Production techniques
Using computer aided design and computer aided manufacture in a manufacturing setting
Developments in mass productionWhen the same product is manufactured many times. techniques have led to a variety of production methods being created to improve efficiency by saving time and cutting costs.
Automation
The automationUsing automatic equipment in production. of workplaces has led to an increase in skilled workers but a decrease in job opportunities, as machines have taken over the jobs previously done by humans. Automation has streamlined the manufacturing system by increasing production and reducing errors.
Computer aided design (CAD)
computer aided design (CAD)The process of creating a 2D or 3D design using computer software. now has the capability to design new products in 3D, visualise them in a variety of materials and send images around the world for collaboration and consultation. Once production is finalised, these designs are sent to CAM machines to be formed. Autodesk and Solidworks are common forms of CAD software used.
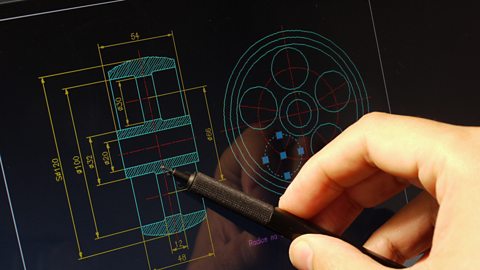
| Advantages of CAD | Disadvantages of CAD |
| Ideas can be drawn and developed quickly | Expensive to set up |
| Designs can be viewed from all angles and with a range of materials | Needs a skilled workforce |
| Some testing and consumer feedback can be done before costly production takes place | Difficult to keep up with constantly changing and improving technology |
| More accurate drawings can be achieved | Files can be corrupted or lost |
| Changes can be made to the drawings easily | |
| Easier to store drawings as digital files that can be sent all around the world in an instant |
| Advantages of CAD | Ideas can be drawn and developed quickly |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of CAD | Expensive to set up |
| Advantages of CAD | Designs can be viewed from all angles and with a range of materials |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of CAD | Needs a skilled workforce |
| Advantages of CAD | Some testing and consumer feedback can be done before costly production takes place |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of CAD | Difficult to keep up with constantly changing and improving technology |
| Advantages of CAD | More accurate drawings can be achieved |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of CAD | Files can be corrupted or lost |
| Advantages of CAD | Changes can be made to the drawings easily |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of CAD |
| Advantages of CAD | Easier to store drawings as digital files that can be sent all around the world in an instant |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of CAD |
Computer aided manufacture (CAM)
By using computer aided manufacture (CAM)The manufacture of a part or product from a computer aided design (CAD) using computer-controlled machinery, such as a 3D printer., designs can be sent to CAM machines such as laser cutters, 3D printers and milling machines.
| Advantages of CAM | Disadvantages of CAM |
| Fast and accurate production | Expensive to set up |
| Machines can run constantly on repetitive tasks | Needs a skilled workforce of engineers |
| Saves on employment costs as fewer workers are needed | Machines need maintaining and parts can be expensive |
| Could cause a loss of manufacturing jobs |
| Advantages of CAM | Fast and accurate production |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of CAM | Expensive to set up |
| Advantages of CAM | Machines can run constantly on repetitive tasks |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of CAM | Needs a skilled workforce of engineers |
| Advantages of CAM | Saves on employment costs as fewer workers are needed |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of CAM | Machines need maintaining and parts can be expensive |
| Advantages of CAM | |
|---|---|
| Disadvantages of CAM | Could cause a loss of manufacturing jobs |
CAM equipment
- computer numerical controlled (CNC) routerA method by a computer to execute a pre-programmed sequence. Machines move via numerical values along X, Y and Z axes. - Used similarly to a hand-held routerA rotary cutter that is not fixed to a machine bed. A hand-held router can be used to cut and shape material. but controlled by a computer following CAD designs. It can be used on a variety of hard materials such as wood, metal and plastic, and is used within engineering for precision cutting.
- CNC embroidery - A design can be created on a computer and then transferred to fabric through a computerised computer numerical controller (CNC) sewing machine. Used to add logos and designs, and to personalise products.
- vinyl cutting - A printer-like CAM machine moves a small blade over the vinyl and cuts bold vectorAn image stored as mathematical instructions for how to draw it. This means its width and height can be increased without the loss of quality.-based illustrations accurately from coloured vinyl. Used for signs, wall decorations, car deco and banners.
- laser cutting - A laser that reflects off mirrors to form an accurate beam and manufacture a variety of products following CAD designs that indicate whether to cut, engrave or etch. Suitable for a wide variety of materials such as plastic, wood, paper, card and fabrics.
- 3D printing - An additive manufacturingA method of shaping a form by building on top of material. CAM process that follows CAD designs to place layers on top of each other repeatedly and create a 3D object. A filamentA material in a thread-like form. of plastic (ABS, PLA, Nylon) is fed into the machine and heated so it is softened and sticks to the previous layer. Used in most industries such as medical (prosthetic limbs), fashion (outfits, footwear), automotive, education and industrial.

Image caption, CNC embroidery

Image caption, Vinyl cutting
Image caption, Laser cutting

Image caption, 3D printing
1 of 4
Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS)
flexible manufacturing system (FMS)A manufacturing process that can be modified at different points to produce different quantities or different parts for a product. are a series of different machines producing different parts for a product. The system is flexible because, at any time, machines in the process can be reprogrammedTo program a computer again with different information. to change their task and production can be changed to produce more or fewer parts without stopping the other areas of the process.
Just in time (JIT)
just in time (JIT) manufacturingMaterials or parts are delivered just before they are needed. is triggered by a customer order. The correct amounts of materials are ordered in to cover the order, and these arrive just as they are needed by production. This saves money on storage, reduces waste and ensures there is no money wasted producing stock that will remain unsold. There are disadvantages to the system in that, if any part of the product cannot be sourced, clientIn business, a client is a person or organisation that wants a product manufactured, eg a retailer. have to wait for their order to be produced.
Lean manufacturing
lean manufacturingA systematic approach to minimising waste within a manufacturing system. is a Japanese concept, based on minimising costs and maximising efficiency by cutting down on waste and the amount of materials and energy used in production. This is done by adapting designs and making changes to the production process. For example, to reduce waste, a packaging net could be redesigned to include a tessellating pattern or, to improve efficiency, changeover times between production runs could be reduced.