Protein synthesis
How the structure of DNA affects the proteins made in DNA synthesis
The DNA code for the proteinOrganic compound made up of amino acid molecules. One of the three main food groups, proteins are needed by the body for cell growth and repair. remains in the nucleusThe nucleus controls what happens inside the cell. Chromosomes are structures found in the nucleus of most cells. The plural of nucleus is nuclei....
...but a copy, called mRNA, moves from the nucleus to the ribosomeThe site of protein synthesis..
The ribosome is where proteins are protein synthesisThe production of proteins from amino acids, which happens in the ribosomes of the cell. in the cytoplasmThe living substance inside a cell (not including the nucleus).. The protein produced depends on the template used. If this sequence changes a different protein will be made.
Carrier molecules bring specific amino acidThe building blocks that make up a protein molecule. to add to the growing protein in the correct order. There are only about 20 different naturally-occurring amino acids.
Each protein moleculeA collection of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. has hundreds, or even thousands, of amino acids joined together in a unique sequence. It is then folded into the correct unique shape. This is very important, as it allows the protein to do its job:
- some proteins are enzymeA protein which catalyses or speeds up a chemical reaction.
- others are hormonesChemical messengers produced in glands and carried by the blood to specific organs in the body.
- others form structures within the body, such as collagenThe most common protein found in connective tissue of animals.
Each of these proteins needs a different shape.
1 of 2
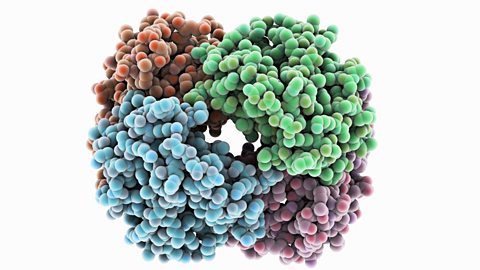
Cells express their genes by converting the genetic message into protein. This process of protein synthesis occurs in two stages - transcription and translation.