Sexual reproduction, meiosis and gamete formation
Sexual reproduction
Two parents are needed in sexual reproductionThe formation of a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms.. During this process the nuclei of the male and female gameteSex cell (sperm in males and ova/eggs in females). are fused in order to create a zygoteA fertilised egg cell.. This process is known as fertilisation. Gametes contain half the number of chromosomes of all other cells in the organism. This means they are haploidA sex cell (gamete) that contains one set of chromosomes.. When the male and female gametes combine in fertilisation they create an embryo with the full complement of chromosomes (diploid). Cells which are diploidA cell that contains two sets of chromosomes. have two sets of chromosomes - for most organisms this means the cells have one set of chromosomes from their mother and one set from their father.
The gametes in animals are sperm (male) and eggs (female).
The gametes in flowering plants are pollen (male) and ovules (female).
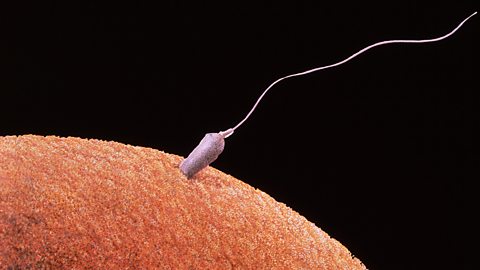
The offspring produced in sexual reproduction are geneticallyTo do with the genes that an organism contains. different to each other and to their parents. This process results in variation within a population because it involves the mixing of genetic information.
Meiosis
This short video explains the role of meiotic cell division
Sexual reproduction uses the process of meiosisReduction division in a cell in which the chromosome number is halved from diploid to haploid., which creates gametes. The process of meiosis happens in the male and female reproductive organs.
As a cell divides to form gametes:
- A copy of all of the genetic information is made.
- The cell divides twice to form four gametes, each with a single set of chromosomes (haploidA sex cell (gamete) that contains one set of chromosomes.). This means the chromosome number has halved.
- All gametes are genetically different from each other.
Fertilisation
Gametes have half the total number of chromosomes that the organism needs to develop and are referred to as haploidA sex cell (gamete) that contains one set of chromosomes.. For example, humans need 46 chromosomes to develop, therefore a human gamete has 23 chromosomes. Fertilisation is the fusion of the nucleusThe nucleus controls what happens inside the cell. Chromosomes are structures found in the nucleus of most cells. The plural of nucleus is nuclei. of a male gameteSex cell (sperm in males and ova/eggs in females). with the nucleus of a female gamete.
When the two gametes combine, they merge the two sets of chromossome to create a cell with the total number of chromosomes needed to develop, known as a diploidA cell that contains two sets of chromosomes. cell. In humans when the haploid sperm and egg cell join in fertilisation the resulting zygote has a total of 46 chromosomes the correct number to develop. By having gametes which are haploid, when the gametes combine, diploid cells are maintained. Also, the mixing of chromosomes in fertilisation is a source of genetic variation.
Fertilisation produces a zygoteA fertilised egg cell., which will mature into an embryo. The number of cells increases by mitosis, and as the embryo develops, the cells begin to differentiate (or specialise).