Key points
Following the American Civil War and the abolition of the slave trade, there were still many people who wanted to keep racist rules and systems. This was particularly the case in the southern states of the USA.
Jim Crow laws denied Black people rights by enforcing segregation and discrimination in southern states.
The Ku Klux Klan targeted Black, immigrant, Jewish and Catholic people in the 1920s.
The 1954 Brown v Topeka case was an important turning point in the civil rights movement, as it showed that the Supreme Court was prepared to take action to end segregation in the USA.
Video about the origins of the civil rights movement
Narrator:
In 1865, the Civil War in America ended. The northern states had defeated the southern states. The years immediately after the war were known as the Reconstruction era. The Government changed the Constitution, so slavery was abolished across the whole of the United States, freed black Americans were granted citizenship and black men were allowed to vote. But many, especially in the defeated southern states, disagreed with these changes.
White supremacist groups like the Ku Klux Klan emerged furious that Black Americans who had once been enslaved were now considered equal to them. They violently opposed black equality and voting rights. They murdered Black people, assassinated elected officials and intimidated voters.
Jim Crow laws were established in some southern states. These laws were implemented by individual states and they were designed to keep Black Americans separate from white Americans, limit freedom and undermine the progress made during the Reconstruction period. Black people couldn't use the same public facilities, go to the same schools or live in the same towns as white people.
Marriage between the races was against the law and many Black Americans were prevented from voting, as they were unable to pass new voter literacy tests that were deliberately created to exclude poorly educated Black people. Black workers were further oppressed by job discrimination and low wages and the violence continued. Black Americans were brutally murdered, lynched and assaulted by individuals, mobs, the police and the KKK.
Between 1916 and 1970, over six million Black Americans moved from the southern to the northern states. Many viewed the northern cities as a more secure place with greater opportunities, but the growing population meant there was more competition for work and housing. Racial tensions increased and cities became divided into different areas for different ethnicities.
Housing policies created white only areas and throughout Black Americans, indigenous Americans and other ethnic minorities resisted through lawsuits, education, political lobbying and protests. The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People was established by a W.E.B. Du Bois, Ida B. Wells-Barnett and Mary White Ovington in 1909.
They began working to abolish segregation and discrimination and to oppose racism but by the 1950s many felt that if change was truly going to happen, more direct action was needed.
Background
In 1865, the American Civil War between the northern and southern states ended. The southern states were also known as the ConfederateThe Confederate states in America decided to secede, meaning break away, from the United States, and fought against the union during the American Civil War. This was known as the Confederacy, and existed from February 1861 to May 1865. states.
The northern states declared victory and the years immediately after were known as the Reconstruction era. Slavery was abolished, emancipatedTo be freed from the status of an enslaved person. Black Americans were granted American citizenship, and Black men were allowed to vote.
The racist attitudes of some southern states meant that they opposed these changes. Some people turned to violence against Black Americans and those who supported them, including other white Americans.
The Ku Klux Klan
In 1865, a white supremacismThe belief that white people are superior to other races, including Black people and Jewish people, and that white people should therefore hold the power in a society. This is based on incorrect and unscientific ideas about evolution. organisation called the Ku Klux Klan (KKK) was formed. Membership of the KKK was kept secret. Klan members wore white robes and white pointed hats, which also covered their faces, to hide their identities. The KKK leader was known as the ‘Grand Wizard’. Racist members of the KKK carried out violent attacks against many Black Americans. They also targeted other groups of people, including Jews, immigrants and Catholics. Black people were tarred and featheredThe public humiliation of a person by covering them with hot tar and feathers. This causes severe burn injuries to the skin., assaulted and lynchingWhen a group of people kill someone as a punishment, without a fair and legal trial taking place..
In southern states, such as Texas and Mississippi, Klan members would walk openly through the streets. Some police officers, judges and government officials were members of the Klan.
In 1870 and 1871, the government passed the Enforcement Acts, which were laws that aimed to prevent and prosecute crimes committed by KKK members. After this, the KKK’s power declined for several years.
In 1915, the KKK re-emerged after a film called ‘The Birth of a Nation’ was released. Its racist depictions of Black Americans attracted KKK members, and their popularity increased. The KKK also had a surge in membership after World War One, as there was an increased backlashA strong negative response from a large number of people. against immigrationComing to live permanently in a foreign country. from some American people, including politicians.

In 1921, President Warren G. Harding approved the Emergency quotaA fixed number of people that are allowed to do something, such as take a particular job. Act. This placed a limit on the number of immigrants from different countries who were legally allowed to live in the USA. Immigrants faced violence from people already living in the USA, as they wrongly believed that immigrants were taking jobs that belonged to white Americans.
By the mid-1920s, the KKK had 5 million members. To try and escape the violence, many Black Americans moved to northern states, including Illinois, Michigan and New York. This was known as the Great Migration. Northern states did not have the same segregationThe enforced separation of different racial or ethnic groups by providing separate public services and facilities, such as schools, libraries and waiting rooms. laws as the south, but Black Americans still faced racism and discriminationTreating people differently on the basis of a particular characteristic, such as race, religion or sex..

Segregation in the USA
Jim Crow laws
In 1896, a Supreme CourtThe highest court in the country. In the US, it is made up of nine judges, who rule on cases where people claim that the US Constitution has been broken. case determined that segregation between Black and white Americans did not violateTo break or act against something. the US constitutionA set of laws by which a country is governed., as long as the facilities for each group were of the same quality. This became known as ‘separate but equal’.
Jim Crow laws enforced segregation in the south, meaning it was legal to have separate facilities for Black and white Americans. Segregated spaces included:
- Schools
- Waiting rooms
- Public transport
- Libraries
- Cinemas
Even though facilities were meant to be equal, the reality was very different. Facilities for Black Americans were frequently of much poorer quality than those for white citizens. Many schools for Black Americans were overcrowded, and would only have access to a limited curriculum. School buildings would have structural issues, such as leaky roofs. Some cities would only have enough funding for one school and would prioritise schools for white American children, leaving Black American children without an education.

