Factorising quadratic expressions
Factorising an expression means finding the factors that multiply together to give that expression.
A quadratic expression is one that has an ‘𝓍²’ term as its highest power.
\(\mathbf {x^2}\), \(\mathbf {2x^2 -3x}\), \(\mathbf {x^2 - 9}\) and \(\mathbf {x^2 + 5x + 6}\) are all quadratic expressions.
Some quadratic expressions cannot be factorised.
Factorising quadratic expressions of the form \(\mathbf {x^2 + bx + c}\)
To find a method for factorising an expression such as \(\mathbf {x^2 + 5x + 6}\), look at how that expression was arrived at by expanding two brackets.
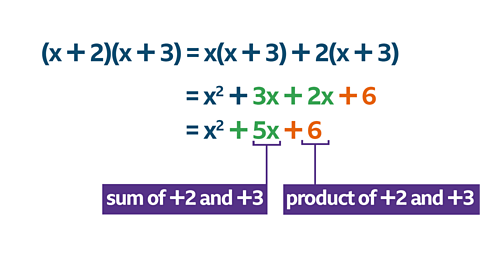
There are three terms in the expanded expression:
First term:
𝓍²
Second term:
sum of +2𝓍 and +3𝓍
Third term:
product of +2 and +3
This information gives us a method for factorising.
Examples
Factorise \(\mathbf {x^2 + 2x – 15}\):
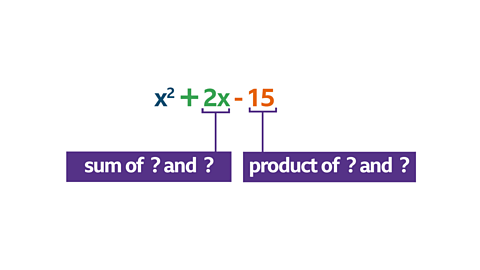
To Factorise:
- Find two numbers whose sum is +2 and whose product is –15
The product is minus 15, so one of factors must be negative.
The numbers needed are either:
+5 and -3 or -5 and +3 As the sum is positive, the pair with the higher + value is the one to choose i.e.
+5 and -3
- Write down the factors:
\(\mathbf {x^2 + 2x – 15 = (x + 5)(x – 3)}\)
- Answer:
\(\mathbf {x^2 + 2x – 15 = (x + 5)(x – 3)}\)
\(\mathbf {(x - 3)(x + 5)}\) is also a correct answer. The order of the factors does not matter.
Question
Factorise \(𝓍² + 5𝓍 – 24\)
Solution
Identify the product and sum of the two key values that we need to find.
Product = -24
Sum = +5
+8 and -3 add to give +5 and multiply to give -24
The factors are (𝓍 + 8) and (𝓍 – 3)
Answer: \(\mathbf {x^2 + 5x – 24 = (x + 8)(x – 3)}\)
E𝓍ample
Factorise 𝓍² - 9𝓍 + 20
Solution
Identify the product and sum of the two key values that we need to find.
Product = +20
Sum = - 9
-4 and -5 add to give -9 and multiply to give +20The factors are (𝓍 - 4) and (𝓍 - 5)
Answer:𝓍² - 9𝓍 + 20 = (𝓍 - 4)(𝓍 - 5)
Question
Factorise x² - 17x + 70
Identify the product and sum of the two key values that we need to find.
Product = +70
Sum = - 17
- -7 and -10 add to give -17 and multiply to give +70
The factors are (𝓍-7) and (𝓍-10)
Answer:
𝓍² - 17𝓍 + 70 = (𝓍-7)(𝓍-10)
Factorising expressions of the form 𝓍²-a² (difference of two squares)
Expressions such as 𝓍²-a² can be factorised using the difference of two squares method.
To understand how this works, look at the result when (𝓍 + 5)(𝓍 – 5) is expanded.
(𝓍 + 5)(𝓍 – 5) = 𝓍(𝓍 -5) + 5(𝓍 – 5)= 𝓍² – 5𝓍 + 5𝓍 – 25 Since = 𝓍²– 25 Expanding (𝓍 + 5)(𝓍 – 5) gives 𝓍² – 25
The inverse of this means that 𝓍² – 25 factorises to give (𝓍 + 5)(𝓍 – 5)
- Note that in the expression 𝓍² – 25 𝓍 is squared
- 25 = 5² and there is a minus sign in between so we have the difference of two squares!
In general, 𝓍² – a² can be factorised to give (𝓍 + a)(𝓍 – a)
Both 𝓍² and 100 (10²) are squares and there is a - sign in between.
Use the difference of two squares method - DOTS.
The factors can be written down without any further working.
𝓍² – 100 = 𝓍² – 10²
= (𝓍 + 10)(𝓍 – 10)
Question
Factorise 𝓍² - 49
Solution
𝓍² - 49 = 𝓍² - 7²
Use DOTS
Answer
𝓍² - 49 = (𝓍 + 7)(𝓍 - 7)
Example
Factorise 9 - 𝓍²
DOTS can still be used here – the expression does not have to start with ‘𝓍²”
9 - 𝓍² = 3² - 𝓍²
Factors are (3 + 𝓍)(3 – 𝓍)
Answer:
9 - 𝓍² = (3 + 𝓍)(3 – 𝓍)
Difference of two squares (DOTS) often appears on exams
Test yourself
More on M3: Algebra
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 5