Revision guides: Electricity
Revise: Electrical charge carriers
Electrical current is electrical charge transferred in a particular time. These three properties can be calculated using the equation Q=It. Current can be a.c. or d.c.

Revise: Potential differences (voltage)
The potential difference (or voltage) of a supply is a measure of the energy given to the charge carriers in a circuit.
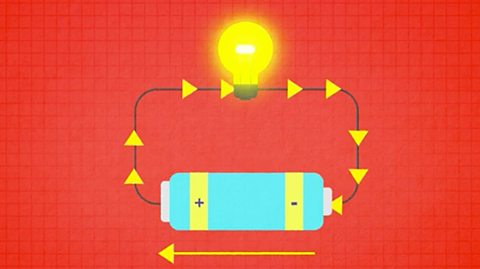
Revise: Ohm's Law
Ohm’s law relates the resistance of a component to its voltage and current. Applying circuit rules for current and voltage with Ohm’s Law allows us to formulate rules to determine total resistance.

Revise: Practical electrical and electronic circuits
Measurement and analysis of current and voltage in simple circuits allows us to formulate rules and predict unknown values.

Revise: Electrical power
Power is a measure of the rate of energy transfer and relates to the current and voltage for an electrical circuit.

Video playlist
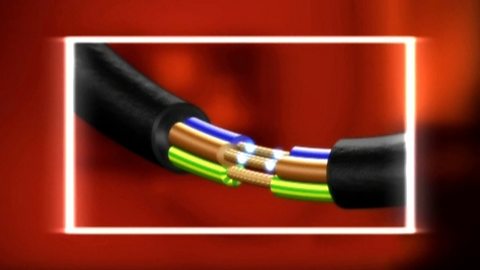
Video: Conductors and insulators. Video
Why does a metal wire conduct electricity while the plastic sheath does not?
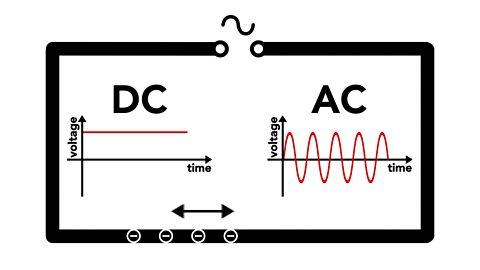
Video: Electrical charge carriers and electric fields. Video
Explaining how current is created and the difference between AC and DC
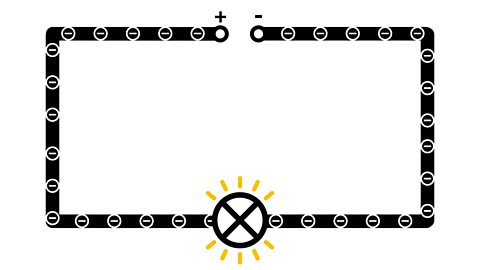
Video: Energy sources. Video
Understand how energy sources supply electrical energy to circuits
Video: Ohm's Law. Video
Understanding the relationship between voltage, current and resistance in a circuit.

Video: Conductors. Video
Conductors such as wires and resistors are used so current can flow in a complete circuit.

Video: Electrical power. Video
Electrical charge carriers and electric fields
Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link