index form or scientific notation. numbers as ordinary numbers.
- Do the addition or subtraction.
- Write the answer in standard form.
A good understanding of standard form is needed for this method.
Examples
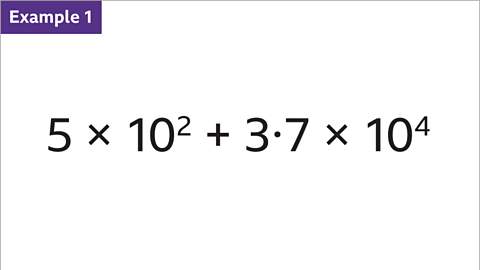
Image caption, Add 5 × 10² and 3∙7 × 10⁴
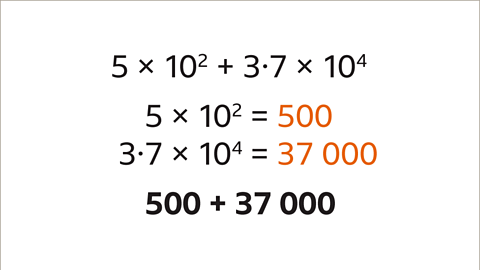
Image caption, Convert each standard form number to an ordinary (decimal) number. The calculation is now 500 + 37,000
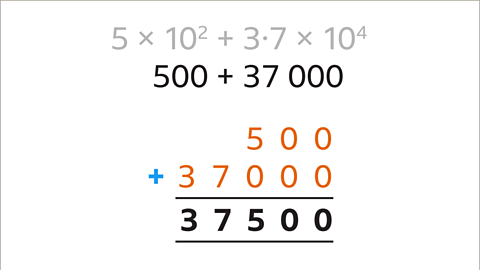
Image caption, Add the decimal numbers. 500 + 37,000 is 37,500
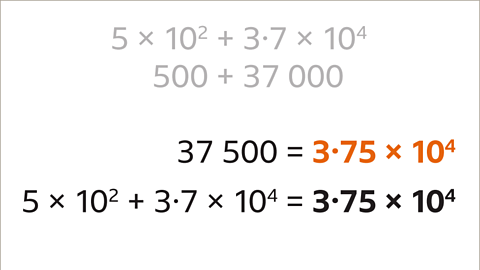
Image caption, Write the answer (37,500) in standard form. 5 × 10² + 3∙7 × 10⁴ = 3∙75 × 10⁴
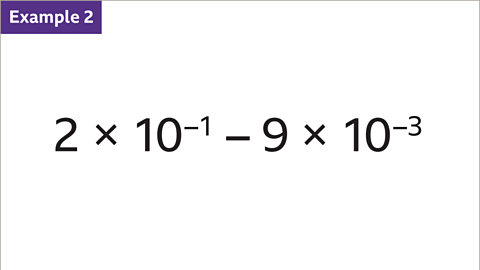
Image caption, Subtract 9 × 10⁻³ from 2 × 10⁻¹
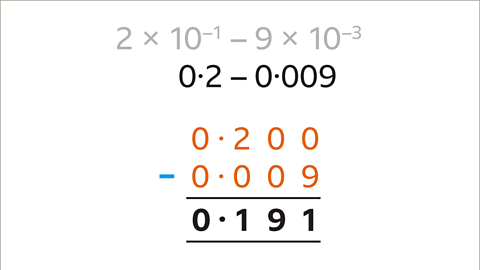
Image caption, Subtract the decimal numbers. 0∙2 – 0∙009 = 0∙191
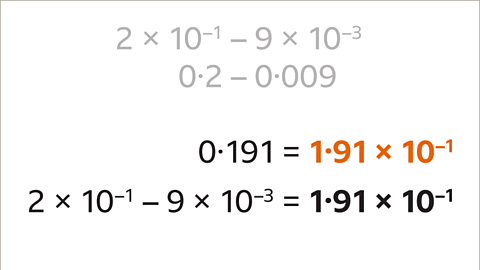
Image caption, Write the answer in standard form. 2 × 10⁻¹ − 9 × 10⁻³ = 1∙91 × 10⁻¹
1 of 7
How to multiply and divide numbers in standard form
To multiply numbers in standard form:
- Multiply the values of A. These are the numbers that are between 1 and 10.
