Medicines
drugA substance that can change chemical reactions in the body. are chemical compounds that affect the person taking them. These can have a positive effect like medicines, or a negative one like many illegal drugs.
Medicinal drug types include:
- painkillerA chemical taken to relieve pain associated with disease.
- antibioticSubstance that controls the spread of bacteria in the body by killing them or stopping them reproducing.
Painkillers are chemicals that relieve the symptoms but do not kill the pathogenMicroorganism that causes disease.. Common examples include paracetamol and aspirin, and they can relieve a headache or a sore throat.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are substances that kill bacteriaSingle-celled microorganisms, some of which are pathogenic in humans, animals and plants. Singular is bacterium., or slow down or stop their growth.
Examples include amoxicillin - a type of penicillinAn antibiotic produced by a fungus, Penicillium. Discovered by Alexander Fleming. and ciprofloxacin.
Antibiotics can be taken to cure the disease by killing the pathogen, but only cure bacterial diseases - they cannot kill viruses.
Penicillin
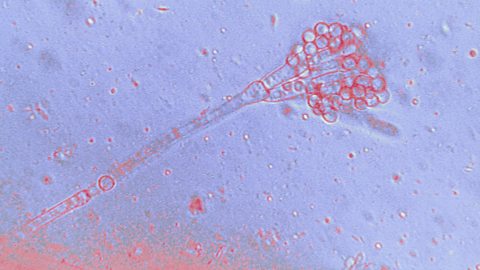
Penicillin was the first antibiotic, discovered in 1928 by Alexander Fleming. He noticed that some bacteria he had left in a Petri dishA clear glass or plastic dish, used to grow living cells from organisms so they can be studied. had been killed by the naturally occurring PenicilliummouldA type of fungus..
How do antibiotics work?
Antibiotics damage the bacterial cells but do not damage the host cells. They have the ability to cure some bacterial diseases that would have previously killed many people. Since their introduction, they have had a large influence on the world's health and death rate.
Antibiotic resistance
Since penicillin was discovered, the use of antibiotics for the treatment of diseases has increased exponentially. Antibiotics are being overused in many ways in our world today.
Commonly prescribed antibiotics are becoming less effective due to a number of reasons:
- their overuse - patients are often prescribed antibiotics when they would get better without them
- failing to complete the fully prescribed course by a doctor - completing the course means that all bacteria are killed, and so none survive and subsequently mutationA random and spontaneous change in the structure of a gene, chromosome or number of chromosomes. to produce resistant strains
- use of antibiotics in farming, where they are used to prevent disease in intensively-farmed animals - antibiotic resistance in farmed animals could spread to humans
These can lead to the effectiveness of antibiotics being reduced, and the incidence of antibiotic resistanceThe ability of bacteria to survive exposure to antibiotics. It is caused by mutations in their genes. increasing. These bacteria are commonly known in the media as superbugs.
Ways to reduce antibiotic resistance:
- only take antibiotics when necessary
- treat specific bacteria with specific antibiotics
- high hospital hygiene levels, including regular hand washing by staff and visitors
- patients who are infected with antibiotic resistant strains of bacteria should be isolated from other patients
The future
Some antibiotics are kept in reserve as a last resort - when others fail. But some bacteria are now becoming resistant to these.
The development of new antibiotics has slowed in recent years. Drugs companies have little financial incentive to develop antibiotics that would only be used very occasionally if none of the other types worked.
Antibiotic development has now increased again, however, as governments realise that this will be required to avert a global catastrophe. Drugs companies are also adopting new strategies to kill bacteria - one approach might make bacteria suicidal. Researchers are also investigating the genomeThe complete set of DNA found in an organism. of pathogens and researching genomicsThe study of the structure and function of genomes. This includes gene sequencing and bioinformatics. approaches to fighting disease.