Communicable diseases
Viral diseases
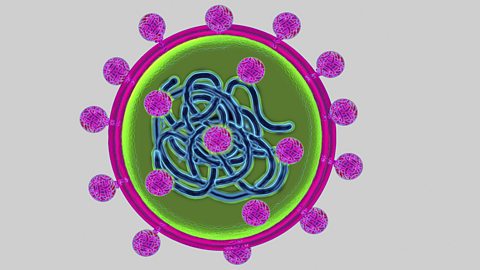
virusAn ultramicroscopic infectious non-cellular organism that can replicate inside the cells of living hosts, with negative consequences. are infective agents made up of genetic material - DNADeoxyribonucleic acid. The material inside the nucleus of cells, carrying the genetic information of a living being. or RNARibonucleic acid, a type of genetic material. - surrounded by a protein coat.
A virus can live only inside the cells of its hostThe organism lived on or in by a parasite.. Most viruses can only live for a short period of time - from a few minutes to several hours - outside a host cell, though some can live longer.
When viruses have infected a suitable host cell or cells, they take over the cells and replicate themselves - producing new genetic material and protein coats - thousands of times. These are then assembled into new virus particles. The host cell or cells then burst and other nearby cells can be infected with the virus.
Viral infections cannot be treated by antibioticsSubstances that control the spread of bacteria in the body by killing them or stopping them reproducing..
HIV/AIDS
HIVHuman Immunodeficiency Virus, a disease which damages cells in the immune system. stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. This infection is transmitted by body fluids, such as blood, often during unprotected sex, but also through cuts and injecting drugs using shared needles.
Immediately after infection, people often suffer mild flu-like symptoms. These pass and for a period of time infected people might not know they are infected.
Months or years after the infection of the HIV virus, it becomes active and starts to attack the patient's immune systemThe body's defence system against entry of any foreign body, including pathogens and agents such as pollen grains. The role of the immune system is to prevent disease.. HIV at this point has become AIDSAcquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome – a disease of the human immune system caused by infection with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).. AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
When a patient has AIDS, their immune system is no longer able to deal with other types of infections or cancer.
There is currently no cure for HIV/AIDS, although treatments are very effective, and patients can live long healthy lives. Currently, infected people are given combinations of antiviralsDrugs that prevent viruses replicating., which can slow the development of the condition.
Measles
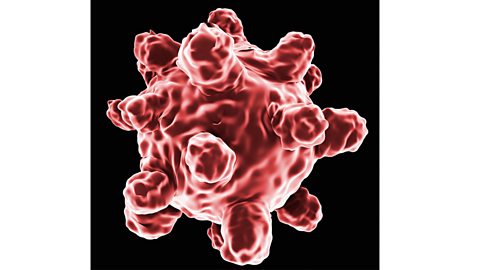
measlesAn infectious disease of the respiratory system caused by a virus. is a very infectious viral disease that is often caught by young children. It is transmitted through the air in tiny droplets after an infected person sneezes or coughs.
The virus causes a fever and skin rash. Measles is usually a mild disease, but if complications arise, it can be very serious. It can cause infection of the eye, ear, respiratory system and brain, and can cause brain damage. It is serious if caught during pregnancy.
In the UK, most children in developed countries are given vaccineSubstances containing disabled antigens of a particular disease, usually administered via injection. Vaccines stimulate the body to produce antibodies to provide immunity against that disease. against measles, but this is not the case throughout the whole world.
Bacterial diseases
Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by a bacteriaSingle-celled microorganisms, some of which are pathogenic in humans, animals and plants. Singular is bacterium.. It is a common infection, especially amongst people aged 15-24.
Gonorrhoea causes a burning pain when urinating and often forms a thick yellow or green dischargeGreen or yellow liquid containing pus that arises from an infection. from an infected person's penis or vagina. If untreated, gonorrhoea can result in infertileNot being able to have children..
To prevent infection, people can:
- abstain from having anal, oral or vaginal sex
- use a barrier-type of contraceptionAny form of birth control used to prevent pregnancy. such as a condom
Gonorrhoea is treated by penicillinAn antibiotic produced by a fungus, Penicillium. Discovered by Alexander Fleming., an antibiotic, but resistant strains of the bacterium are developing. It may soon not be possible to treat the disease.
Salmonella
Salmonella is a genusA rank in classification below family and above species. of bacteria that causes food poisoning.
The toxinA type of natural poison produced by an organism, often as a form of protection. produced by the bacteria cause fever, abdominal cramps, vomiting and diarrhoeaLiquid faeces. .
Salmonella is spread by the presence of the bacterium in food. It can be spread:
- in unhygienic kitchens
- when food such as meat, eggs and poultry, contaminated with the bacterium, is not cooked properly
Learn more about communicable diseases with Dr Alex Lathbridge.
Listen to the full series on BBC Sounds.
In this podcast, learn the key facts about communicable diseases. Listen to the full series on BBC Sounds.