- Multiply the powers of 10The second power of 10 for example is 100. Powers of 10 are 10, 100, 1000 and so on. by adding the indices.
- Write the answer in standard form.
To divide numbers in standard form:
- Write the calculation as a fraction.
- Divide the values of A.
- Divide the powers of ten by subtracting the indices.
- Write the answer in standard form.
After multiplying or dividing, the answer may not be in standard form. To adjust the number so it is in standard form:
- First, write the value A in standard form multiplied by the given power of ten.
- simplify (a fraction)To reduce a fraction to its simplest form, also known as its lowest terms. the powers of ten by adding the indices.
It may be useful to review the laws of indices and how to write a number in standard form.
Examples
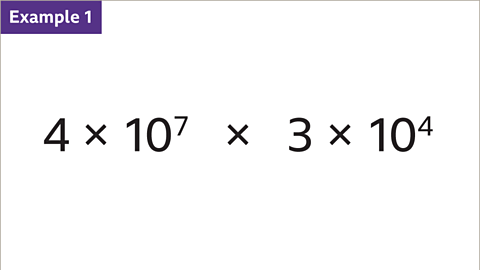
Image caption, Multiply 4 × 10⁷ by 3 × 10⁴
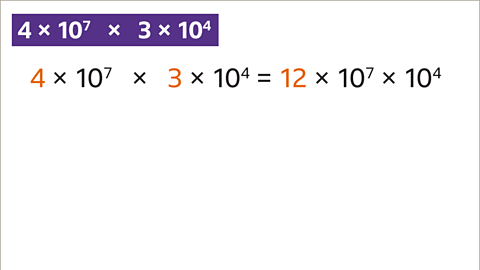
Image caption, Multiply the values of A (4 × 3 = 12).
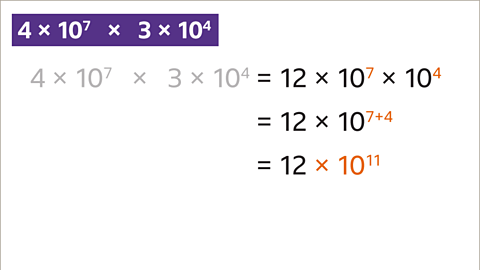
Image caption, Multiply the powers of ten by adding the indices (7 + 4 = 11).
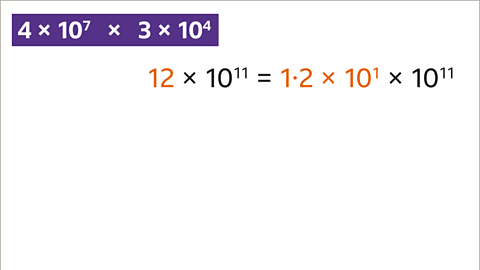
Image caption, The answer is 12 × 10¹¹, but this is not in standard form yet. A number is in standard form when written as a number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of ten. Write the number (12) in standard form (1∙2 x 10¹), followed by the previous power of ten (x 10¹¹).
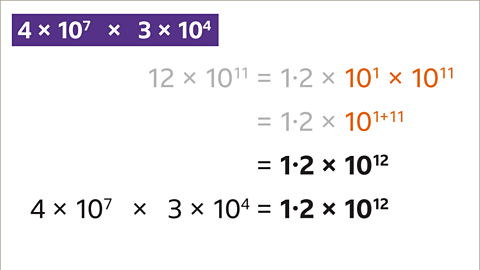
Image caption, To simplify the powers of ten using the laws of indices, add the indices (1 + 11). 12 × 10¹¹ is 1∙2 × 10¹² in standard form.