Legal and financial inequalities
Racist attitudes were often reflected in the law. The fifteenth amendment of 1870 gave every man the right to vote, regardless of their race or colour. Some states then passed a law that meant people had to pass a literacy test to be allowed to vote in democratic elections. Black Americans were more likely to have literacy issues due to a lack of investment in Black education.
Some states also imposed ‘grandfather’ clauses, which gave a person an automatic right to vote if their grandfather had voting rights in that state. This meant that most white Americans were eligible to vote without ever having to take the literacy test.
Racist discrimination was also clear in wages. Black Americans were often paid less than white Americans in the same job.
National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
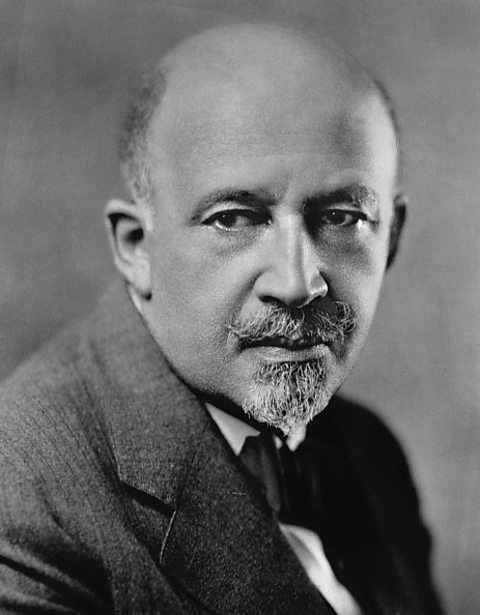
In 1909, the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) was set up by W.E.B. Du Bois, Mary White Ovington and Ida B. Wells-Barnett. They campaigned for changes to the law and equal treatment for Black Americans. The NAACP also provided funding so that Black people could have access to legal representationWhen a lawyer represents someone in court during a court case. .
After World War Two, the NAACP started to take legal action to challenge the ‘separate but equal’ ruling and bring an end to segregation.
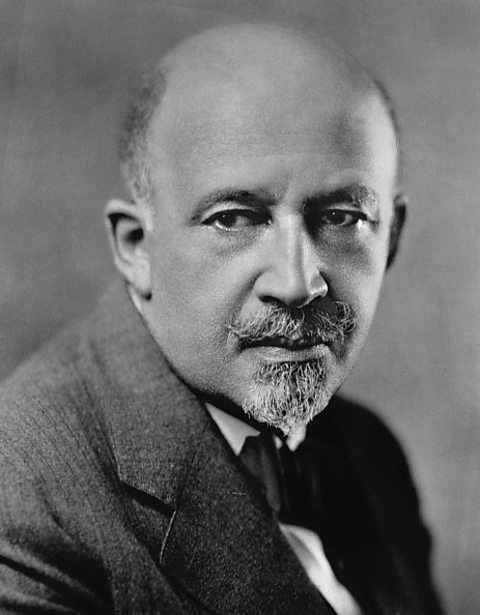
Brown v Topeka
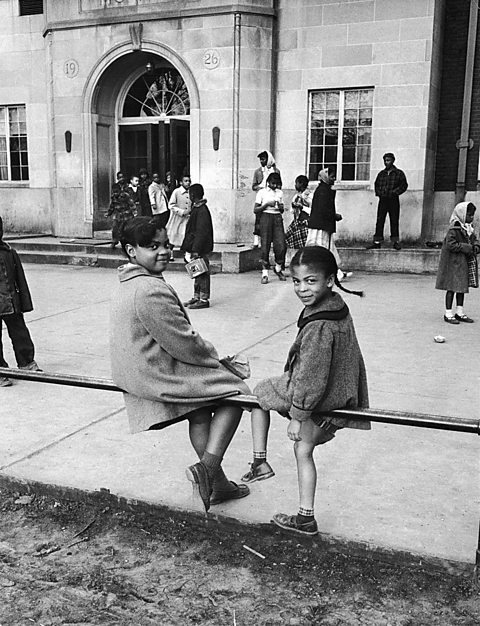

In 1951, an eight-year-old Black girl named Linda Brown wasn’t allowed to attend her nearest school in Topeka, Kansas, as it was for white children only. She had to travel much further, on the bus, to a school for Black children. Linda’s father, Oliver Brown, and the NAACP took legal action against the Topeka Board of Education in the Supreme Court.
In 1954, the Supreme Court passed a ruling determining that segregated schools in Topeka were not of equal quality. It said that they violated the ‘separate but equal’ policy. The Supreme Court went on to rule that segregation in schools should end immediately. This decision was met with anger and resentment in some southern states, but the ruling was supported by President Eisenhower, along with his successors, John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson.
The Brown v Topeka case was a landmark in showing that the Supreme Court was willing to take action to end segregation in America.

What did the Supreme Court ruling say?
In May 1954, the Supreme Court ruling said:
‘To separate Black children from others of similar age and qualifications solely because of their race generates a feeling of inferiority as to their status in the community that may affect their hearts and minds in a way unlikely ever to be undone.’
Test your knowledge
Solve the Story!
An exciting new series from the Other Side of the Story, designed to help young people strengthen their media literacy skills.

More on The civil rights movement in America
Find out more by working through a topic