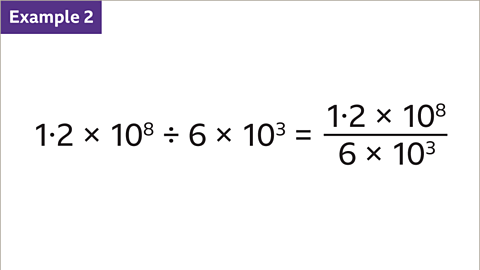
Image caption, Divide 1∙2 × 10⁸ by 6 × 10³ . Write as a fraction.
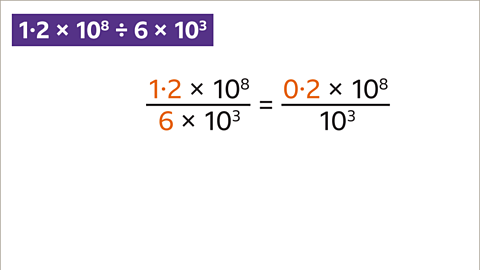
Image caption, Divide the values of A (1∙2 ÷ 6). This gives 0∙2
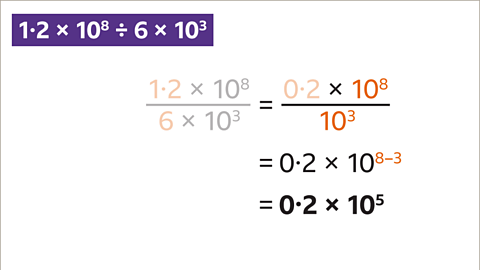
Image caption, Divide the powers of ten by subtracting the indices (8 – 3 = 5). 0∙2 × 10⁵ is not written correctly in standard form. A number is in standard form when written as a number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of ten.
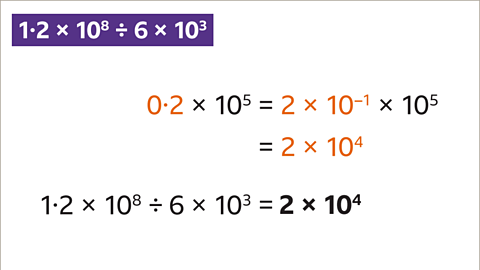
Image caption, Write the answer in standard form by first writing 0∙2 in standard form and then simplifying the powers of ten, using the laws of indices. 1∙2 × 10⁸ ÷ 6 × 10³ is 2 × 10⁴
1 of 9
Question
What is 7 × 10⁻⁹ × 8 × 10²⁰?
Multiply the numbers (7 × 8) giving 56
Multiply the powers of ten by adding the indices (–9 + 20) giving 10¹¹
Write the answer in standard form.
𝟓∙𝟔 × 𝟏𝟎𝟏𝟐
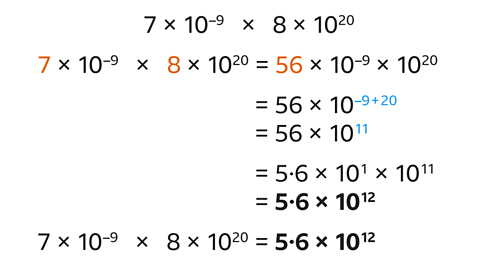
Practise calculations with standard index form
Practise what you've learned about calculations with standard index form in this quiz. You might need a pen and paper to help with your working out.
Quiz
Real-world maths

Calculations in standard form are most often used by scientists working with very small and very large numbers. For example, Earth is 1∙5 × 10⁸ km from the Sun. Neptune is 4∙5 × 10⁹ km from the Sun.
To find the difference in these distances a subtraction in standard form is used. 4∙5 × 10⁹ – 1∙5 × 10⁸ is 4∙35 × 10⁹ km.
Calculating the time that it takes for light to travel from the Sun to the Earth involves a division. The distance of the Earth from the Sun (1∙5 × 10¹¹ metres) divided by the speed of light (3 × 10⁸ metres/second) gives 500 seconds (8 minutes and 20 seconds). The time that light takes to travel distances is used as a measure of distance when looking at far distant galaxies.

Play Sudoku with BBC Bitesize!
Every weekday we release brand new easy, medium and hard Sudoku puzzles. Perfect for testing your skill with numbers and logic.

More on Standard index form
Find out more by working through a topic
- count1 of 2
